Temperature self-adaptation drive method for smectic state liquid crystal display screen
A technology of liquid crystal display and driving method, which is applied in static indicators, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as insufficiency, loss of gray scale, deflection of smectic liquid crystal molecules, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
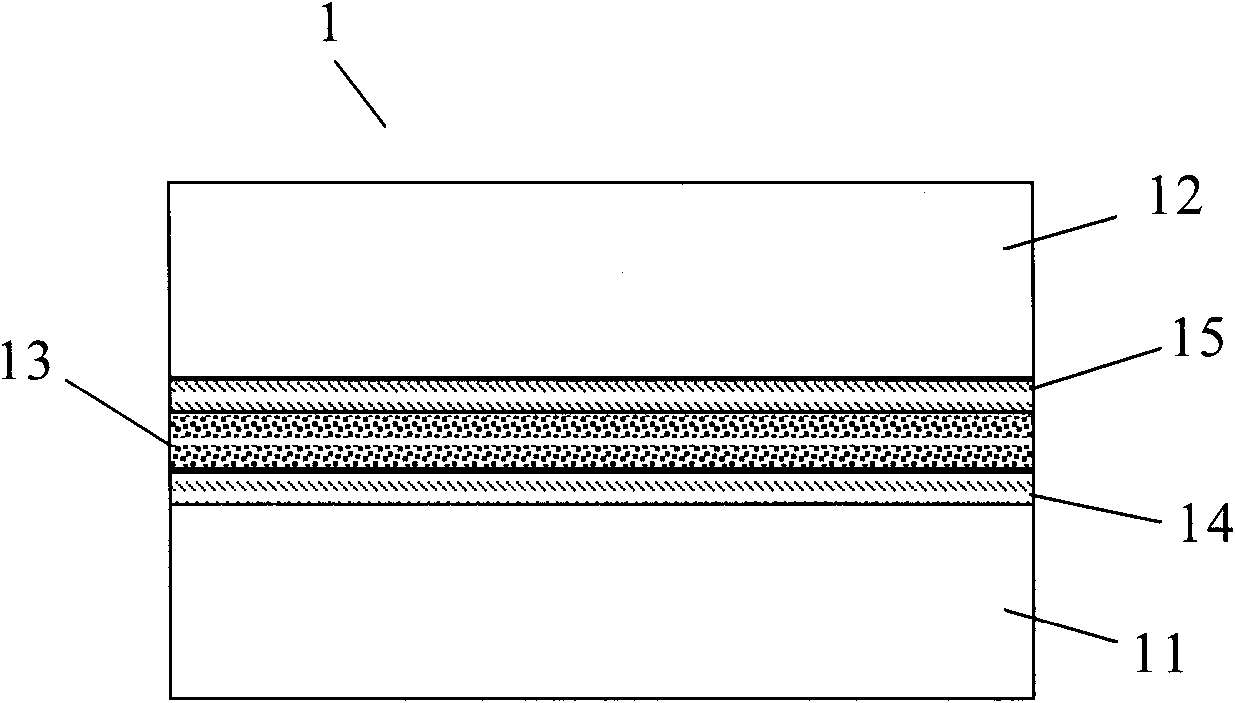
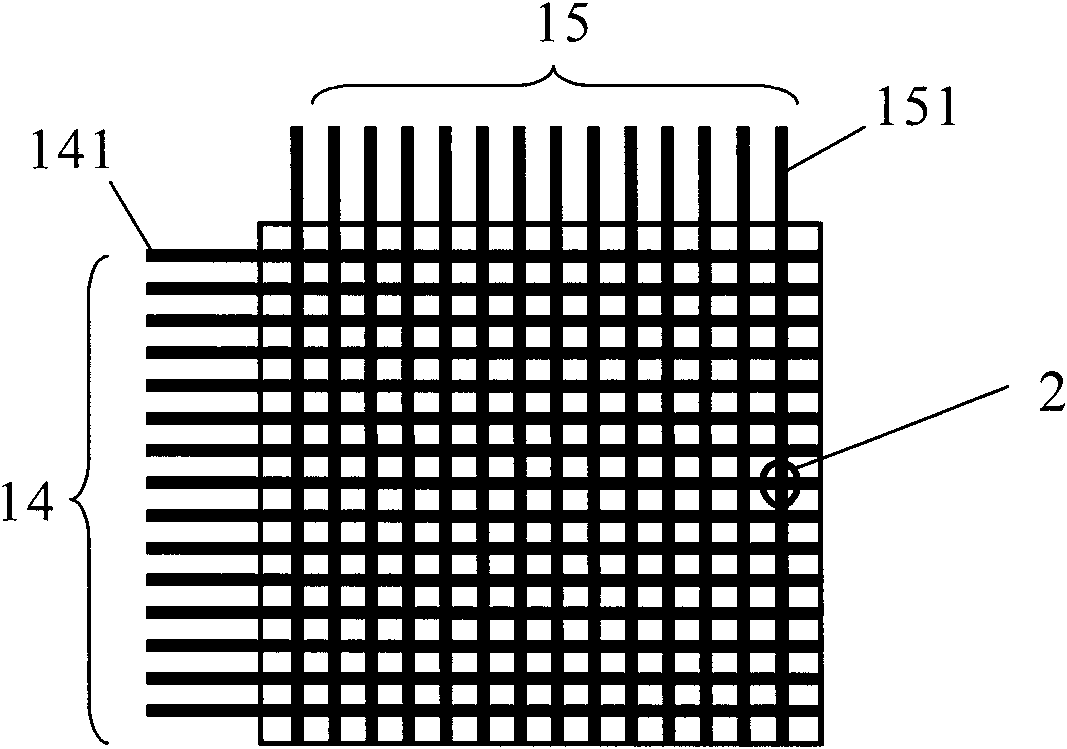
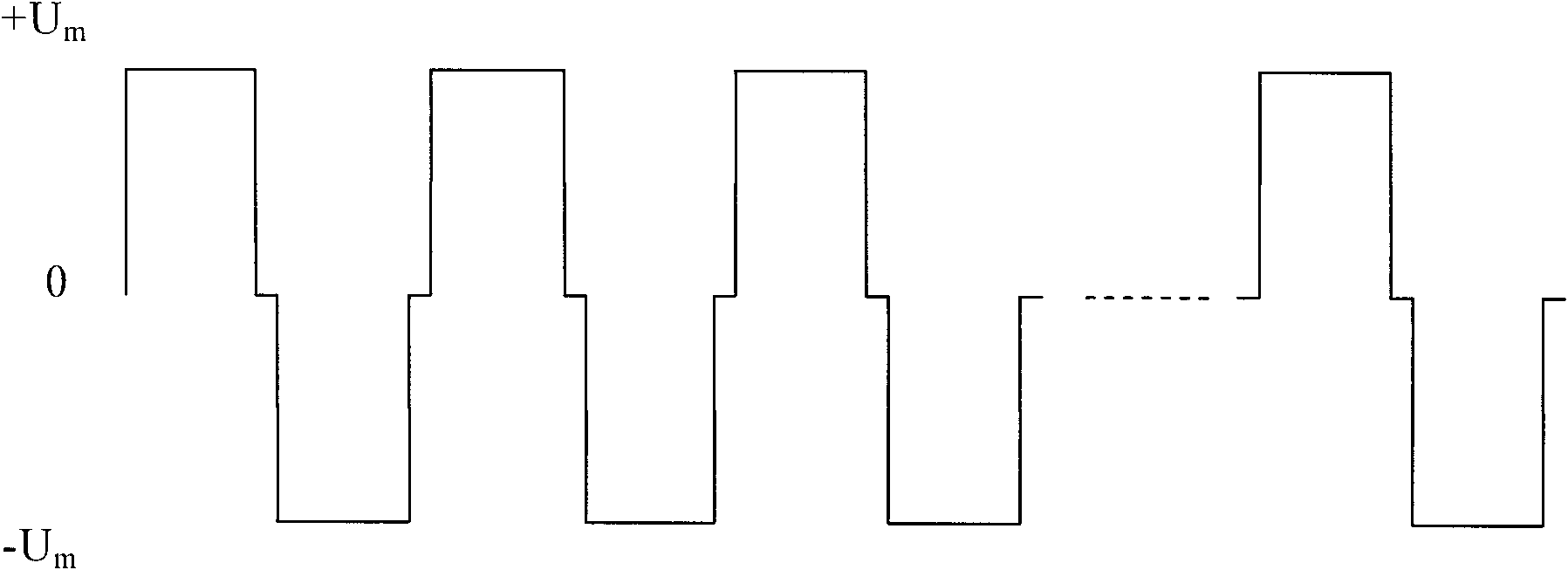
[0022] The temperature self-adaptive driving method of the present invention is designed for the smectic liquid crystal display screen. Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the smectic liquid crystal display screen 1 includes a first base layer 11 and a second base layer 12, and the materials of the first base layer 11 and the second base layer 12 can be glass or plastic. Between the first matrix layer 11 and the second matrix layer 12, there is a mixed layer 13 formed by mixing smectic liquid crystals and additives, that is, by Figure 5 Smectic liquid crystal molecules 131 shown in are mixed with additive molecules 132 . The smectic liquid crystal is a class A smectic liquid crystal (Smectic-A) organic compound, such as a compound with a silicon group, tetracyanotetraoctylbiphenyl, decyl tetraacetate tetracyanobiphenyl, and the like. The additives are compo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Voltage amplitude | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com