Armature magnetic core, armature, rotating electric machine, and compressor
A technology of armature and magnetic core, which is applied in the field of axial gap rotating motors, which can solve the problems of easy generation of eddy current and increase of magnetic circuit reluctance in armature teeth, and achieve simple stamping and increase of contact area , The effect of increasing the duty cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
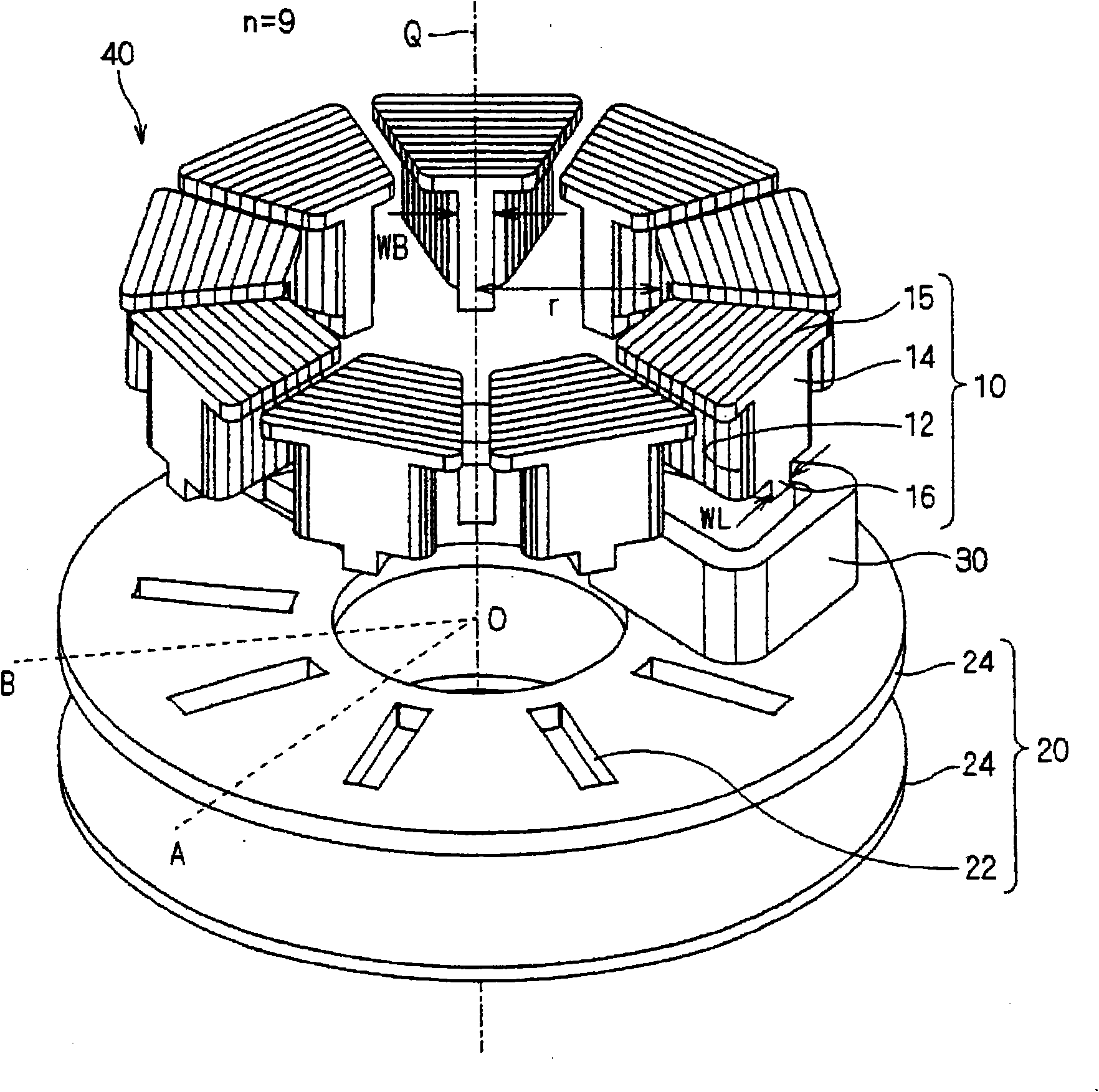
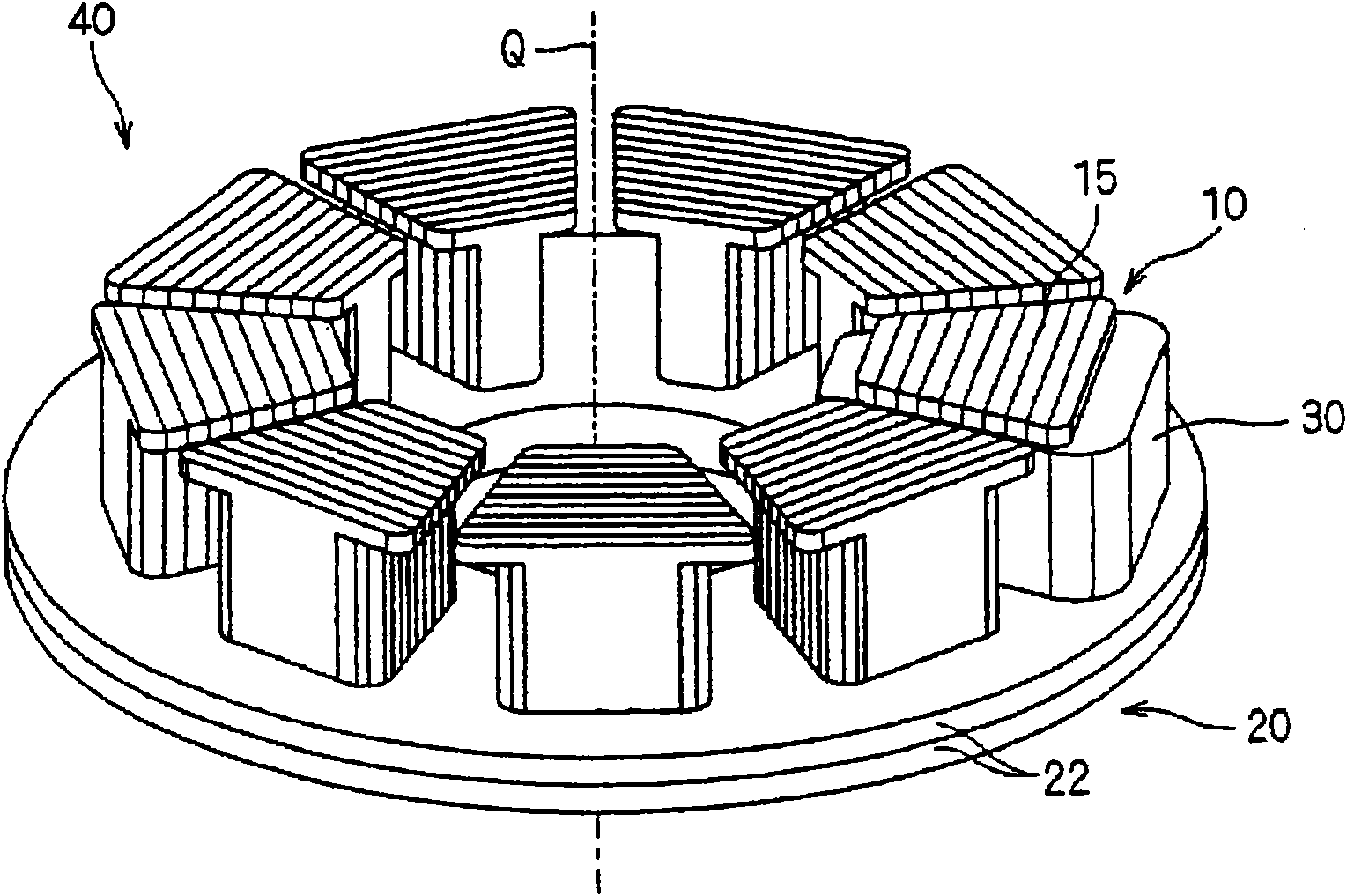
[0091] figure 1 It is an exploded perspective view of the armature 40 according to the first embodiment of the present invention, and is an exploded view along the rotation axis Q direction. also, figure 2 is an assembly drawing of the armature 40 . Such as figure 1As shown, the armature 40 includes the armature core 10, the yoke 20, and the armature winding 30, and is applied to, for example, an axial gap type motor (not shown). In addition, as long as there is no special description in the present invention, the armature winding does not refer to the individual wires that constitute it, but refers to the state in which the wires are wound together. This also applies to the attached drawings. In addition, the lead-out wires of the winding start end and the winding end end, and their connecting wires are also omitted in the drawings. figure 2 Only one armature winding is shown, and the other armature windings are omitted so that the form of the armature core can be illu...
no. 2 approach
[0115] In the above-mentioned first embodiment, the mode in which only the first cuboid portion 16 is buried in the concave portion 22 of the yoke 20 has been described, but the present invention is not limited thereto. Here, as a second embodiment of the present invention, an embodiment in which a flange portion 18 a is further provided at an end portion of the first cuboid portion 16 will be described with reference to the drawings. In addition, in the following description of the embodiment, unless otherwise specified, the same reference numerals are assigned to parts having the same functions as those of the above-mentioned first embodiment, and descriptions thereof will be omitted.
[0116] Figure 4 It is an exploded perspective view of an armature 40a according to the second embodiment of the present invention. Of the plurality of armature cores 10a attached to a yoke 20a, one armature core 10a is separated from the yoke 20a and is separated from the yoke 20a. The arma...
no. 3 approach
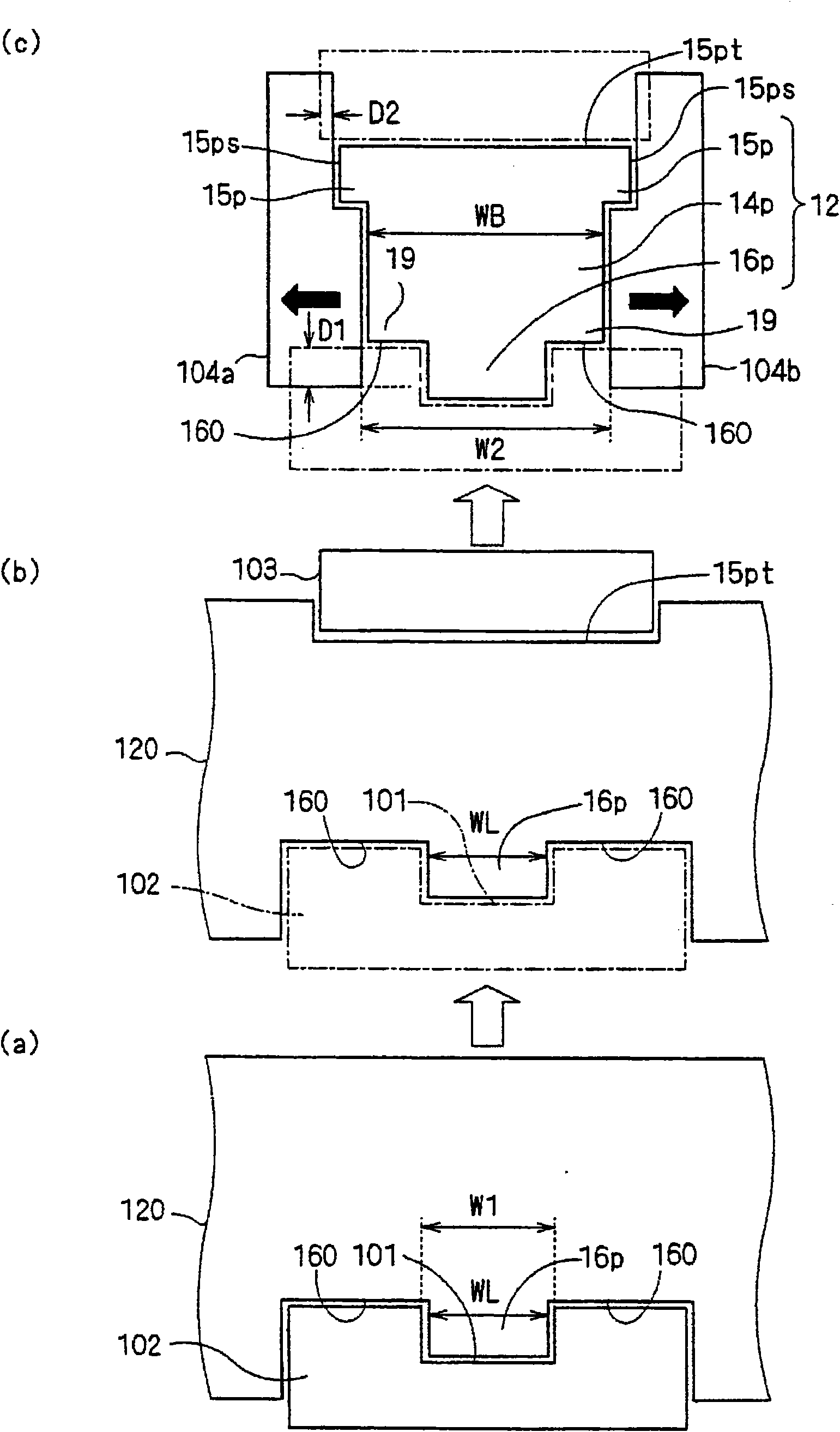
[0132] In the above-mentioned first and second embodiments, the mode in which the width of the first rectangular parallelepiped part 16 is equal to or smaller than the minimum width of the prism part 14 has been described. Although the embodiment in which the flange portion 18a is provided on the lower side of the frame 16 has been described, the present invention is not limited thereto. The width of the first cuboid portion 16 may be larger than the minimum width of the prism portion 14 . Here, as a third embodiment of the present invention, an embodiment in which the width of the first cuboid portion 16c is equal to or greater than the maximum value of the width of the prism portion 14 will be described with reference to the drawings.
[0133] Figure 8 It is an exploded perspective view of the armature 40c according to the third embodiment of the present invention, and is shown exploded in a direction along the rotation axis Q. FIG. also, Figure 9 is an assembly drawing...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com