Compositions and methods for bone formation and remodeling
A bone-related and adipogenesis technology, which can be used in botanical equipment and methods, drug combinations, active ingredients of heterocyclic compounds, etc., and can solve problems such as weakening antagonism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
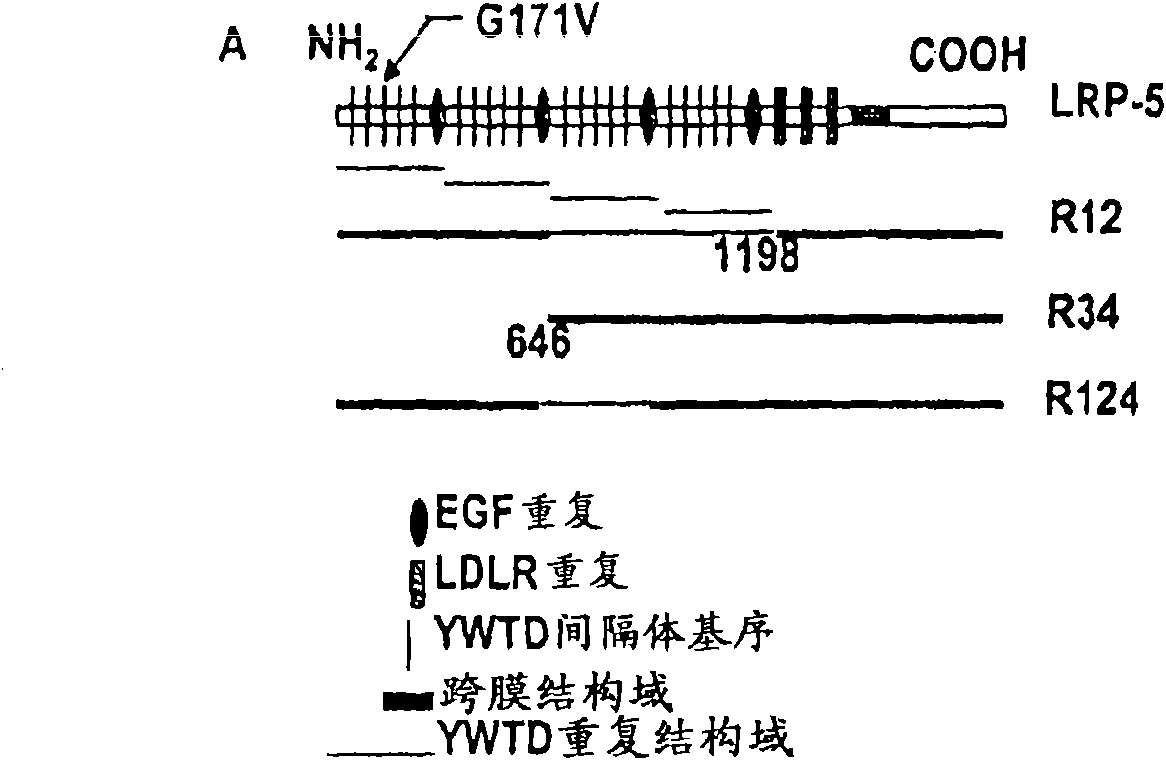
[0280] Example 1. Deletion mutants of LRP5
[0281] A series of PCR primers were designed, PCR reaction was carried out, and PCR fragments were subcloned into vectors to obtain several deletion mutants of LRP5. Deletion of the third and fourth domains (646-1198 residues) produces LRP5R12; deletion of the first and second domains (1-646 residues) produces LRP5R34; and deletion of the third domain (947-1198 residues) produces LRP5R124 (see figure 1 A).
Embodiment 2
[0282] Example 2. LRP5 first domain is essential for Mesd-mediated function of LRP5
[0283] Example 2.1 The G171V mutation in the first domain of LRP5 disrupts LRP5 trafficking
[0284] Interaction of LRP5 with Mesd
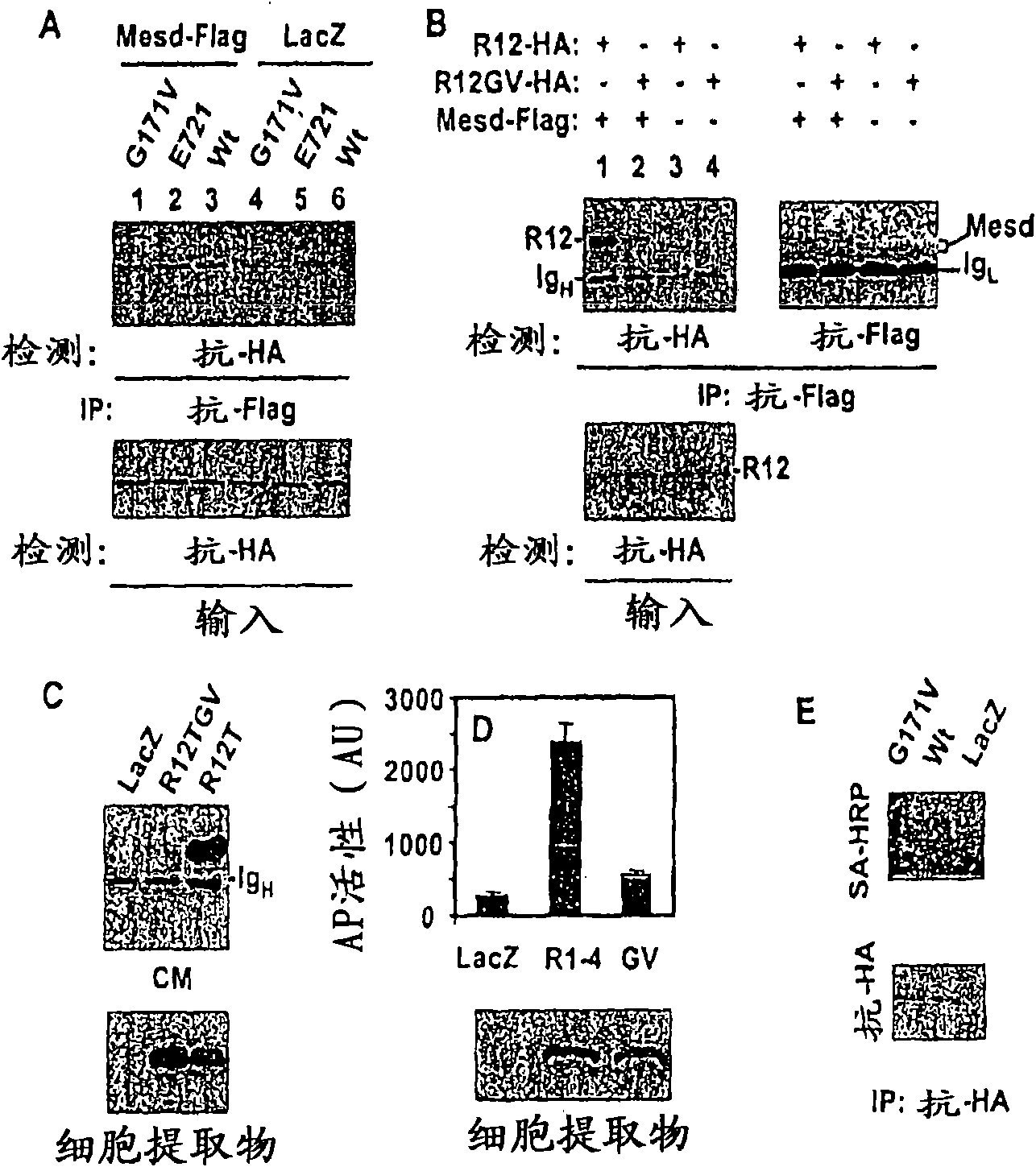
[0285] like figure 2 As shown in A, HEK cells were transfected with expression plasmids. One day later cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody. Mesd is Flag-tagged, while all LRP5 molecules are HA-tagged. The results showed that the G171V mutation in the first domain of LRP5 disrupted the relationship between LRP5 and Mesd ( figure 2 A, lanes 1 and 3) and between R12 and Mesd ( figure 2 B, the interactions of lanes 1 and 2), but the E721 mutation in the third domain had no effect on these interactions ( figure 2 A, lanes 2 and 3).
[0286] Mutants of LRP5 cannot efficiently present themselves to the cell surface.
[0287] like figure 2 B and figure 2 As shown in C, HEK cells were transfected with Mesd plasmid and expre...
Embodiment 3
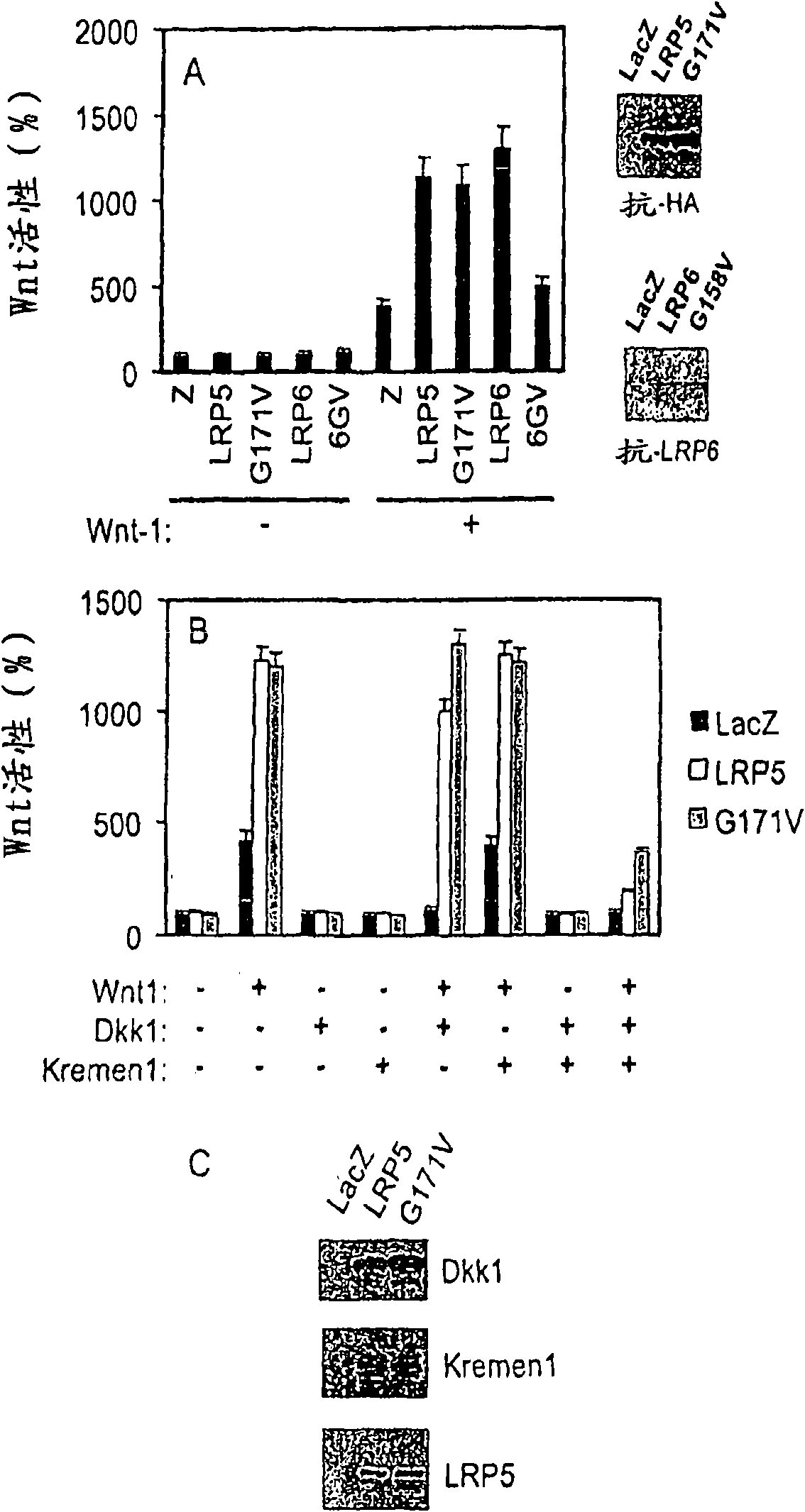
[0297] Example 3. Wnt activity requires the second domain of LRP5
[0298] like Figure 5 HEK cells were transfected with LEF activity reporter plasmid and expression plasmid as indicated. Expression plasmids LRP5R494Q and LRP5G479V are LRP5 receptors containing a point mutation in the second domain. Cells were lysed one day later. Lysed cells were then assayed for GFP levels and luciferase activity as described in "Materials and Methods" and normalized to GFP levels. Figure 5 display with LRP5 Wt In contrast, LRP5R494Q and LRP5G479V abrogate Wnt signaling. These results indicate that the second domain is required for Wnt activity.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com