Allocation and priority handling of uplink and downlink resources
A downlink, prioritization technique used in allocation and prioritization to achieve fast downloads and short startup delays
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0086] The invention will now be described in more detail with reference to the embodiments described in the detailed description and shown in the accompanying drawings.
[0087] An embodiment of the invention represents a method, Node-B, for allocation and priority handling. The system and the Node-B in the system comprise means for performing the method steps described in the method. Therefore, those skilled in the art should understand the fact that the system and the Node-B execute the method steps, which means that the method embodiments described in the detailed description also include the system and the Node-B, even if they are not described in detail herein.
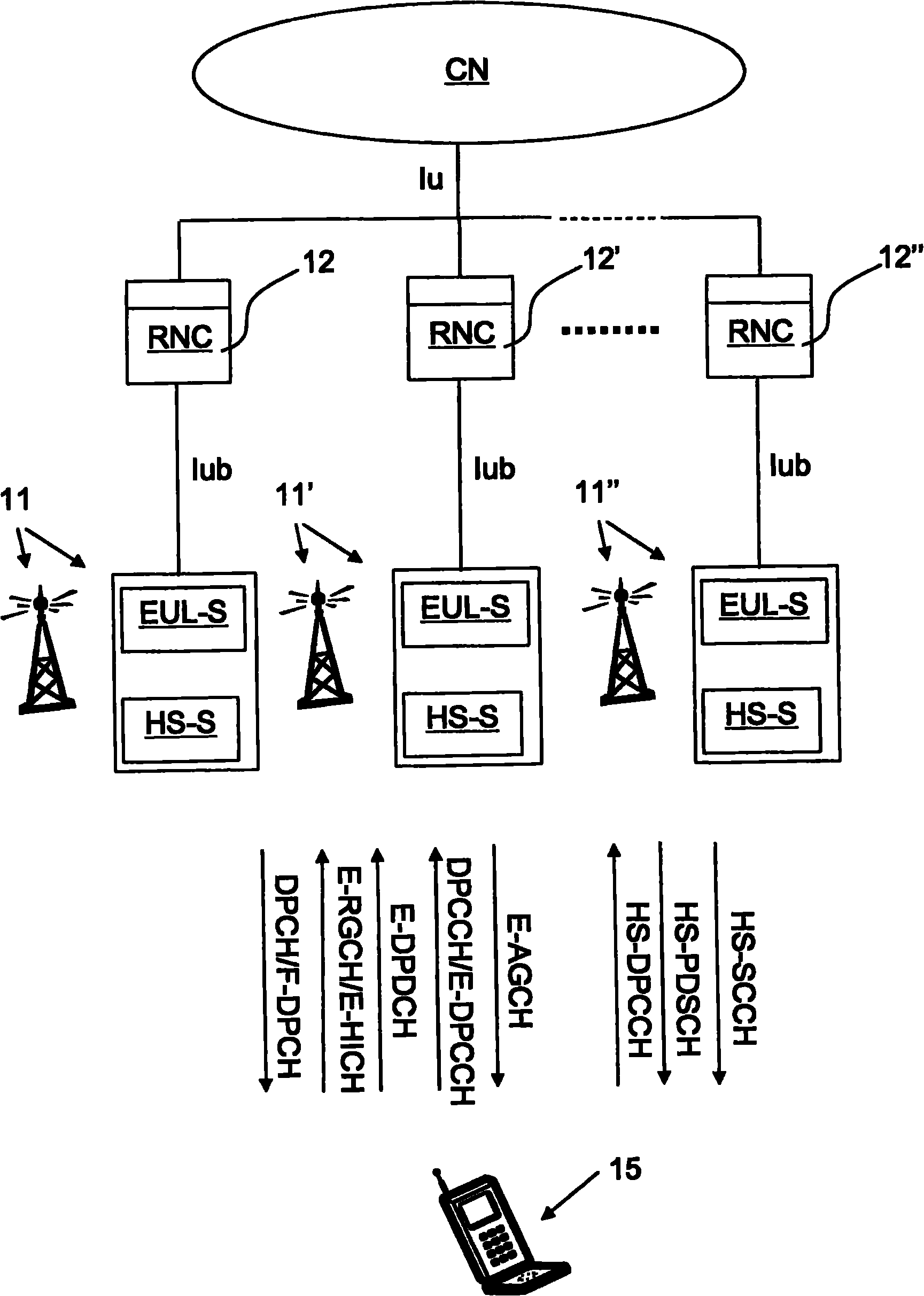
[0088] figure 1 and figure 2 Shows the HSUPA / HSDPA network overview. figure 1 shows a network with only one node of each kind, while figure 2Option to show the same network with more than one node of each category. A user terminal (UE) 15 communicates with a core network (CN) via at least one Node-B (NB) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com