Multi-agent robot cooperative control method based on artificial physics method
A multi-agent, collaborative control technology, applied in non-electric variable control, position/direction control, control/regulation system and other directions, can solve the problem of maintaining formation, no multi-robot moving body, and no multi-robot moving body formation control And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] According to content of the invention, the present invention is further described with examples below:
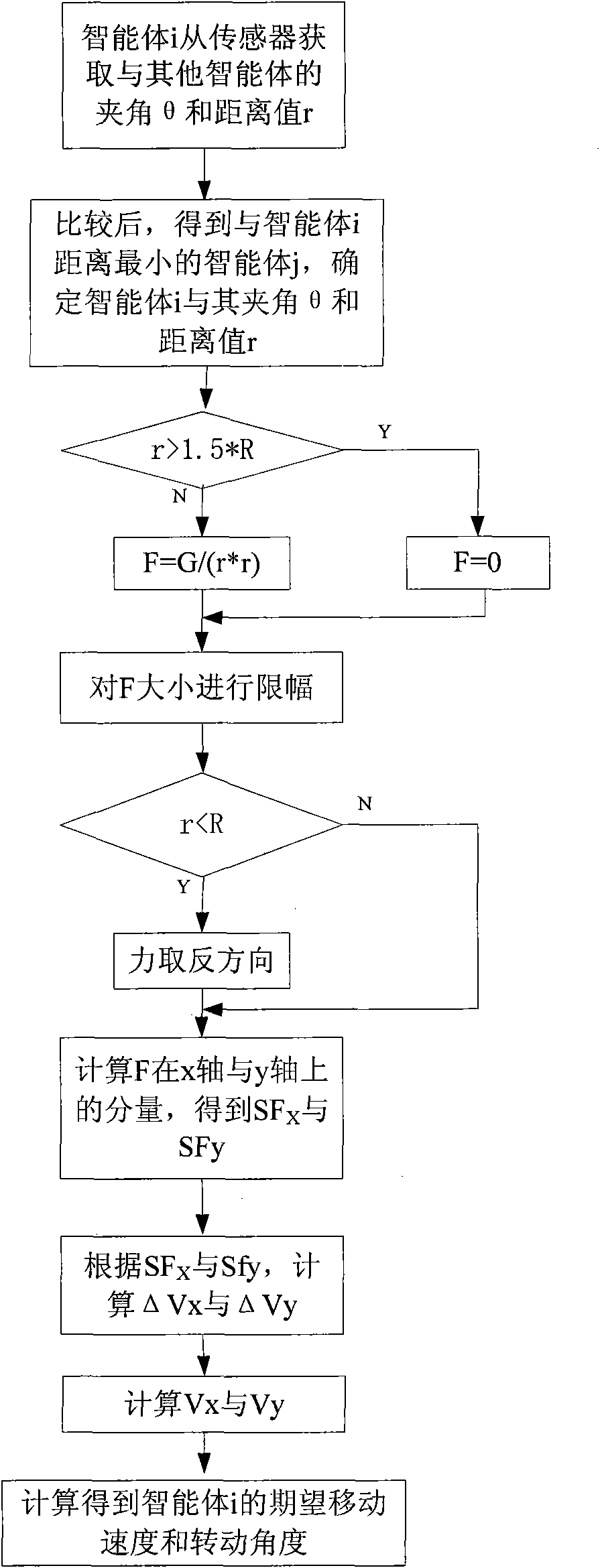
[0075] Step (1): Based on the artificial physics method, the vector force field for the interaction between the intelligent body and the robot is established;
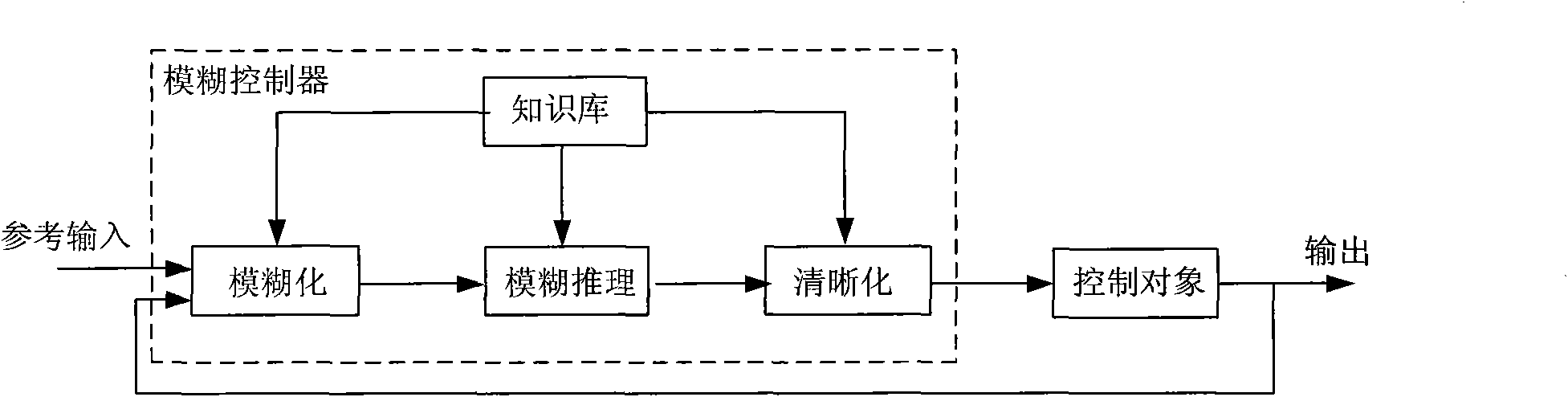
[0076] In the framework of artificial physics (AP), virtual physical forces drive an agent-robot swarm system to achieve a desired state. The state is a shape that minimizes the potential energy of the whole system, and the system behaves as molecular dynamics Among them, F stands for force, m stands for mass, and a stands for acceleration.
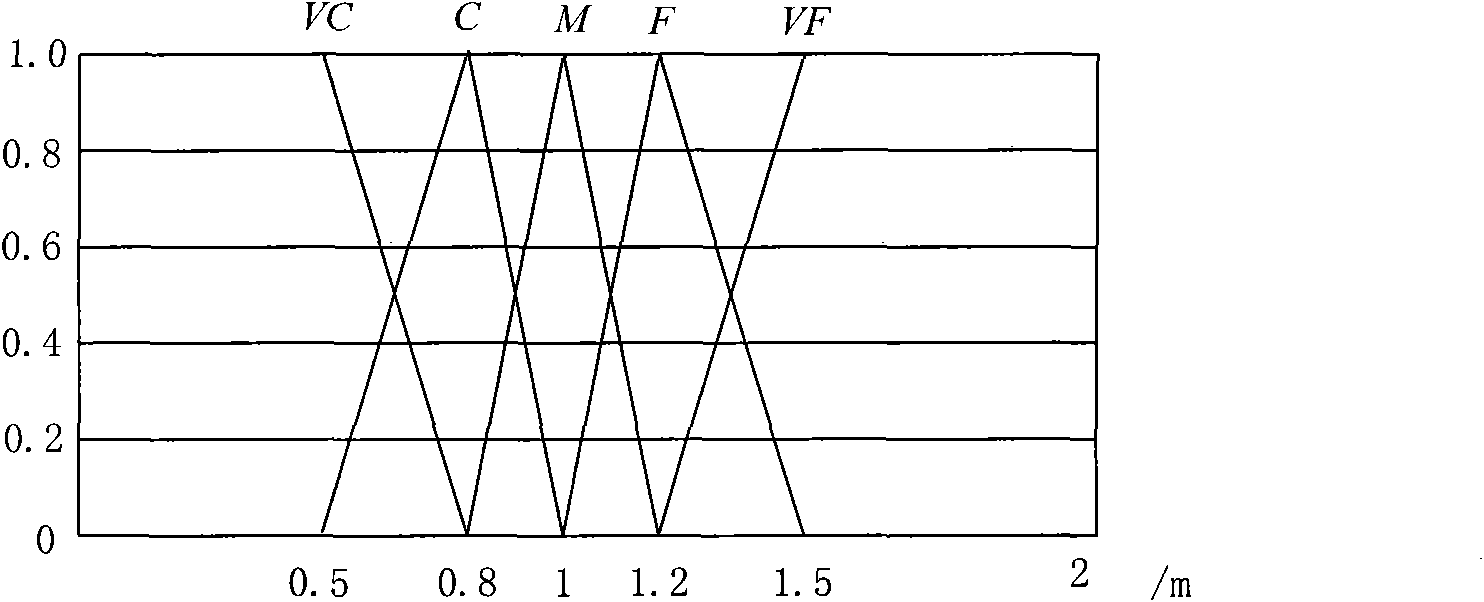
[0077] Define force rule: F=Gm i m j / r p . where F is the magnitude of the force between the agent robot i and the agent robot j, m i 、m j is the mass of the i and j agents, r is the distance between the two agents, G is a parameter representing the clustering characteristics, p is an adjustable parameter, the larger p is, the greater the influence of F is on t...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Step (1): Based on the artificial physics method, the vector force field for the interaction between the intelligent body and the robot is established;
[0109] In the framework of artificial physics (AP), virtual physical forces drive an agent-robot swarm system to achieve a desired state. The state is a shape that minimizes the potential energy of the whole system, and the system behaves as molecular dynamics Among them, F stands for force, m stands for mass, and a stands for acceleration.
[0110] Define force rule: F=Gm i m j / r p . where F is the magnitude of the force between the agent robot i and the agent robot j, m i 、m j is the mass of the i and j agents, r is the distance between the two agents, G is a parameter representing the clustering characteristics, p is an adjustable parameter, the larger p is, the greater the influence of F is on the change of r. R is the threshold distance, if r≤R, the force is repulsion, if r>R, the force is attraction. E...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com