Application of methylation sensitive amplification polymorphism technique in toxicity analysis of transgenic plants
A transgenic plant, transgenic technology, applied in the field of molecular biology and biology, to achieve important economic and social benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
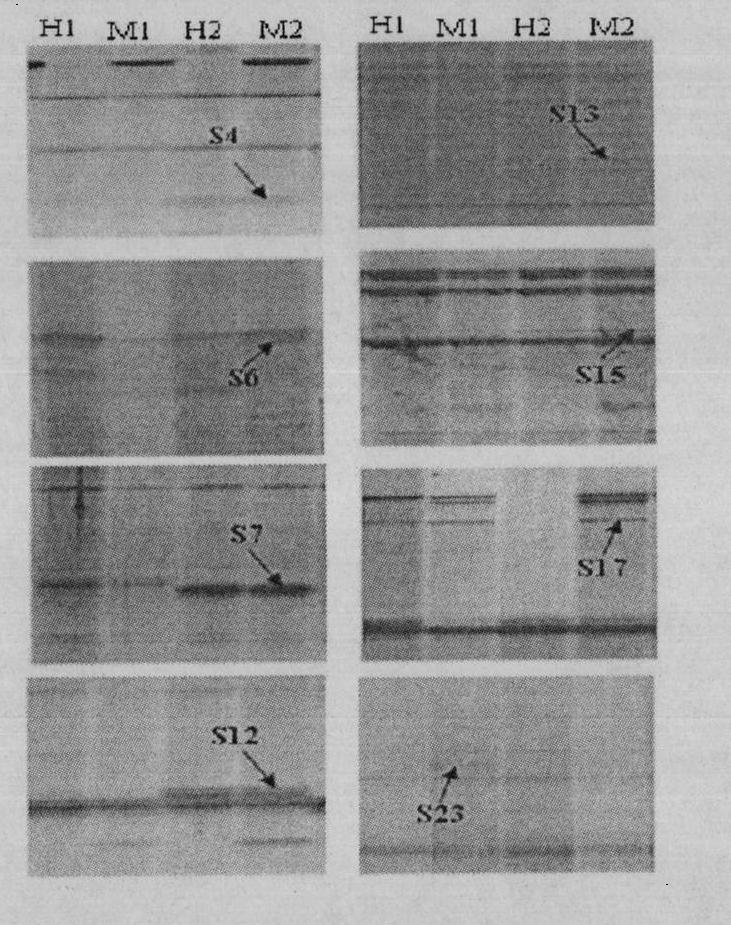
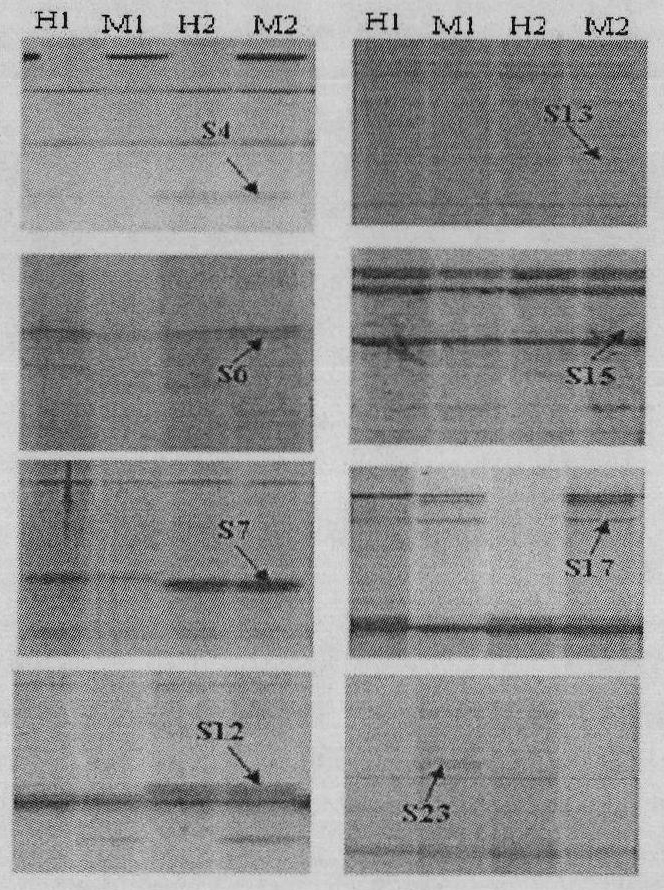
[0022] Example 1: Obtaining of Differential Fragments of Methylation Sensitivity Polymorphisms in Transgenic Plants
[0023] 1. Extraction of genomic DNA from transgenic plants
[0024] Under the same cultivation conditions, transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana and wild-type Arabidopsis seedlings with fhy3 and GUS genes were cultured, and their genomic DNA was extracted by traditional CTAB method.
[0025] 2. Enzyme digestion and ligation of genomic DNA of transgenic plants
[0026] Entrust Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Technology Service Co., Ltd. to synthesize the following primer sequences: EcoR I linker 1 (5'-CTCGTAGACTGC GTACC-3'), EcoR I linker 2 (5'-AATTGGTACGCAGTC-3'), MspI / Hpa II linker 1 (5'-GATCATGAGTC CTGCT-3'), Msp I / Hpa II linker 2 (5'-CGAGCAGGACTCATGA-3'). EcoR I linker 1 and EcoR I linker 2 were dissolved in distilled water and mixed uniformly, placed at 95 °C for 5 min, and then cooled at room temperature to prepare 5 pmol of EcoR I linker. MspI / HpaII adapter 1...
Embodiment 2
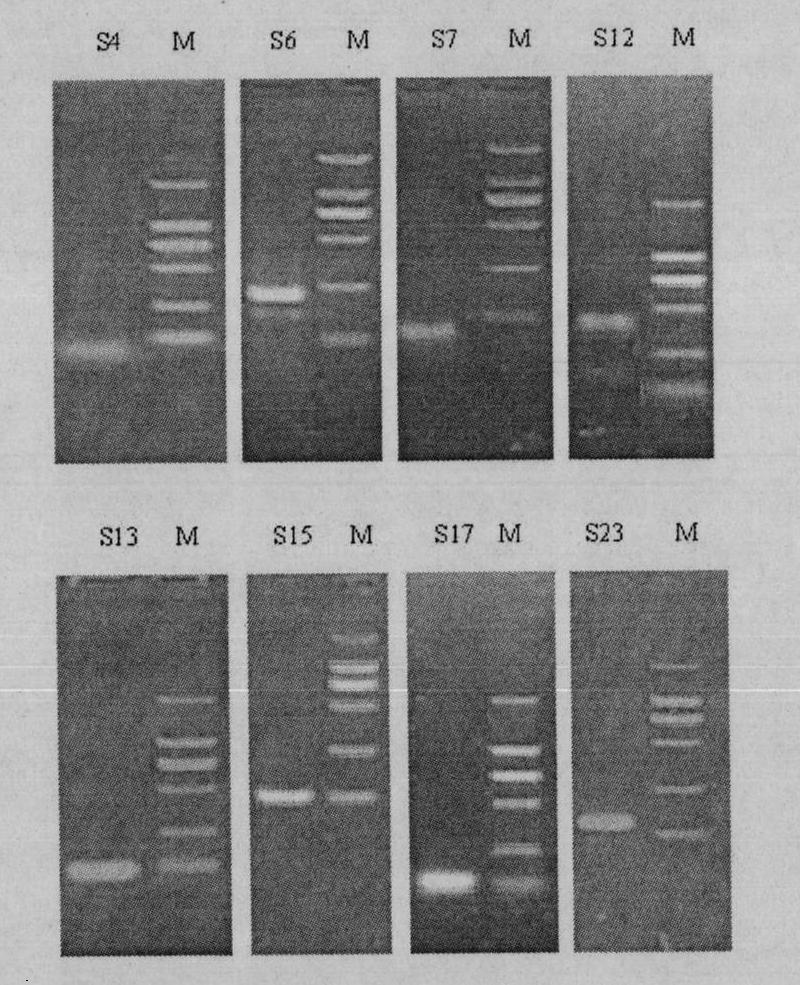
[0033] Example 2: Recovery, cloning and sequencing of differentially methylated DNA fragments in transgenic plants
[0034] 1. Recovery of differentially methylated DNA fragments
[0035] The methylation-sensitive polymorphic differential fragments excavated from transgenic plants were placed in 30 μl of double-distilled water and boiled for 5 minutes. After slowly cooling down to room temperature, centrifuge and recover the supernatant. Take 4 μl of the supernatant as a template for PCR amplification, and the PCR reaction conditions are consistent with the pre-amplification PCR reaction. The PCR product was recovered and purified according to the instructions of the DNA recovery and purification kit (product of Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Technology Service Co., Ltd.).
[0036] 2. Cloning of differentially methylated DNA fragments
[0037]According to the instructions of the ligation kit (product of Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Technology Service Co., Ltd.), the recov...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3: Analysis of Unexpected Toxicity of Transgenic Plants
[0041] 1. Open the KEGG database, input the DNA sequence without methylation in the transgenic Arabidopsis but methylated in the wild-type Arabidopsis, and analyze whether the metabolic pathway involved in the sequence is related to the synthesis of toxic substances. If the metabolic pathway involved in the sequence is related to the synthesis of toxic substances, it indicates that the transgenic plants may have unexpected toxicity.
[0042] 2. Southern hybridization verification
[0043] Genomic DNA of transgenic Arabidopsis and wild-type Arabidopsis were extracted by traditional CTAB method. If the metabolic pathway involved in the sequence of the differentially methylated DNA fragment of the transgenic plant is related to the synthesis of toxic substances, the sequence is labeled as a probe according to the instructions of the digoxin labeling and detection kit (product of Roche Company), and then res...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com