Nucleic acid aptamer capable of identifying HCV E1E2 (hepatitis C virus E1E2), nucleic acid aptamer derivatives and screening method and application thereof
A nucleic acid aptamer and E1E2 technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of patients interrupting treatment, large side effects of combination therapy, and expensive treatment, and achieve the effect of high cost, good affinity, and specific inhibition of HCV infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
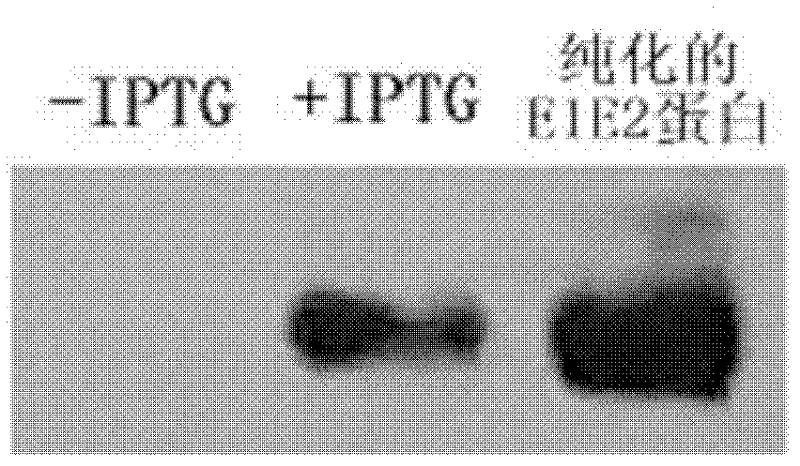
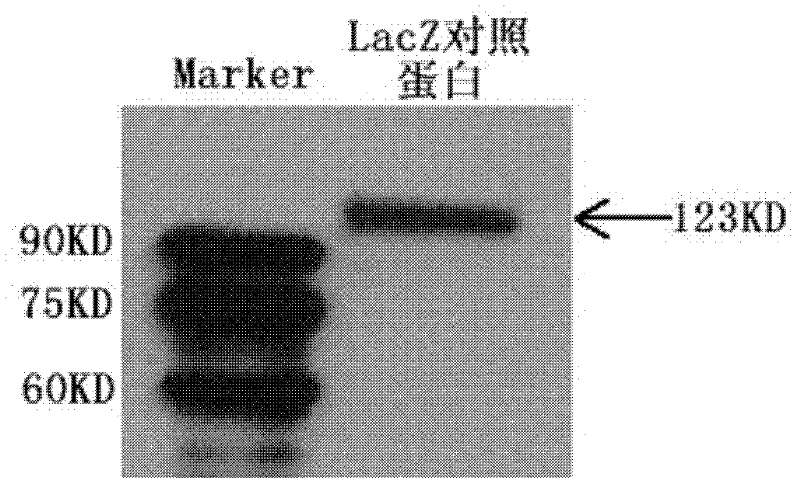
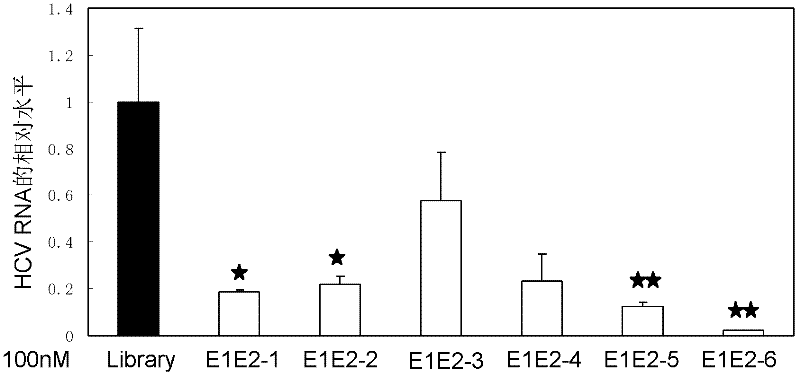
[0051] Example: nucleic acid aptamers capable of recognizing HCV E1E2 protein, derivatives of nucleic acid aptamers, screening methods and applications thereof.
[0052] 1. Preparation of related proteins.
[0053] 11 Preparation of HCV envelope protein E1E2 (target protein) with histidine tag.
[0054] 1.1.1 Amplification of the gene encoding HCV envelope protein E1E2
[0055] Using the pJFH1 plasmid as a template for PCR amplification, the E1E2 gene was amplified by PCR with the first primers consisting of the following primers 1 and 2 (PCR reagents were purchased from Roche, and 100 microliters of PCR tubes were purchased from Eppendorf):
[0056] Primer 1 (upstream primer):
[0057] 5'-CGCGCGAATTCGCCCAGGTGAAGAATACCAGTAGCAGCTAC-3';
[0058] Primer 2 (downstream primer):
[0059] 5'-CTGCAGAAGCTTTGCTTCGGCCTGGCCCAACA-3';
[0060] The 5' ends of the upstream and downstream primers were respectively introduced with EcoR1 restriction site and HindIII restriction site;
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com