Method of joining a thermoplastic material to a fibre composite material
A fiber composite material, thermoplastic material technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, synthetic resin layered products, household components, etc., can solve problems such as disadvantages
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] According to Example 1, a stent comprising a thermoplastic material is shown in Figure 5 In this case, the bracket is bonded to a fiber composite material, which in this embodiment is a fiber reinforced plastic.
[0051] In this embodiment, the bracket 33 comprises a disc-shaped connecting portion 34 which is connected with fiber-reinforced plastic and a seat 35 . The connection part 34 and the support 35 have a polyamide PA66 content of 70% and a glass fiber content of 30%. The stand 35 is used to support objects such as electrical leads or heavier objects. The thickness of the connecting portion is 2.2 mm in this embodiment, and the diameter of the connecting portion is 24 mm in this embodiment.
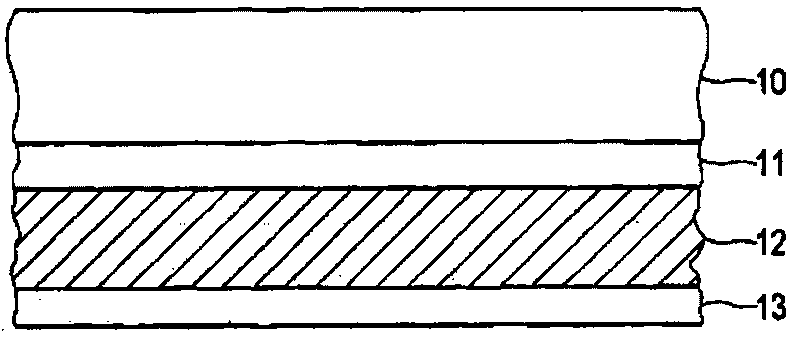
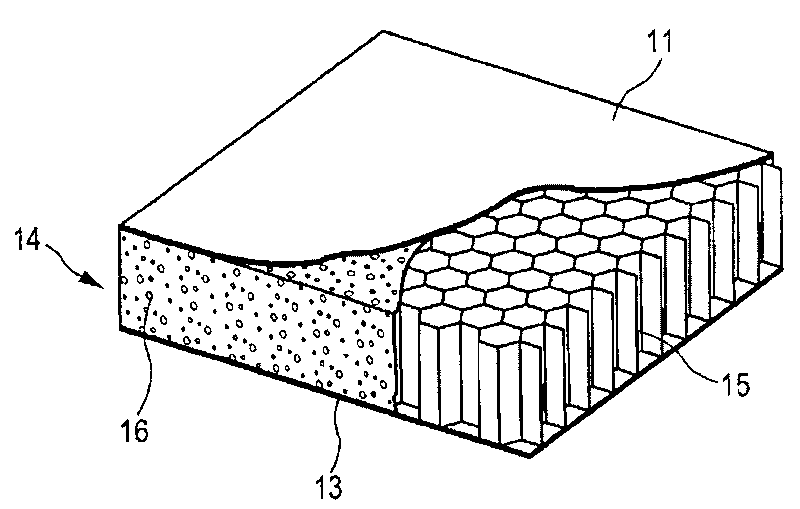
[0052] In this embodiment the fiber reinforced plastic is a sheet of glass reinforced plastic and the top outer layer of the sheet to which the surface 36 of the bracket 33 will be joined is 40% resin and 60% glass fiber braid. The thickness of the flakes is 2 mm in tota...
Embodiment 2
[0057] In this embodiment, the bracket shown in Embodiment 1 is also used. In this embodiment, the fiber-reinforced plastic is a carbon fiber-reinforced plastic sheet, and the top outer layer of the sheet connected by the bracket is 45% resin and 55% carbon fiber braid. The thickness of the sheet was 2 mm.
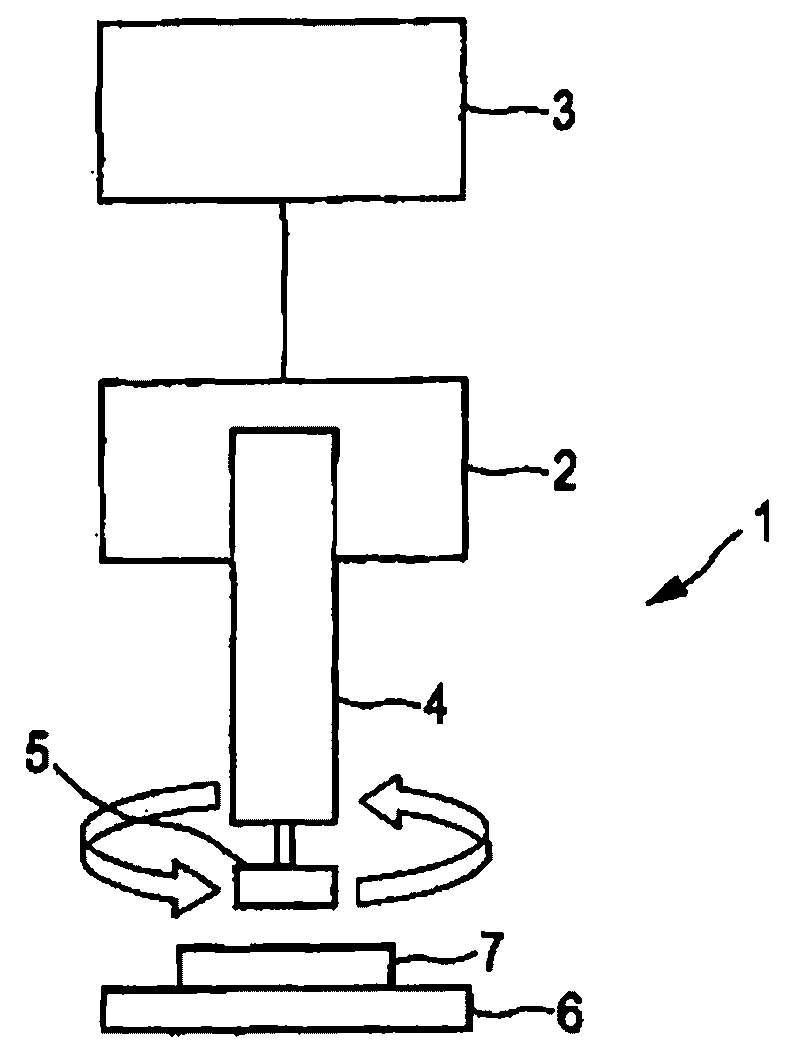
[0058] The method according to the invention for joining thermoplastic material (stent) to fiber reinforced material (carbon fiber reinforced plastic sheet) by using figure 1 The device 1 shown is realized.
[0059] In this embodiment, the angular frequency is 160 Hz and the welding time is 3 seconds. The welding time is the time during which the bracket moves relative to the fibre-reinforced plastic, the predetermined pressure between the thermoplastic material and the fibre-reinforced plastic being 1.0 bar in this example. In this exemplary embodiment, the welding process is regulated by the welding time, ie each welding process is 3 seconds. In these examples, tensi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com