Two-degree-of-freedom robot wrist
A robot and degree-of-freedom technology, applied in the field of robot wrists, can solve the problems of complex structure, large overall weight, and difficult control of robot wrists, and achieve the effects of simple structure, light overall weight, and high integration.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
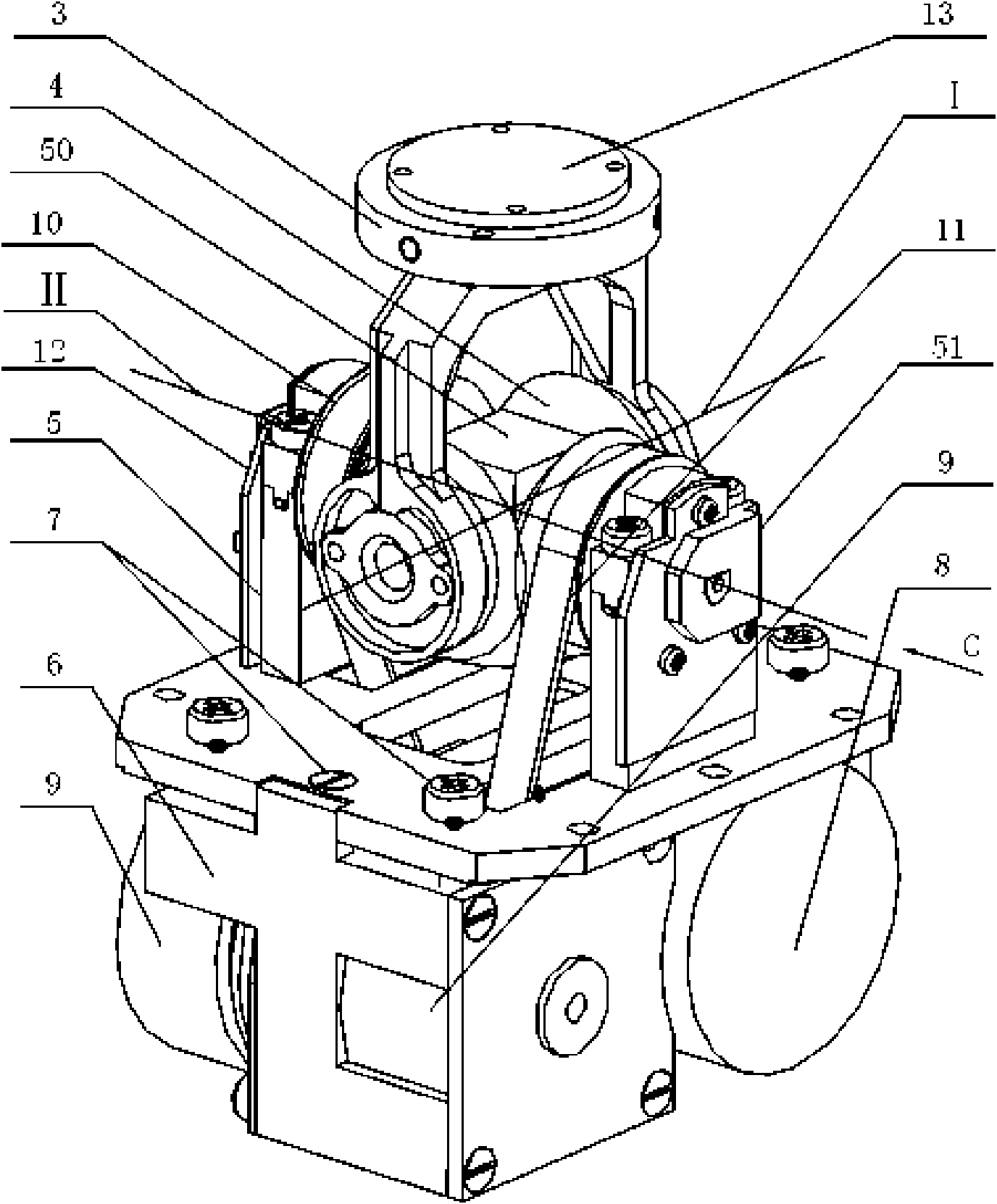
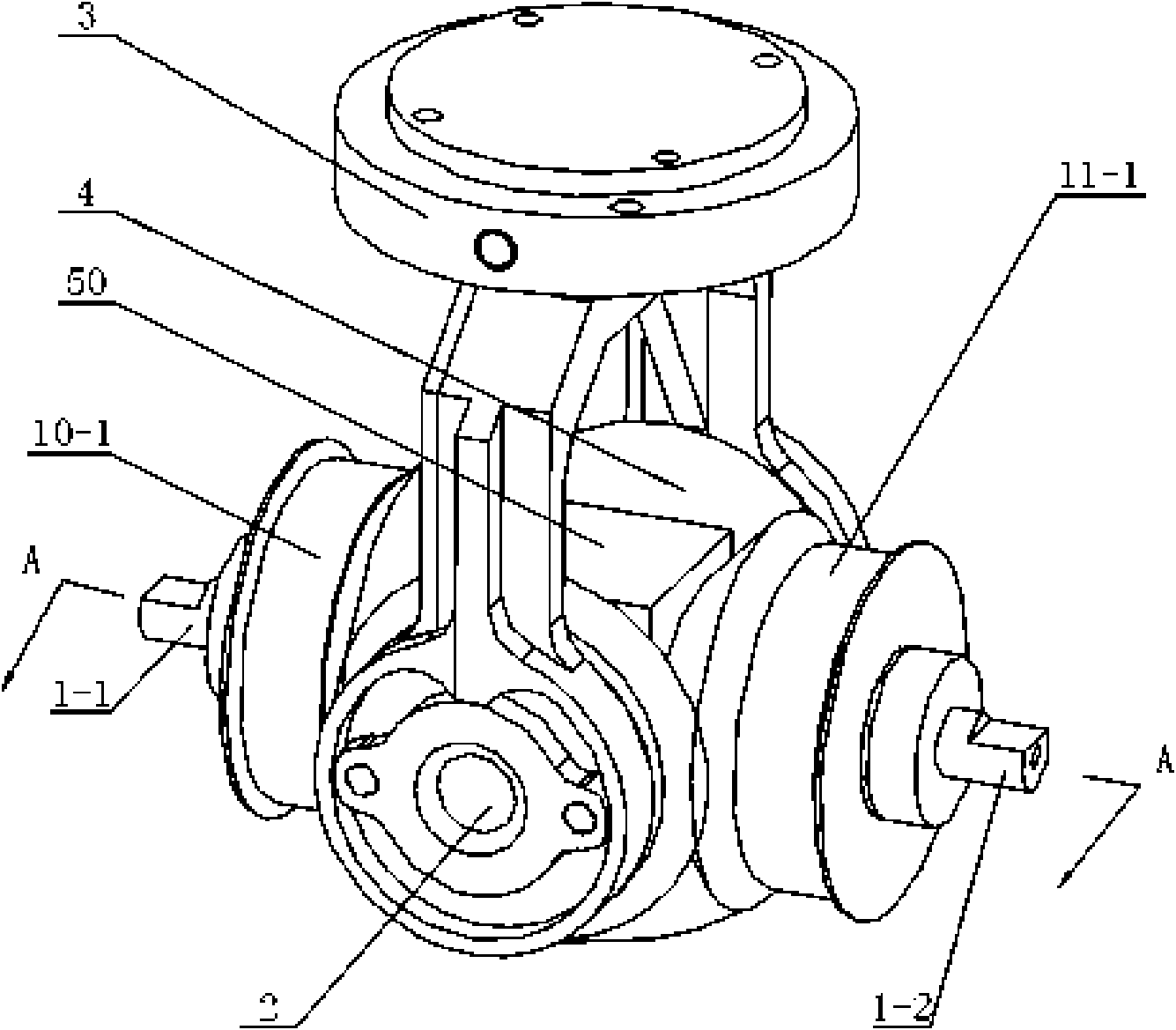
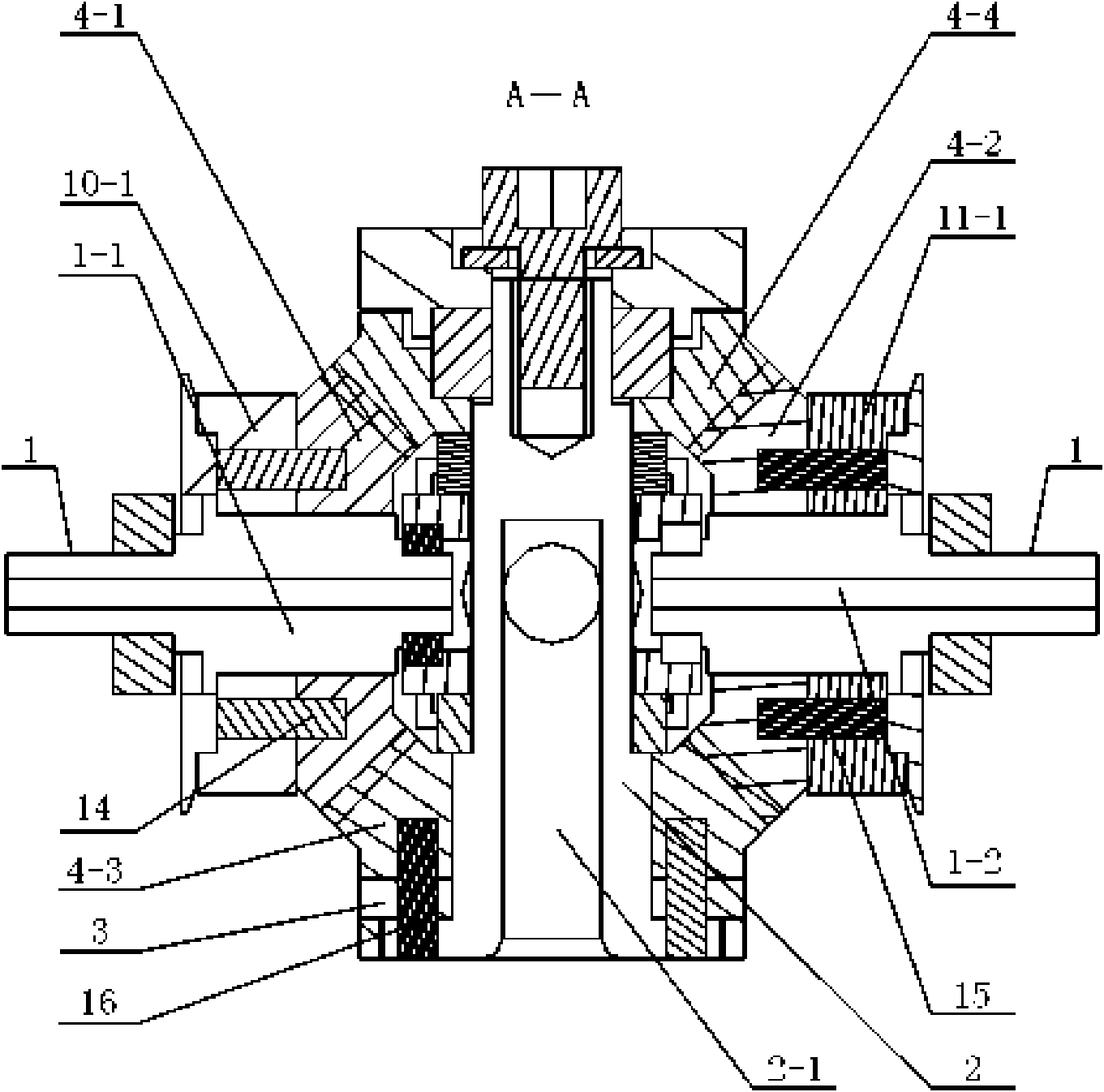
[0007] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 1-Figure 19 Describe this embodiment, the robot wrist of this embodiment is composed of torque sensor 3, differential mechanism 4, support frame 5, support block 50, driving frame 6, pretensioning mechanism 7, first driver 8, second driver 9, first Toothed belt transmission mechanism 10, the second toothed belt transmission mechanism 11, the first position sensor 12, the second position sensor 51, the end circuit board 13, the electrical wiring 25 and the wrist electrical equipment 52 constitute; The central axis I of the driving shaft 2 and the central axis II of the driving shaft 1 are arranged in the same horizontal plane and vertically intersect each other. The driving shaft 1 of the differential mechanism is composed of the first driving half shaft 1-1 and the second driving half shaft 1-2 Among the two input bases 3-1 of the torque sensor 3, the one adjacent to the first driven bevel gear 4-3 of the differential me...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0010] Specific implementation mode two: combination figure 1 and Figure 10 Describe this embodiment, the support frame 5 of this embodiment is made up of support bottom plate 5-1 and two support arms 5-2; The two support arms 5-2 are respectively the first support arm 5-2-1 and the second support arm 5-2-2, and four pre-tightening threaded holes are arranged on the support bottom plate 5-1, and four pre-tightening threaded holes Corresponding to the four top corners of the bracket base plate 5-1, a keyway 5-3 is respectively arranged on the two opposite sides of the bracket base plate 5-1, and two key grooves 5-3 are arranged oppositely. The bracket base plate 5 There are two screw vias on -1. With such arrangement, the structure is simple and the installation of the differential mechanism 4 is easy. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0011] Specific implementation mode three: combination figure 1 , Figure 16 and Figure 17 Describe this embodiment, the torque sensor 3 of this embodiment is made up of cross-shaped strain beam 3-2, four strain gauges 3-3, input base 3-1 and output base 3-4; Output base 3-4 A cross-shaped strain beam 3-2 is fixed between the input base 3-1, there are two input bases 3-1, and the two input bases 3-1 are arranged oppositely, the cross-shaped strain beam 3-2 A strain gauge 3-3 is bonded on the upper surface of each strain beam. The torque sensor 3 detects the force and strain of the cross-shaped strain beam 3-2, and the opposite pair of strain beams respectively detects the strain in the pitch and roll directions; the output base 3-4 of the torque sensor 3 is connected to the wrist end effector , the end circuit board 13 is affixed to the output base 3-4 of the torque sensor 3, and it has no force contact with the cross-shaped strain beam 3-2 of the torque sensor 3, and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com