Decarburization method adopting diethyl carbonate as absorbent
A technology of diethyl carbonate and absorbent, applied in the field of chemical engineering, can solve the problems of small absorption capacity of absorbent, large investment in equipment, long process flow, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing energy consumption, equipment investment and solvent price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
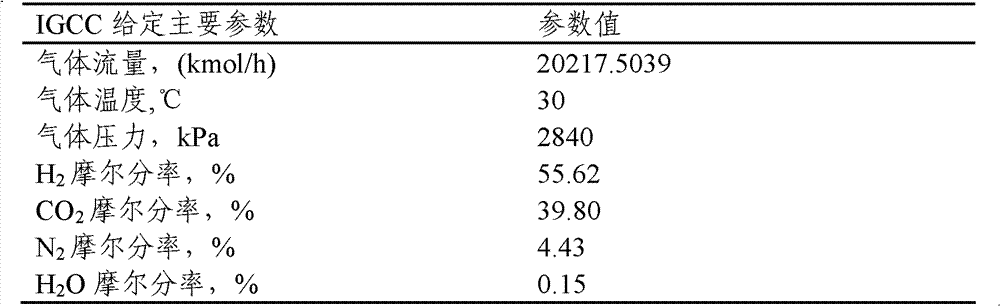
[0026] Contains CO 2 The mixed gas, temperature 30 ℃, pressure 2800KPa, composition (mol fraction) as shown in Table 1:
[0027] Table 1 Feed gas flow rate and composition
[0028]
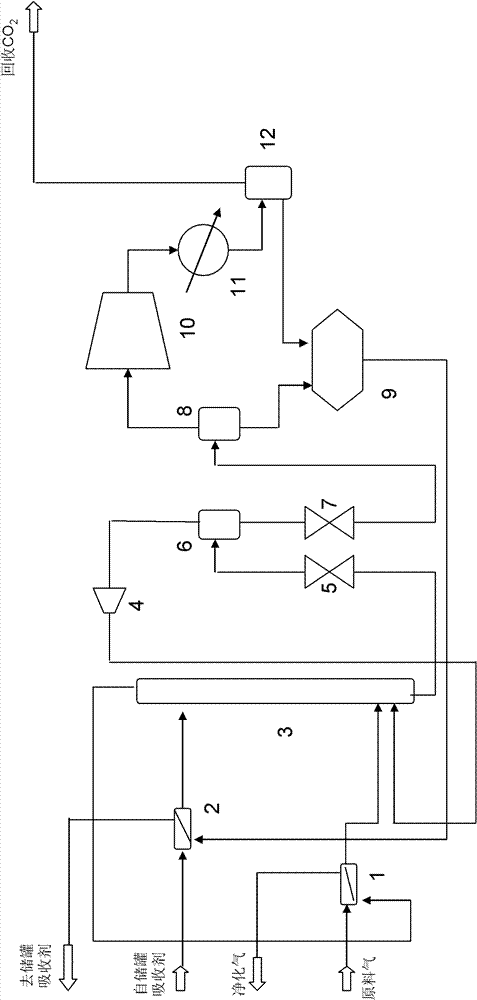
[0029] CO removal with absorber overhead 2 After heat exchange, the purified gas is lowered to 20°C and enters the absorption tower from the lower part, and the diethyl carbonate from the absorbent storage tank at 25°C exchanges heat with the desorbed circulating absorbent lean liquid and enters the absorption tower from the upper part after heat exchange to 5°C. The agent flow rate is 36809.15kmol / h. The two phases of gas and liquid are in countercurrent contact in the tower and absorption and mass transfer occur. The temperature at the top of the absorption tower is 21°C and the pressure is 2800KPa; the temperature at the bottom of the tower is 26°C and the pressure is 2840KPa. CO removal 2 After heat exchange between the purified gas and the raw material gas, the temperature is lowered ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Contains CO 2 The mixed gas, temperature 30 ℃, pressure 2800KPa, composition (mol fraction) as shown in table 4:
[0040] Table 4 Feed gas flow rate and composition
[0041]
[0042] CO removal with absorber overhead 2 After heat exchange, the purified gas is lowered to 24°C and enters the absorption tower from the lower part, and the diethyl carbonate from the absorbent storage tank at 25°C exchanges heat with the desorbed circulating absorbent lean liquid and enters the absorption tower from the upper part after heat exchange to 5°C. The agent flow rate is 44919.15kmol / h. The two phases are in countercurrent contact in the column and absorption mass transfer occurs. The temperature at the top of the absorption tower is 19°C and the pressure is 2800KPa; the temperature at the bottom of the tower is 24°C and the pressure is 2840KPa. CO removal 2 After heat exchange between the purified gas and the feed gas, the temperature is lowered to 24°C and discharged from ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Contains CO 2 The mixed gas, temperature 30 ℃, pressure 2800KPa, composition (mol fraction) as shown in Table 7:
[0053] Table 7 Feed gas flow rate and composition
[0054]
[0055] CO removal with absorber overhead 2 After heat exchange, the purified gas drops to 24°C and enters the absorption tower from the lower part. The diethyl carbonate from the absorbent storage tank at 25°C exchanges heat with the desorbed circulating absorbent poor liquid and enters the absorption tower from the upper part after heat exchange to 7°C. The agent flow rate is 33737.37kmol / h. The two phases of gas and liquid are in countercurrent contact in the tower and absorption and mass transfer occur. The temperature at the top of the absorption tower is 19.0°C and the pressure is 2800KPa; the temperature at the bottom of the tower is 28°C and the pressure is 2840KPa. CO removal 2 After heat exchange between the purified gas and the feed gas, the temperature is lowered to 25°C and dis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com