Method for reducing intracranial pressure
An intracranial pressure and receptor antagonist technology, which can be used in pharmaceutical formulations, resistance to vector-borne diseases, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., and can solve problems such as expensive and complex
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
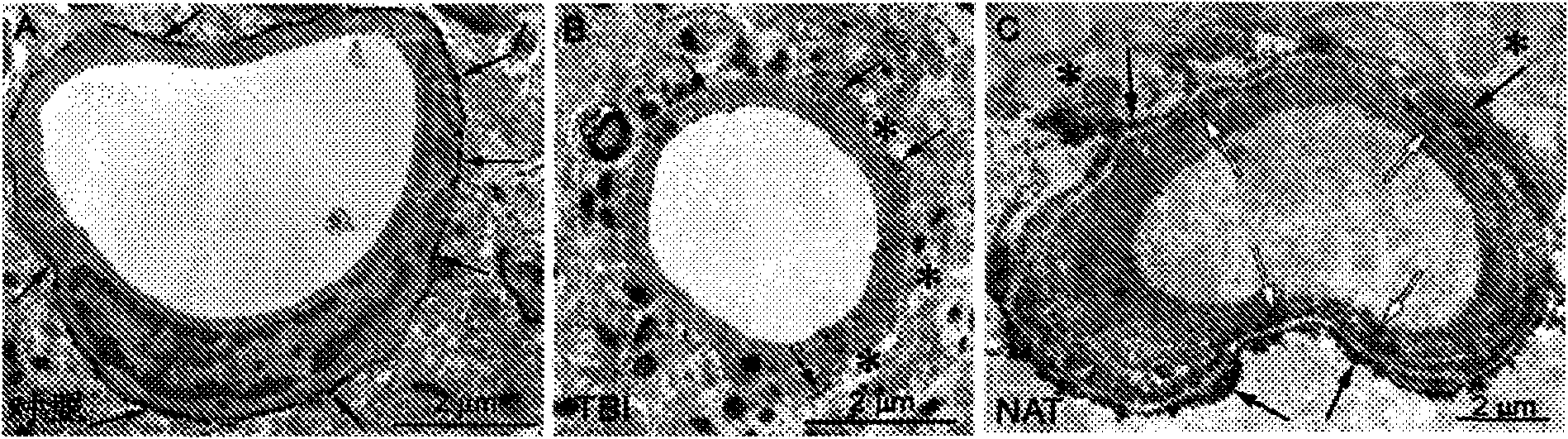
[0156] Aquaporin-4 expression decreased after traumatic brain injury
[0157] In an attempt to lower intracranial pressure, osmotic diuretics such as mannitol are routinely used, although their efficacy is considered to be very limited. These substances are pharmacologically inert substances that act by increasing the colloid osmotic pressure of the blood, providing the driving force for water reabsorption from tissues into the circulation. However, their ability to draw water from the brain in conditions of elevated intracranial pressure is questionable.
[0158] This suggested to us that after injury, there must be changes in the blood vessels of the brain that limit the ability of water to move back out of the brain. We decided to study the water channels associated with brain blood vessels, specifically aquaporin 4 (AQP-4), to see if there were any changes in the expression of these channels. For these studies, a rat model was used and ICP elevation was induced by diffus...
Embodiment 2
[0164] Administration of N-acetyl-L-tryptophan induces the expression of aquaporin 4 after traumatic brain injury
[0165] We postulate that substance P may play a role in causing these changes in vascular function, so if we inhibit the action of substance P using, for example, NK1 receptor antagonists, we may be able to reverse these changes.
[0166] Currently, a variety of commercially synthesized substance P receptor antagonists are available from standard scientific chemical suppliers. We chose to use the NK1 receptor antagonist N-acetyl-L-tryptophan.
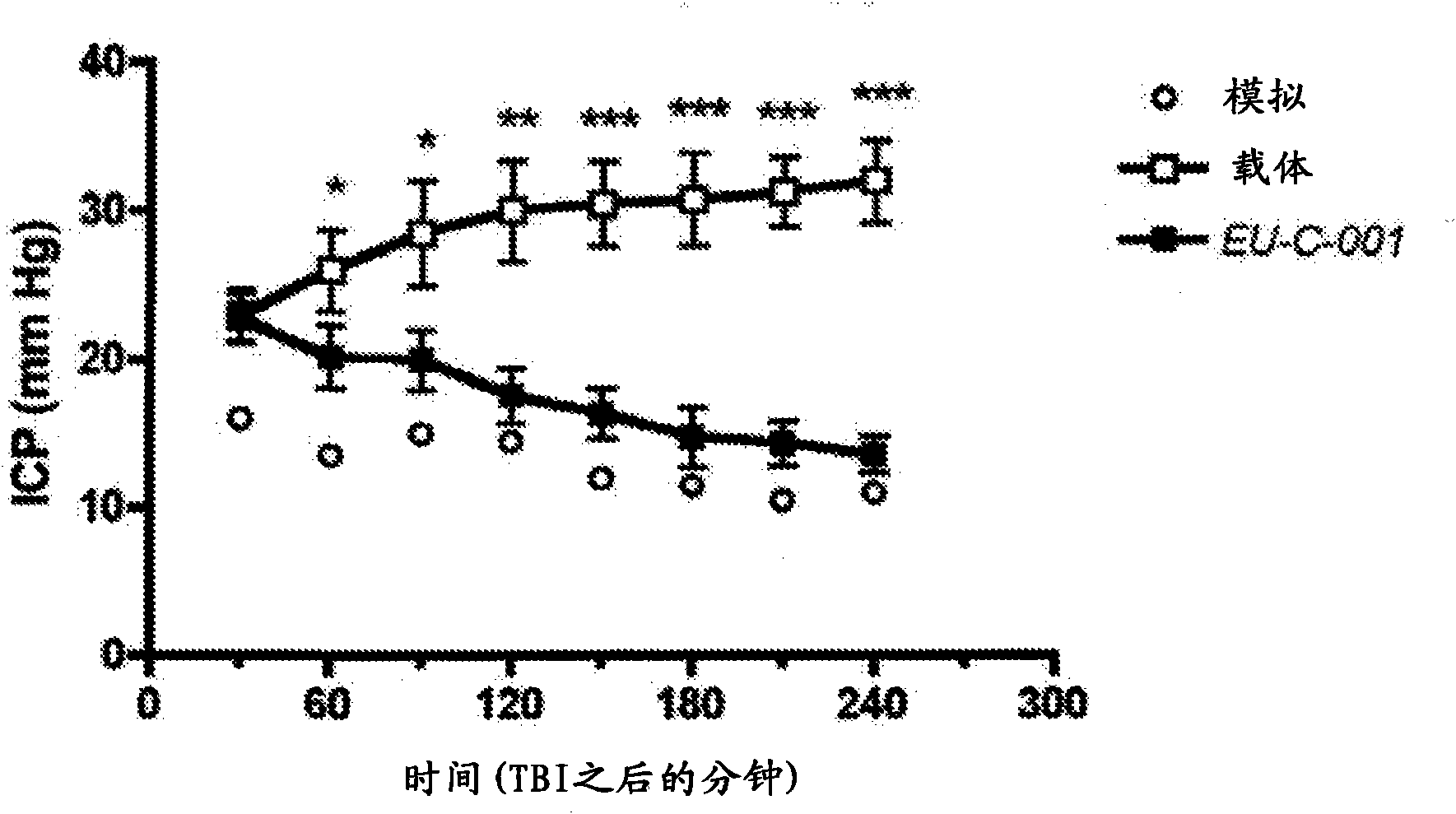
[0167] N-acetyl-tryptophan was dissolved in sterile saline and administered intravenously 30 minutes after injury induction. It has been found that administration of N-acetyl-L-tryptophan after injury leads to increased expression of aquaporin-4, or even higher than pre-injury levels ( figure 1 , right). Based on the drug's ability to reduce the permeability of the blood-brain barrier after injury, the optimal dose is 2.5...
Embodiment 3
[0169] Administration of N-acetyltryptophan promotes water removal from brain tissue into circulation in a rat model of traumatic brain injury
[0170] Changes in aquaporin-4 expression and the ability of substance P receptor antagonists to restore its normal expression levels suggest that these substances may be able to move water out of the brain, which helps reduce intracranial pressure.
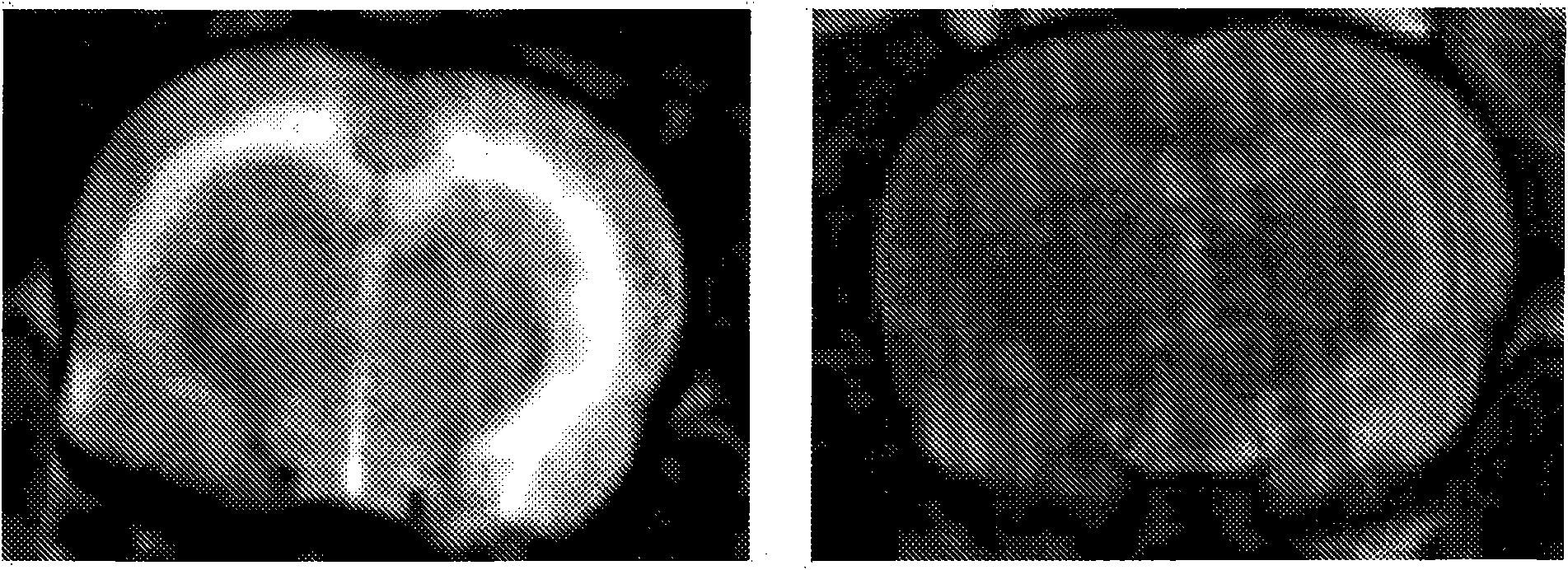
[0171] To see if substance P receptor antagonists could facilitate water removal from the brain, we performed nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) studies using a rat model of traumatic brain injury. Diffusion-weighted NMR images produced after trauma ( figure 2 , left).
[0172] After injury, many "bright" areas are evident in the brain. These "bright" areas are associated with areas in the brain where extracellular water accumulates.
[0173] Apply 10 after damage -5 mol / kg of N-acetyl-L-tryptophan, showed no accumulation of any water in these areas ( figure 2 , left pan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com