Dry land farmland water potential soft measuring method based on microenvironment information and soft measuring network
A soft measurement and micro-environment technology, applied in the direction of testing water, material inspection products, etc., can solve the problems of inability to adapt to continuous automatic monitoring of crop water potential, high price, inconvenient maintenance, etc., to achieve continuous automatic monitoring, low cost, and informatization. high degree of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0058] Specific embodiments are given below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings to further illustrate how the dryland farmland water potential soft-sensing method and soft-sensing network based on micro-environmental information of the present invention are realized.
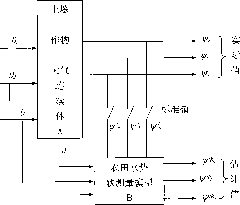
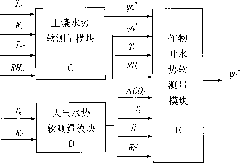
[0059] The dryland farmland water potential soft-sensing method and soft-sensing network based on micro-environmental information of the present invention are connected by several farmland water potential soft-sensing stations (FWP soft-sensing stations) and precision irrigation (PI) decision-making centers to form an upper star network, relying on public wireless Communication platform (GMS / GPRS) for long-distance data transmission. The PI decision-making center receives farmland water potential information sent by all FWP soft-sensing stations in the area under its jurisdiction, and combines remote sensing, geographic coordinates (GPS), agricultural meteorological information, crop cultivation models,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com