Level shifter circuit incorporating transistor snap-back protection
A technology of level shifter and voltage shift, which is applied in the direction of logic circuit coupling/interface, logic circuit, logic circuit connection/interface arrangement using field effect transistors, etc., which can solve the problem that level shifter circuits cannot be used.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
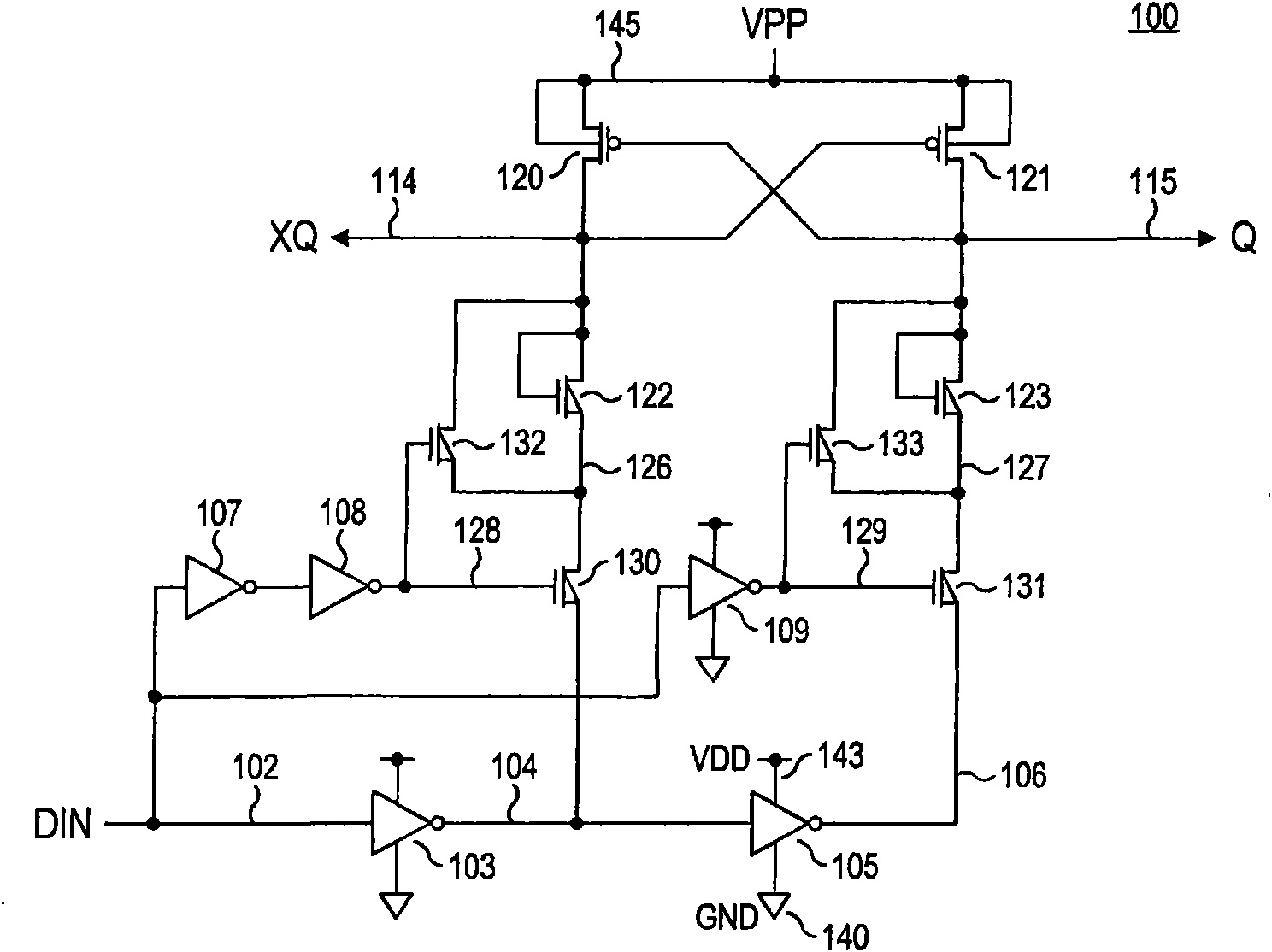
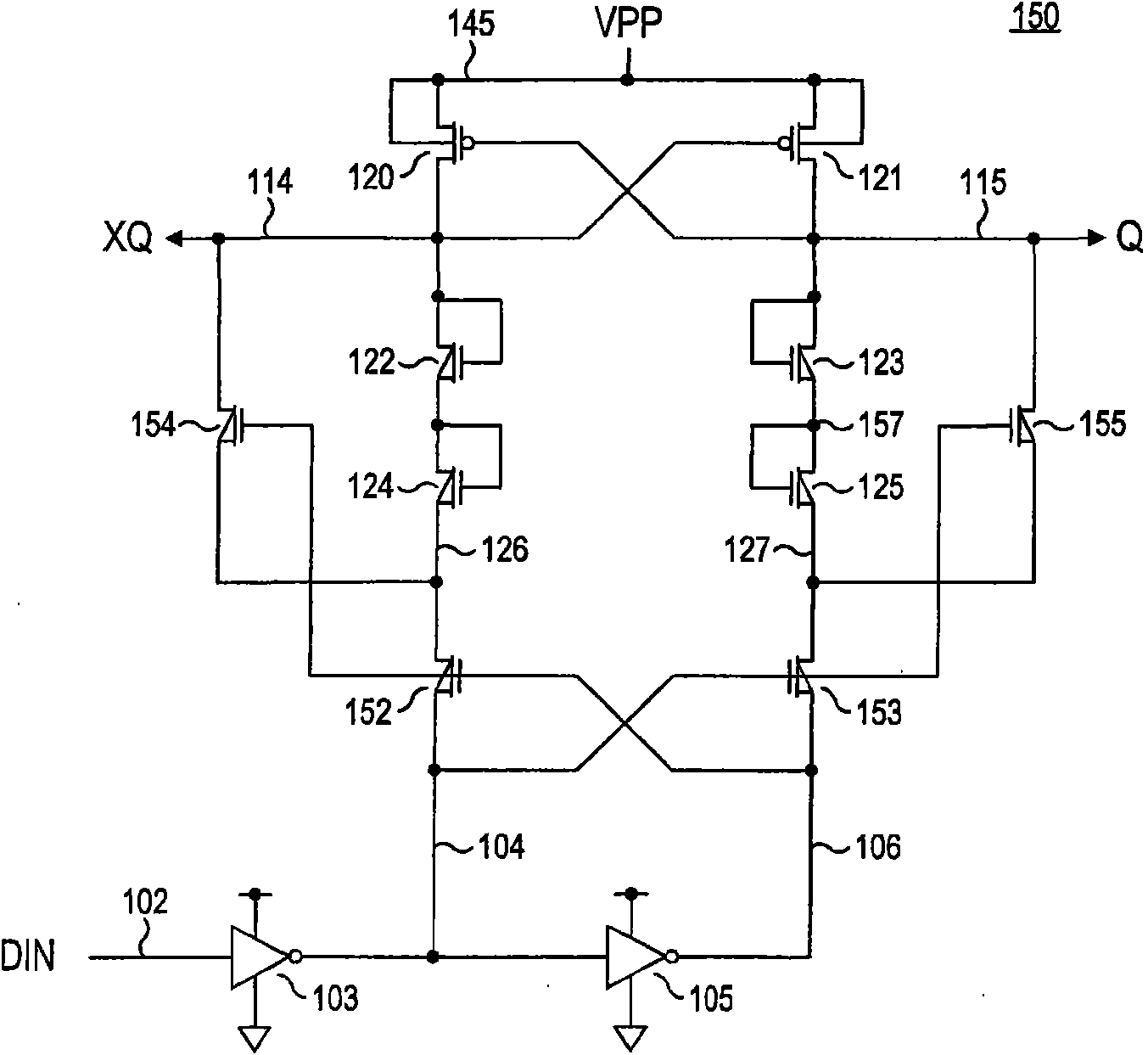
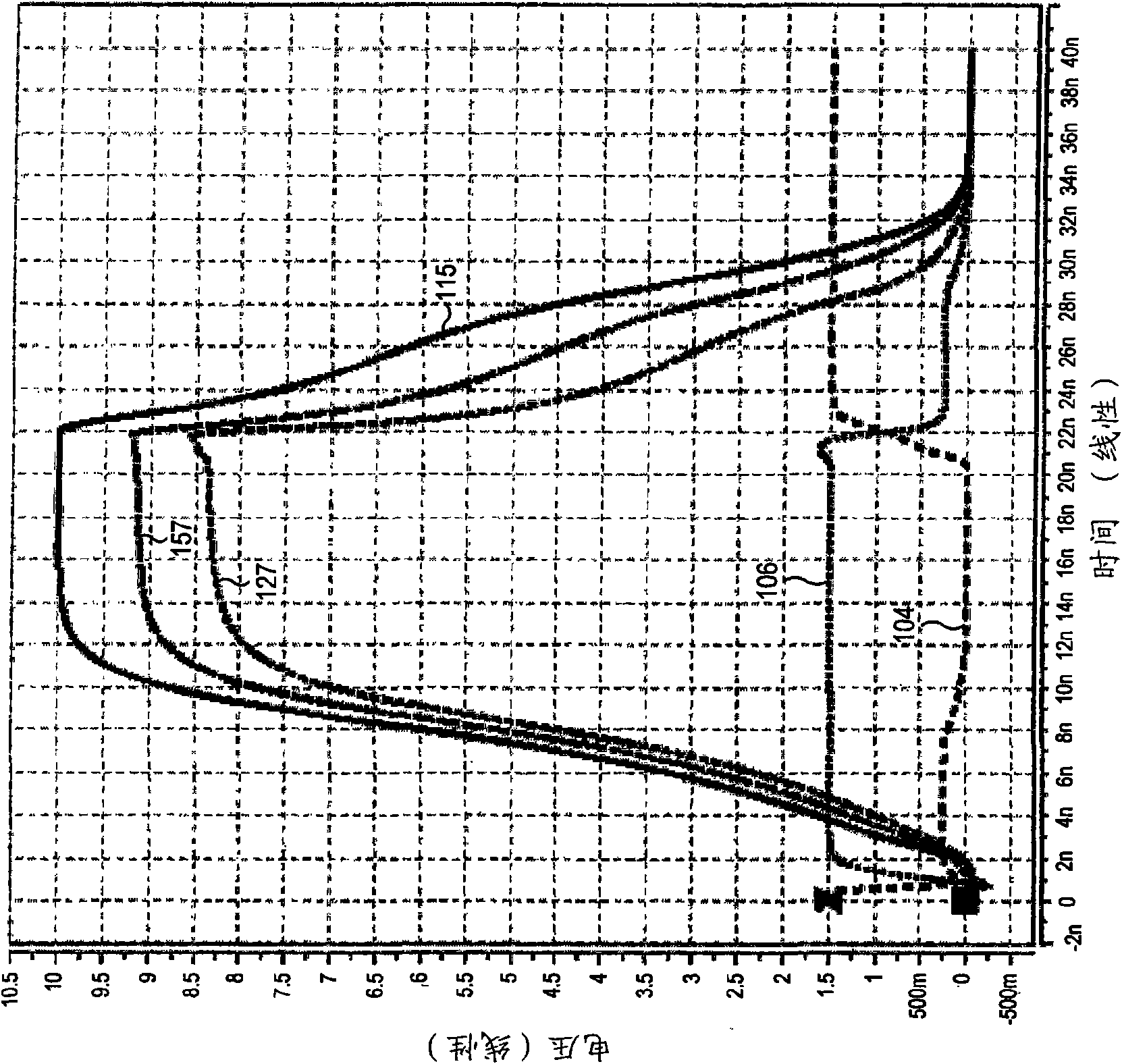
[0027] now refer to figure 2 , shows a level-shifting circuit that does not require intentional weakening of the pull-down path and that is protected from the jump-through effect regardless of the output load. As before, logic signal DIN is transmitted on node 102 and inverted by low voltage inverter 103 to generate a VDD level control signal at node 104 which is inverted by low voltage inverter 105 phase to generate a VDD level control signal at node 106 . The inverters 103, 105 can be regarded as belonging to the VDD voltage range (ie, the low voltage range), and the input signal DIN transmitted on the node 102 and the control signals transmitted on the nodes 104, 106 can be regarded as having a voltage corresponding to VDD and VDD respectively. The high level and low level VDD range (that is, low voltage range) signals corresponding to the ground.
[0028] Complementary XQ, Q output nodes 114, 115 are coupled to VPP through cross-coupled PMOS transistors 120, 121 and to g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com