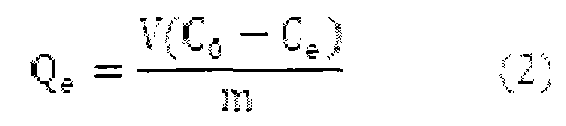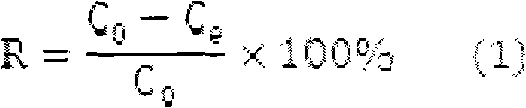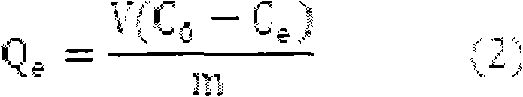method for preparing aminopropyl-MCM-41 for adsorbing heavy metal ions in waste water
A -MCM-41, heavy metal ion technology, applied in the field of aminopropyl-MCM-41 adsorbent and its preparation, can solve the problems of small adsorption capacity, low selectivity and the like, achieve short production cycle, simple process and low price Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] First, dissolve 3ml of silane coupling agent KH-550 in 50ml of ethanol at room temperature, stir well, then add 5g of roasted mesoporous molecular sieve MCM-41, reflux in 70°C water bath for 8 hours, and the product is centrifuged Wash with ethanol and dry in a vacuum oven at 60°C to obtain aminopropyl-MCM-41.
[0014] The invention adopts a static adsorption method (batch method) to measure the removal rate and adsorption capacity of an adsorbent for mercury ions and lead ions. Specific steps are as follows:
[0015] Add 50ml of a certain initial concentration of mercury ion and lead ion solution to a 100ml dry Erlenmeyer flask, place it in a constant temperature water bath at 25°C, and then accurately weigh a certain amount of adsorbent aminopropyl-MCM-41 and place it in the solution , sealed Erlenmeyer flask, stirred and adsorbed at constant temperature for 2 hours, filtered with a sand core funnel, measured the concentration of mercury ions and lead ions remaining ...
Embodiment 2
[0021] The initial mercury ion concentration was 100 mg / L, and the other conditions were the same as in Example 1. Experiments showed that the removal rate under this condition was 90.92%, and the adsorption capacity was 45.46 mg / g.
Embodiment 3
[0023] The initial mercury ion concentration was 150 mg / L, and the rest of the conditions were the same as in Example 1. Experiments showed that the removal rate under this condition was 79.00%, and the adsorption capacity was 59.25 mg / g.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com