Multiphase long-stator primary permanent magnet linear motor
A permanent magnet linear motor and stator technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, electromechanical devices, electric components, etc., can solve the problems of motor magnetic circuit and winding asymmetry, magnetic circuit and winding asymmetry, back EMF is not symmetrical, etc., to achieve structural Compactness, reduced thrust fluctuation, and high power density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
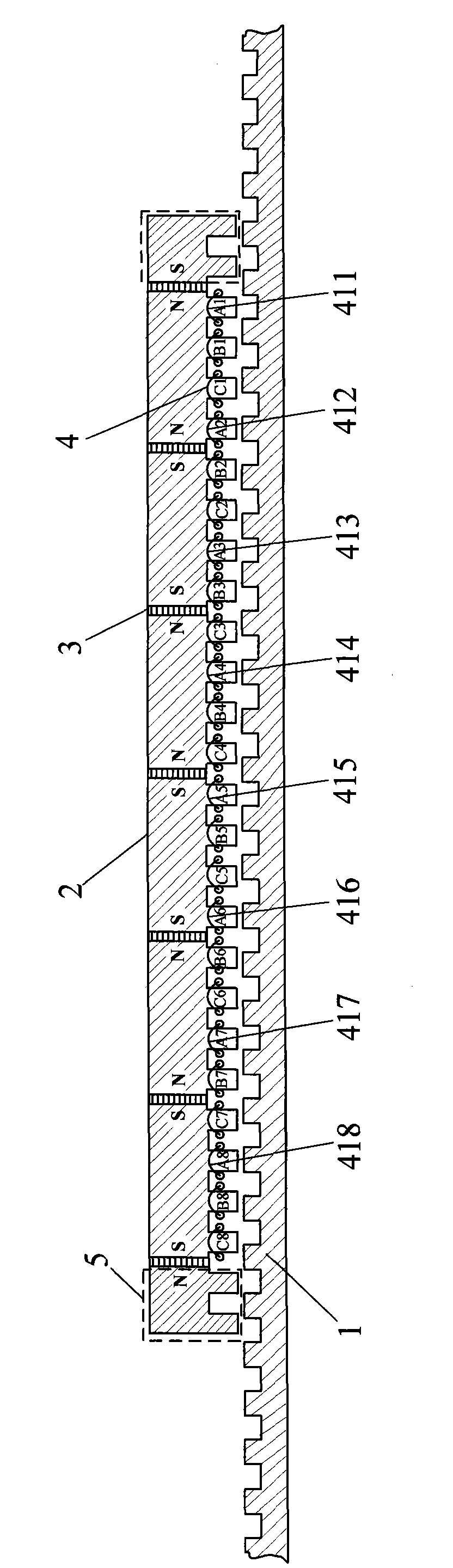
[0019] Specific implementation mode one: figure 1 It is a cross-sectional view of a 3-phase permanent magnet series-connected plate-type long stator primary permanent magnet linear motor designed by the technology of the present invention. If m=3, k=1, and j=1, the number of permanent magnets is N PM =2k×m+2=8, the number of teeth of the mover sleeve with winding is N mt =(N PM -2)(m+1)=24, the range of additional teeth at each end of the motor is between [2 and 4], and there is no winding on the additional teeth. τ p / τ s =m / (m-0.5j)=6 / 5 The permanent magnet is a flat plate structure, and adopts the parallel magnetization method. Each non-additional permanent magnet corresponds to m+1=4 teeth, wherein the concentrated windings on the first tooth and the fourth tooth belong to the same phase, and the windings on the remaining teeth belong to other phases in turn. The magnetization directions of adjacent permanent magnets are opposite.
[0020] The motor of the present in...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0025] Specific implementation mode two: combination figure 1 , figure 2 This embodiment is described. The first difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment is that the motor structure is a cylindrical structure. Its axial section view is as figure 2 shown. The stator 1 is a cylindrical structure, the mover 2 is a cylindrical structure, and the permanent magnet 3 is composed of a ring-shaped cylindrical permanent magnet material or N tile permanent magnet materials, and radial magnetization is adopted. 6 is a non-magnetic conductive material. When needed, 6 can be filled in the middle of the stator slot, and the stator is a slotless cylindrical structure at this time. At the same time, the winding groove of the mover is sealed with material 6, and the contact surface between the mover and the stator is also a smooth groove-free structure. Other composition and connection methods are the same as those in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0026] combine figure 1 , image 3 This embodiment is described. The first difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment is that the permanent magnet of this motor adopts the second magnet placement method described in the technical solution. In this embodiment, m=3, k=1, j=1, then the number of permanent magnets is N PM =2k×m+1=7, the number of teeth of the mover sleeve with winding is N mt =(N PM -2)(m+1)=24, the number of additional teeth at both ends of the motor is between [2 and 4], and there is no winding on the additional teeth. τ p / τ s =m / (m-0.5j)=6 / 5, the permanent magnet is a flat plate structure, and adopts the parallel magnetization method. There are m+1=4 teeth between adjacent permanent magnets, wherein the concentrated windings on the first tooth and the fourth tooth belong to the same phase, and the windings on the remaining teeth belong to other phases in turn. The magnetization directions of adjacent permanent magnets are opposite. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com