Medium supporting structure applied to radio-frequency coaxial connector
A support structure, radio frequency coaxial technology, applied in the direction of connection, two-part connection device, fixed/insulated contact member, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing the volume ratio and reducing the effective dielectric constant
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
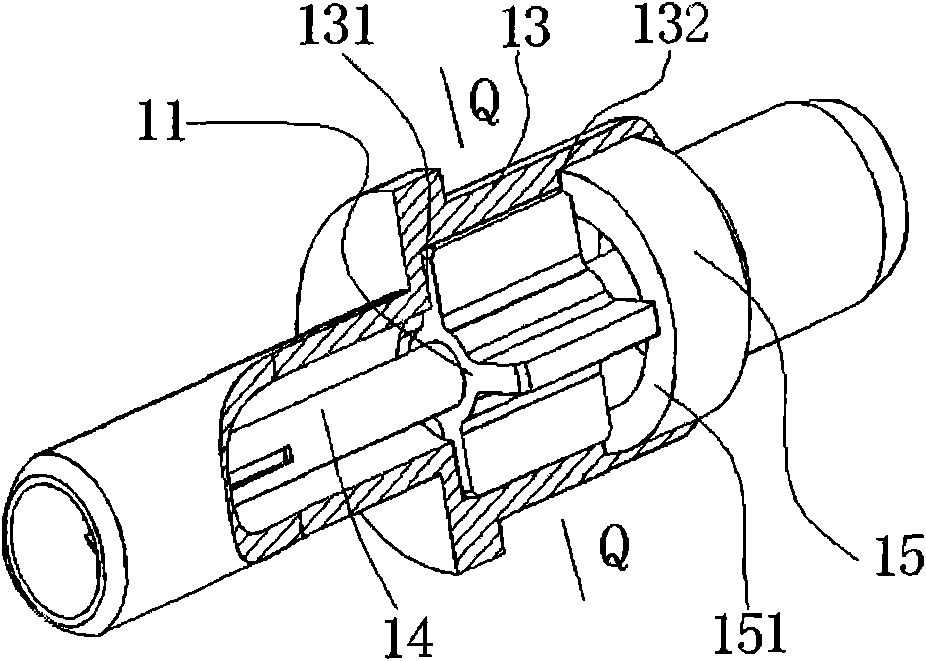
[0023] Such as figure 1 As shown, a dielectric support structure applied to a radio frequency coaxial connector includes an insulating support 11, a first positioning structure 13, and a second positioning structure.
[0024] In order to reduce the effective dielectric constant of the dielectric support to a greater extent, the insulating support 11 is designed with a plurality of thin-walled insulating support ribs 111 . The insulating support member 11 of this embodiment has four thin-walled insulating support ribs 111, the four thin-walled insulating support ribs 111 are of equal length, and the insulating support member 11 is a cross-shaped structure with a hole in the center.
[0025] In this embodiment, the second positioning structure is the slotted positioning structure 12, and the first positioning structure 13 may be the outer conductor of the coaxial connector.
[0026] Such as image 3 As mentioned above, the groove width La of the slotted positioning structure 1...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that: for the application of the medium support structure where the degree of freedom of rotation does not need to be limited, the second positioning structure can be selected as the non-slotted positioning structure 15, such as figure 2 , Figure 4 shown.
[0031] At this time, the distance La between the axial positioning planes 131 and 132 of the first positioning structure 13 is consistent with the length Lb of the insulating support 11. After being installed in place, the insulating support 11 is placed on the axial positioning plane 131 of the first positioning structure 13 and 132, then the positioning plane 151 of the positioning structure 15 without slots coincides with the axial positioning plane 132 of the first positioning structure 13 to define the axial degree of freedom of the insulating support 11, and then through riveting and interference and other ways to fix their relative positions...
Embodiment 3
[0033] The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the groove depth of the slot 121 of the slotted positioning structure 12 is shorter than the length of the thin-walled insulating support rib 111 . The limitation of this structure and the limitation of degrees of freedom can refer to the situation of the first embodiment.
[0034] In terms of design, the groove width La of the slotted positioning structure 12 is consistent with the wall thickness La of the thin-walled insulating support rib 111, and the slot depth Lb of the slotted positioning structure 12 is consistent with the length Lb of the thin-walled insulating support rib 111. When the thin-walled insulating support rib 111 snaps into the slotted positioning structure 12, the slot width La of the slotted positioning structure 12 defines the degree of freedom of rotation of the insulating support 11, and the groove bottom plane 1211 of the slotted positioning structure 12 is in line with the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com