A multi-channel allocation optimization method based on physical layer interference information
A technology of interference information and allocation optimization, applied in wireless communication, electrical components, network topology, etc., can solve problems such as ineffective use of multi-channel resources, and achieve the effect of ensuring convergence and fairness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
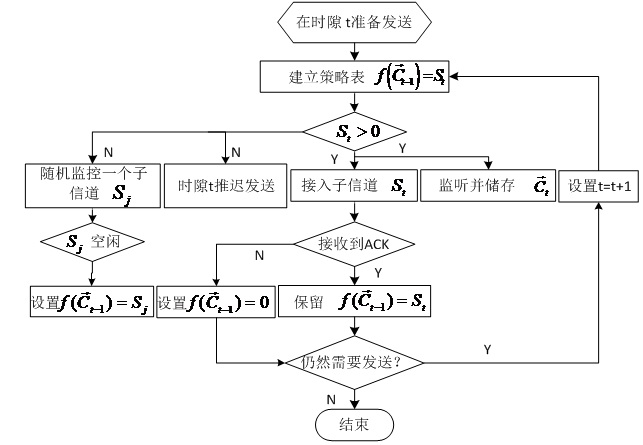
[0041] See figure 1 , Each node stores a channel access strategy. If the node has data to send in the time slot t, the channel access judgment is made according to the coordinated signal fi(Ct-1) monitored at the time t-1. The channel access strategy points out that if fi(Ct-1)=0, the node will postpone the transmission, and randomly monitor a subchannel Sj, while using the second antenna to monitor the coordination signal Ct at this time. If the sub-channels Sj are idle at this moment, the node changes the access strategy to fi(Ct-1)=Sj. If fi(Ct-1)=St, then the node accesses the subchannel St in the time slot t, uses St for data transmission, and uses the second antenna to monitor the coordination signal Ct at this time.
[0042] See figure 1 , When the transmission is completed, when the node finishes sending data, it switches to monitoring mode and waits for ACK. If the node receives the ACK in the time slot t, the data transmission is successful, and the node maintains the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com