Novel method for preparing load nano zero valent iron
A nano-zero-valent iron, loaded technology, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, etc., can solve the problems of high reagent cost, unstable particle size and composition, and non-renewable
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Prepare or purchase a mixed system in which iron oleate is dispersed in a non-polar solvent, a mixed system in which iron hydroxide is dispersed in a non-polar solvent, or FeCl 3 Aqueous solution, take 5ml of a solution of one of the above systems, vacuum filter it and load it on 1.000g of carbon black. Collect the residue on the filter paper, weigh it immediately and let it stand overnight, then treat it in an oven at 60°C for 24h.
Embodiment 2
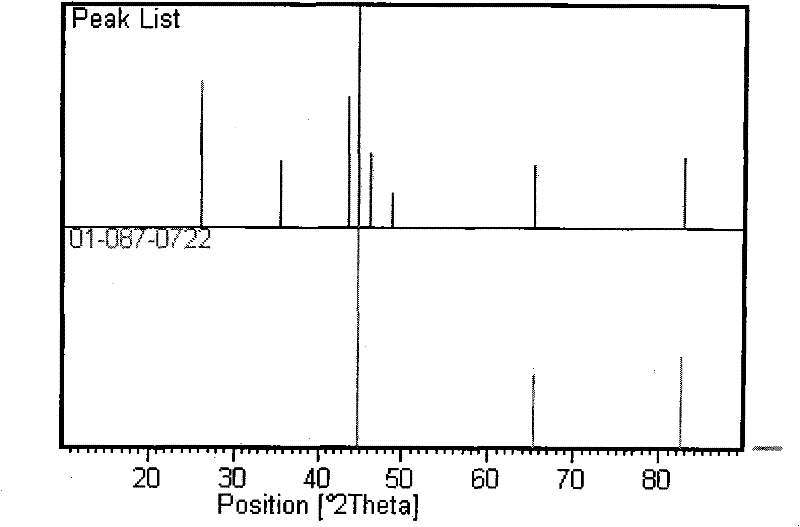
[0025] Take 0.200 g of the iron oleate-carbon black load and place it in the heating zone of the tubular atmosphere furnace. Introduce N into the furnace first 2 , N 2 The flow rate was controlled at 200ml / min for 20min. stop access N 2 After that, H was introduced into the furnace 2 , H 2 The flow rate was controlled at 100ml / min for 20min. close H 2 Open the gas cylinder and turn on the electric furnace, heat up to 1100°C, the cumulative heating time is 3h, and intermittently feed H at a rate of 100ml / min per hour. 2 , ventilation for 5 minutes. For the characterization of the obtained load, see figure 1 (XRD pattern of iron oleate-carbon black load after hydrogen treatment) and figure 2 (XRD peak shape matching diagram of iron oleate-carbon black load and 01-087-0722 type α-Fe).
Embodiment 3
[0027] Take 0.200 g of ferric oleate-activated carbon load and place it in the heating zone of the tubular atmosphere furnace. Introduce N into the furnace first 2 , N 2 The flow rate was controlled at 500ml / min for 20 minutes. stop access N 2 After that, H was introduced into the furnace 2 , H 2 The flow rate was controlled at 100ml / min for 20min. close H 2 Open the gas cylinder and turn on the electric furnace, heat up to 800°C, the cumulative heating time is 10h, and intermittently feed H at a rate of 100ml / min per hour. 2 , ventilation for 5 minutes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com