Image data processing method of electronic document and device thereof
A technology for image data and electronic documents, applied in the field of electronic document data processing, can solve problems such as large storage overhead, merging errors, and difficult technical implementation, so as to improve the compression rate, reduce the number of I/O operations, and reduce redundant information described effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
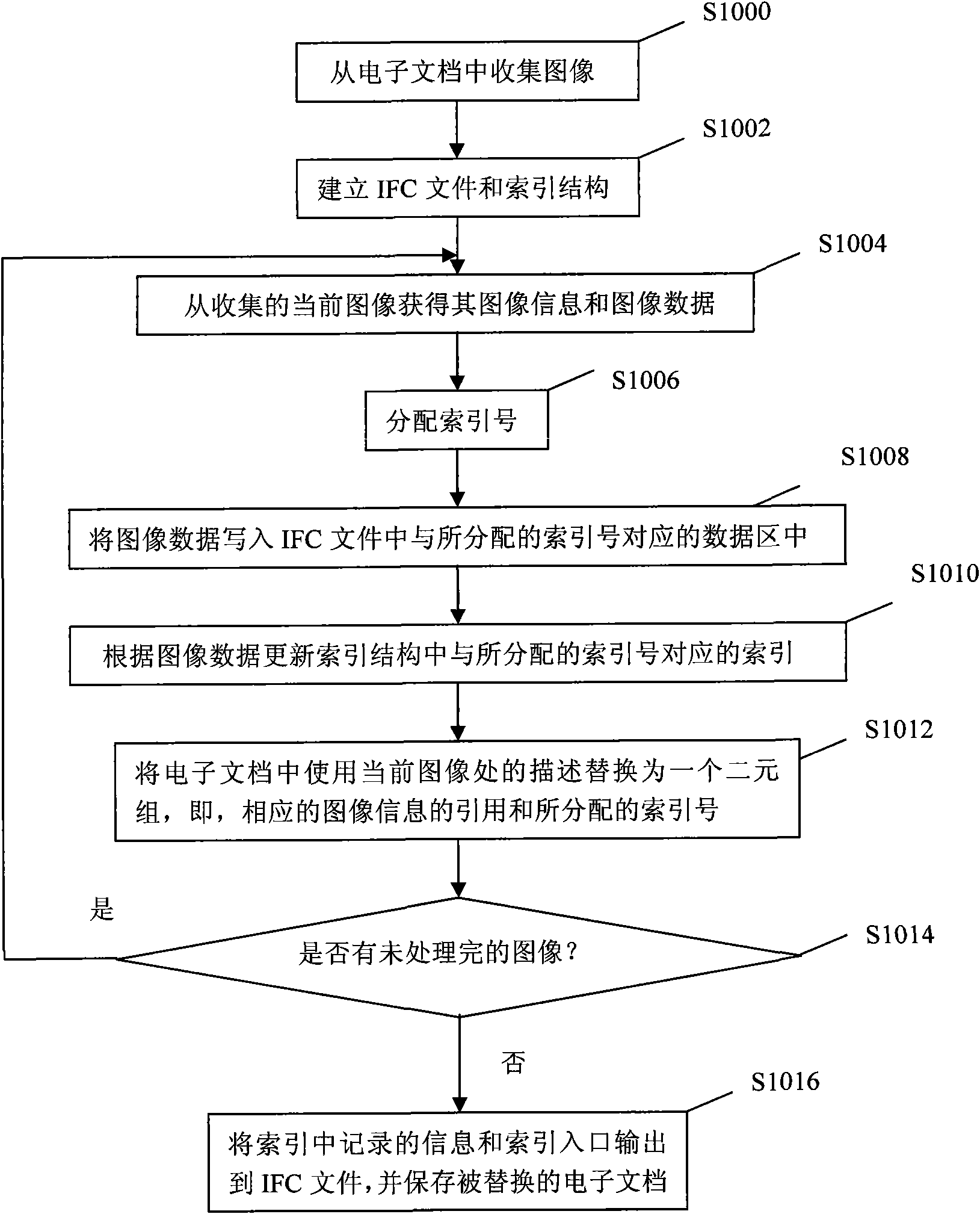
[0026] figure 1 is a flowchart of an image data storage method of an electronic document according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0027] refer to figure 1 , in step S1000, images to be processed are collected from electronic documents. The electronic document formats that can be processed by the present invention include formats such as PDF, XPS, CEB, and MARS. In this step, an array can be used to record the path of the collected images stored on the disk or the location in the electronic file.
[0028] In step S1002, an IFC file and an index structure are established. Here, the IFC file refers to a newly created file for storing image data and recording index information, at least including file header information, data area for storing image data, index, index entry and other parts. File header information must be at the beginning of the file. In the file header information, fields such as file type, version information, compression unit, and compr...
no. 2 example
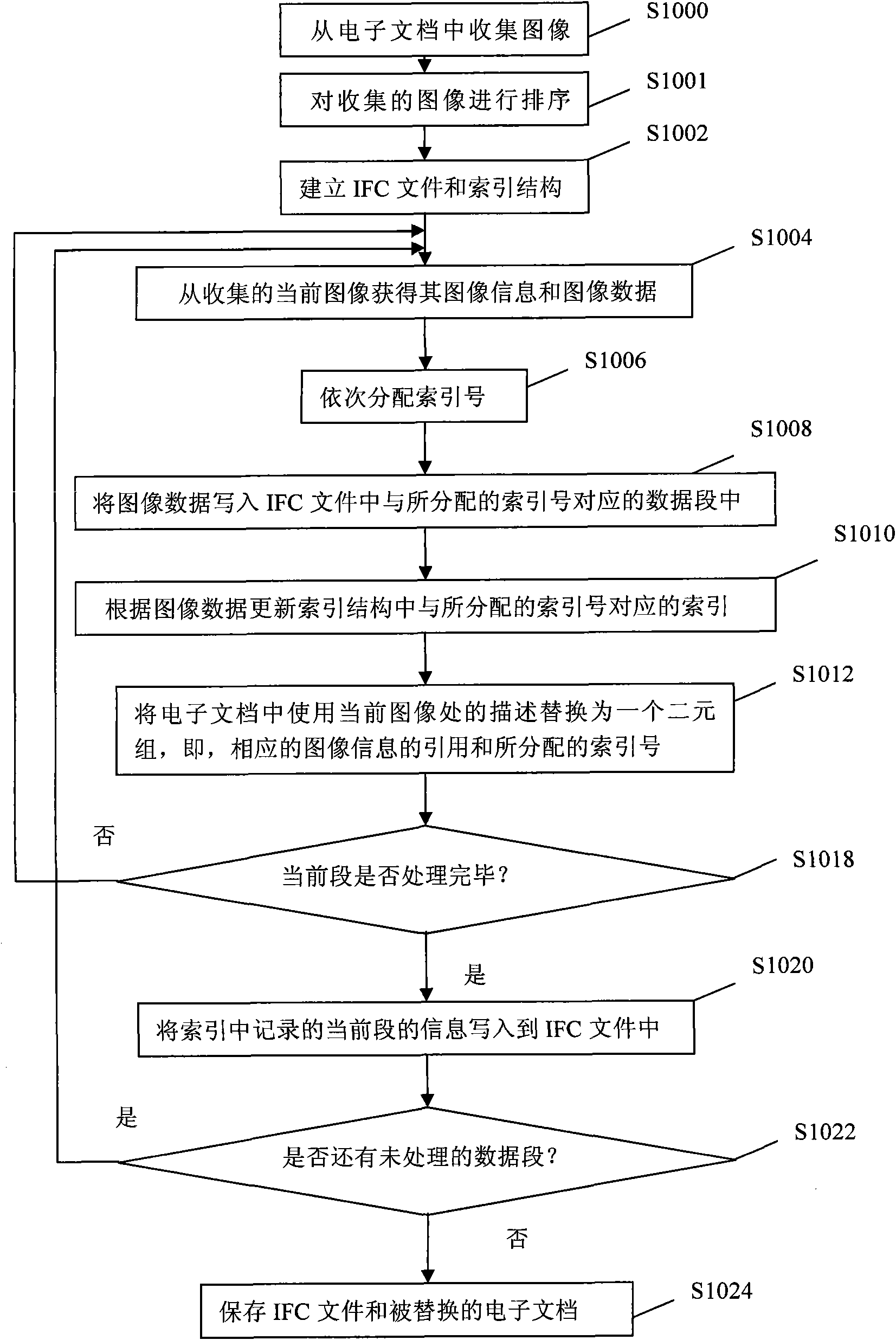
[0038] as in figure 1 As described in step S1006 of , the image data can be meaningfully segmented according to different segmentation strategies. At this time, the index number assigned to the current image is the corresponding number in the data segment to which it belongs. Sometimes, the original image collection sequence itself matches the segment sequence, so the current image data can be assigned index numbers sequentially. However, sometimes, the original image collection order may not be that orderly. At this time, in the case of different segmentation strategies, it is likely that the current image cannot be assigned an index number sequentially, but the current image is assigned the corresponding index number in the data segment to which it belongs according to different data segments. That is, in terms of the order in which images are collected, the assigned index numbers are skipped. In this case, instead of writing the image data segment by segment, a plurality...
no. 3 example
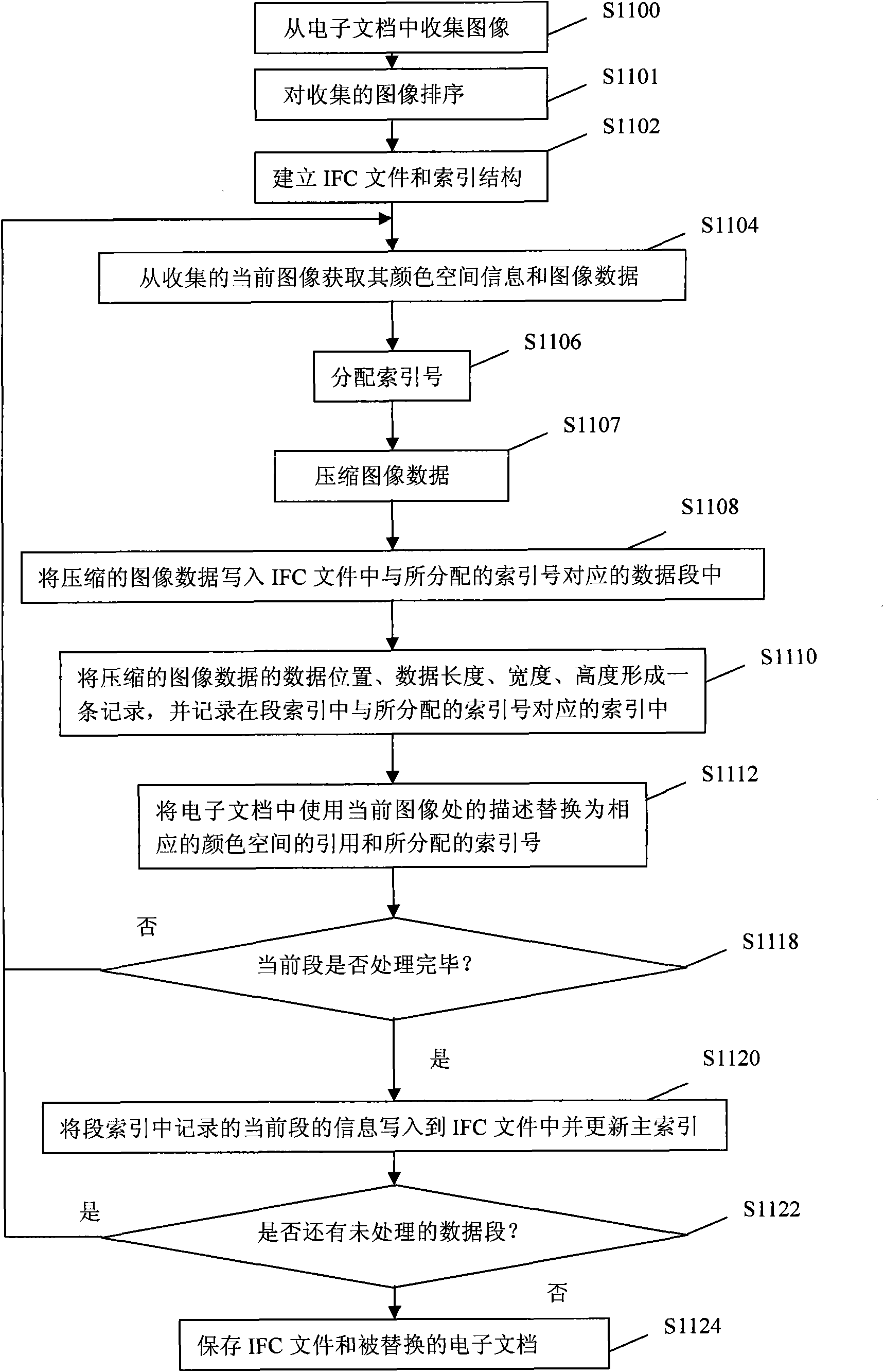
[0046] As mentioned above, collected image data can be meaningfully segmented according to different strategies, so that a certain segment of image data can be used more efficiently by prefetching and caching the image data. For the index structure, it is preferable to use a secondary index structure. The secondary index structure can improve the flexibility of index organization and the speed of index loading, thereby improving the efficiency of operation and wider application range. In the secondary index structure of this embodiment, a primary index and a segment index are set. Correspondingly, the main index entry (the offset position of the main index in the IFC file) is recorded in the IFC file. The main index at least records information such as the number of segment indexes, the offset position of the segment index in the IFC file, and the amount of image data included in the segment. The segment index at least records information such as the offset position of the d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com