Multifocal holographic differential confocal super-large curvature radius measuring method and device
A differential confocal and radius measurement technology, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, optical devices, instruments, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing system errors, high stability, and small moving distances
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
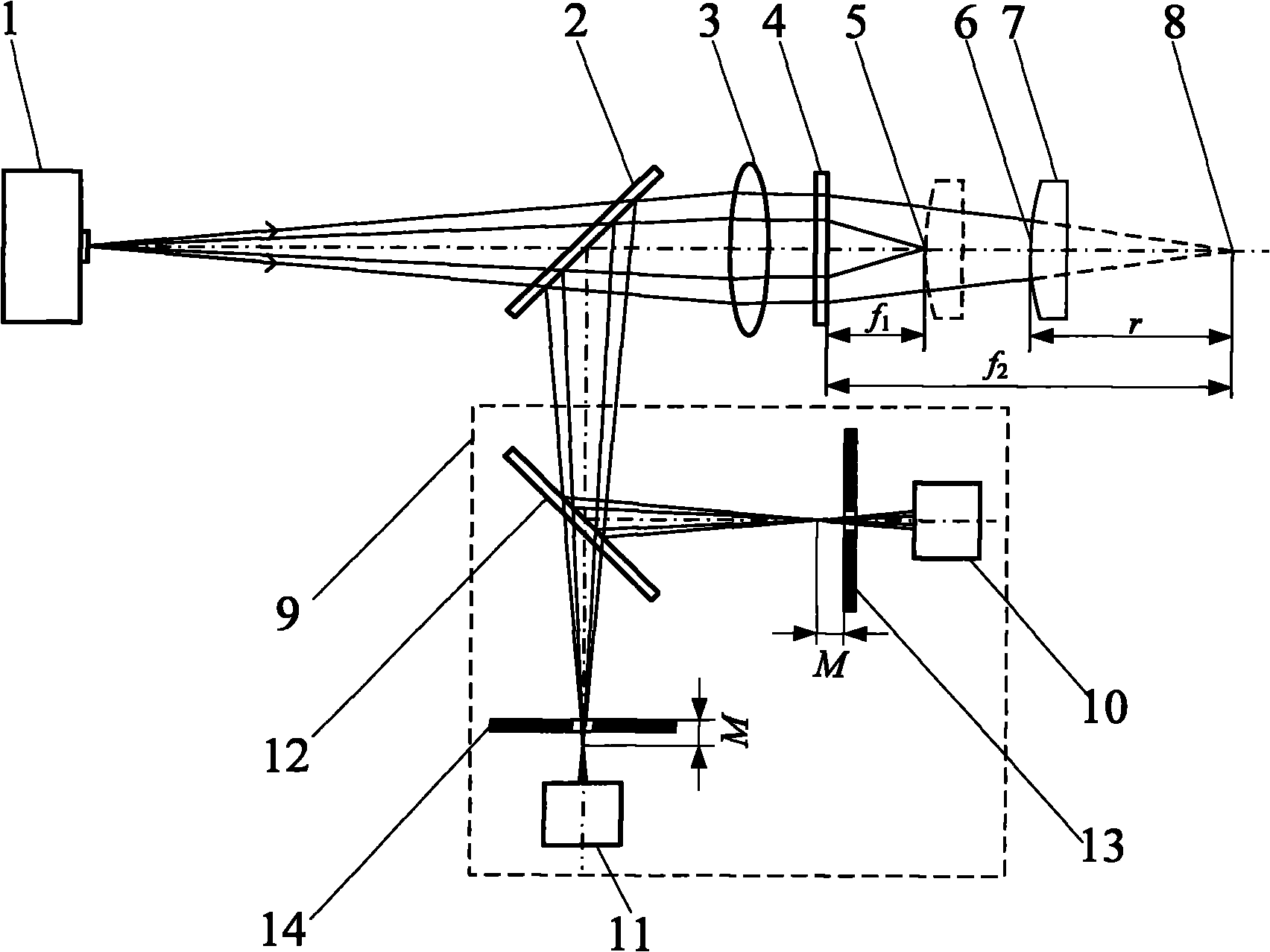
[0047] In this embodiment, a convex lens is adopted as the measured object 7, such as Figure 5 As shown, the multi-focus holographic differential confocal ultra-large radius of curvature measurement device includes a point light source 1, which is placed in turn in the first beam splitter 2, collimator lens 3, multi-focus holographic lens 4 and the measured The component 7 also includes a differential confocal system 9 placed in the reflection direction of the first beam splitter 2;
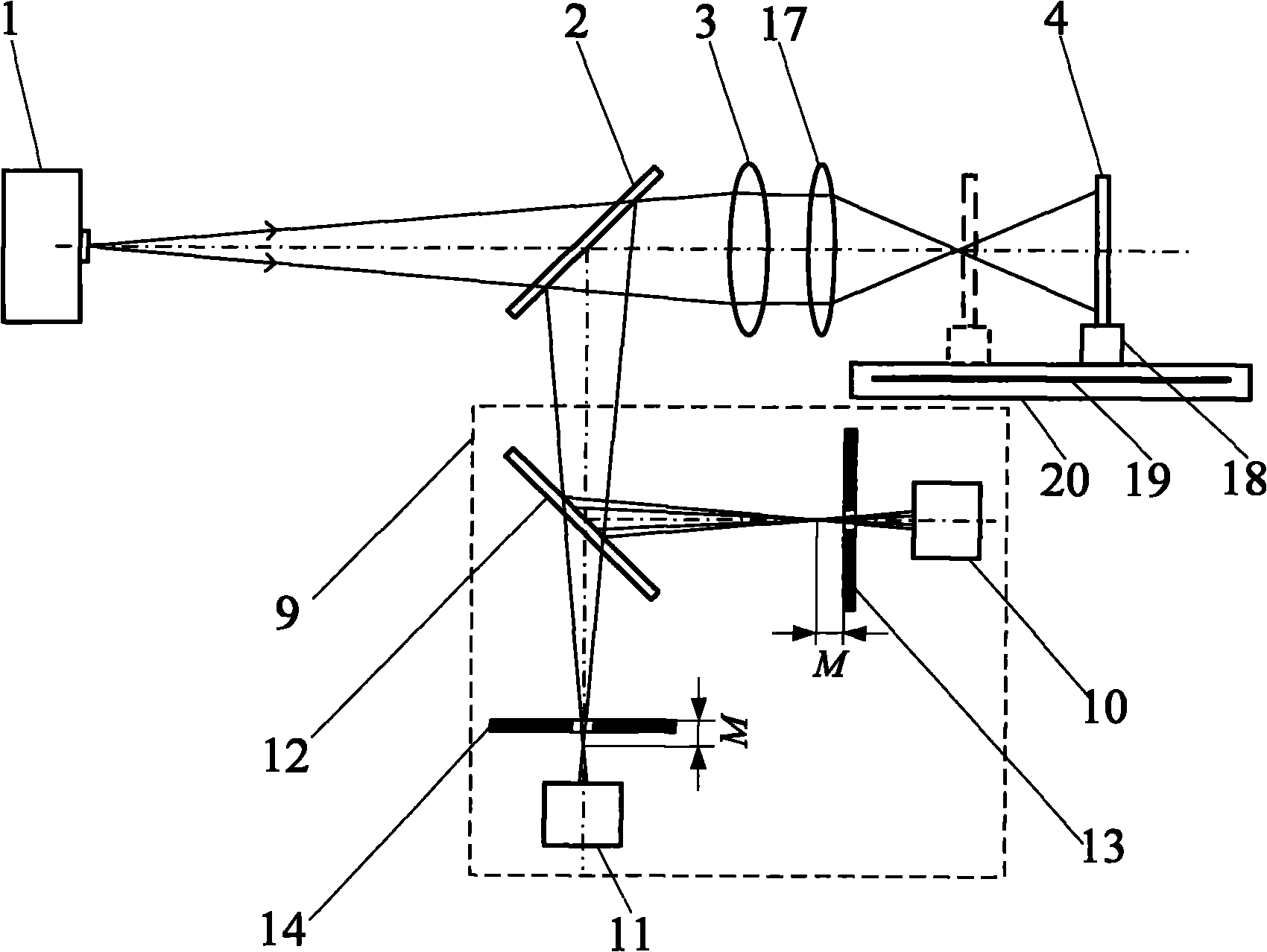
[0048] The device also includes an adjustment frame 18, a length measuring system 19, a moving guide rail 20, a main control computer 22 and an electromechanical control device 21; The length measurement system 19 is installed on the moving guide rail 20, the main control computer 22 obtains the differential confocal response signal through the first light intensity sensor 10 and the second light intensity sensor 11, and the main control computer 22 controls the electromechanical control device ...
Embodiment 2
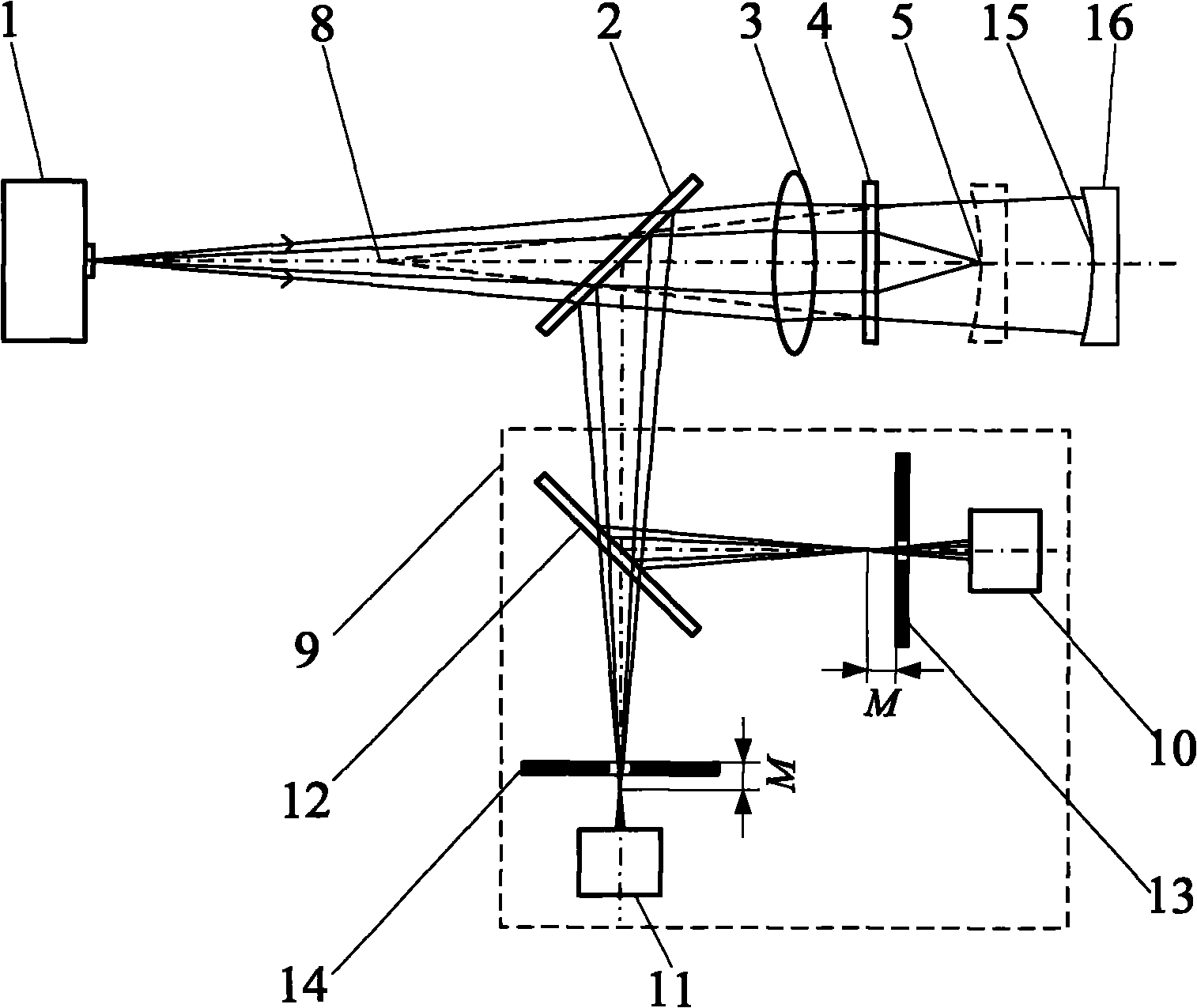
[0062] In the present embodiment, a concave lens is adopted as the measured object 16, such as figure 2 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the measured surface 15 of the measured object 16 has a negative radius of curvature, and the -1st order diffracted light in the telephoto region of the multi-focus holographic lens 4 is used to generate divergent spherical waves during measurement, and the detected The confocal position of the measured surface 6 of the test piece 7 is obtained by the first-order diffracted light in the short-focus area of the multi-focal holographic lens 4. The cat’s eye position of the tested surface 6 of the test piece 7 is obtained; The converging point 5 of the beam locates the apex of the measured surface 15 , and the spherical center of the measured surface 15 is positioned by the converging point 8 of the long-focus measuring beam of the multi-focus holographic lens. All the other measuring methods and devices are the same as in E...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Example 1 Figure 8 The differential confocal system in 9 is replaced by Image 6 The differential confocal system 9 can constitute the embodiment 2. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that after the light enters the differential confocal system 9, the second beam splitter 12 divides the light into two paths, the reflected light illuminates the first light intensity sensor 10 located behind the focus, and the transmitted light illuminates the first light intensity sensor 10 located before the focus The second light intensity sensor 11. All the other measuring methods and devices are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com