Method for efficiently detecting interaction of in vivo proteins
A technology for detecting in vivo and internal proteins, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as complex loss, restriction, and too large tag peptides, and achieve the effect of time-consuming and cost-effective detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
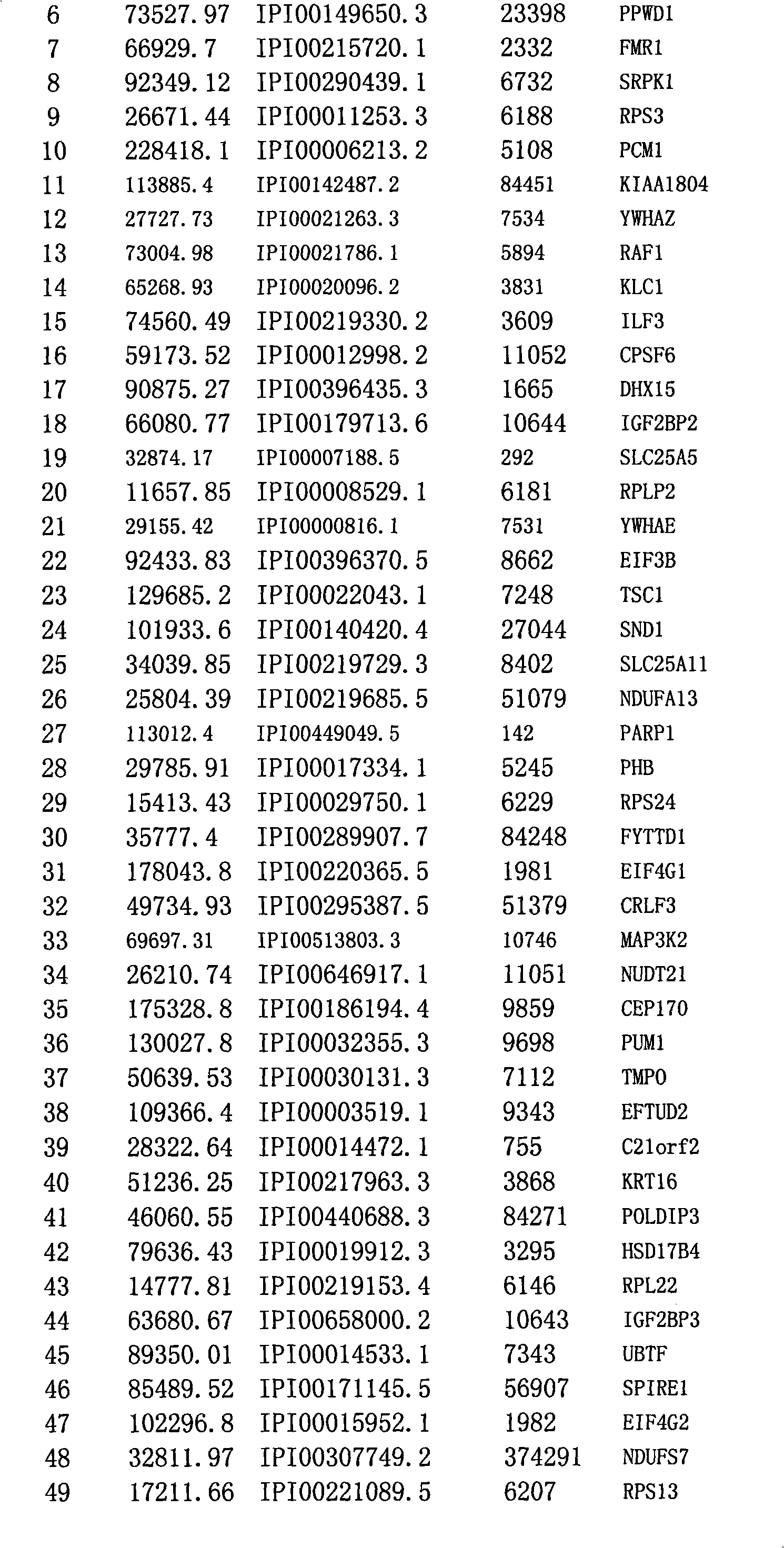
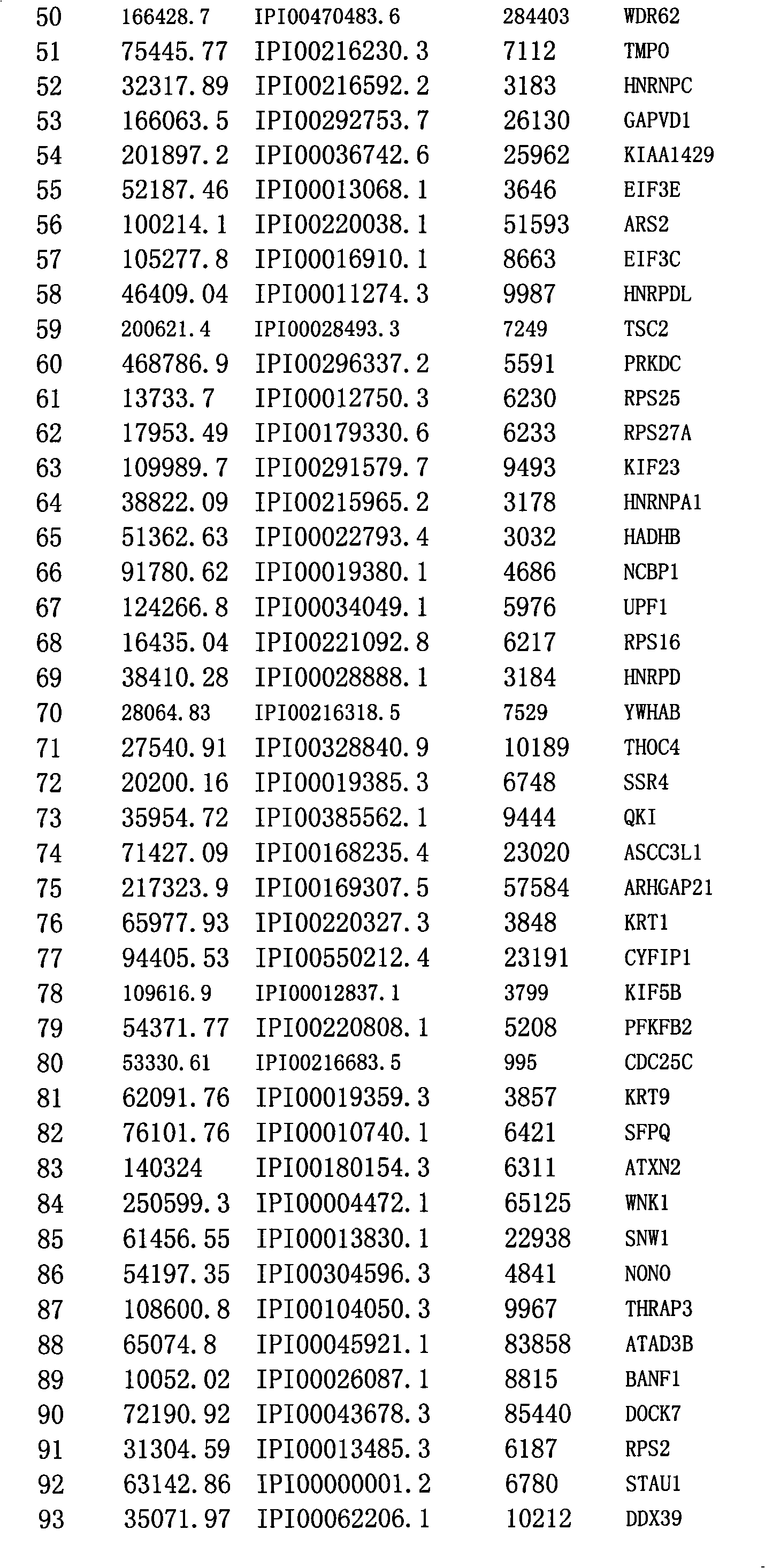
[0039] 1. Construction of plasmid vector
[0040] Based on the plasmid pAP-N that expresses the biotinylated artificial small peptide tag, the plasmid pAP-N-1433 containing 14-3-3ε was constructed. The gene sequence of 14-3-3ε was inserted into the pAP-N Xbal and EcoRV restriction sites. Invitrogen medium extraction kit (Cat. No.: K210004) was used for the medium extraction of plasmids for cell transfection.
[0041] 2. Cell culture
[0042] HEK293T cells (commercially available) are human embryonic kidney cells that grow adherently. The stable cell line was cultured in a 37°C, 5% carbon dioxide incubator, and its medium was normal or d3-Leu-labeled high-glycemic DMEM. 293T cells were labeled with AACT technology and cultured in DMEM medium containing 10% dialyzed fetal bovine serum and labeled amino acids (called 293T-d3), while unlabeled 293T cells were used ordinary DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum Culture medium (referred to as 293T-d0). For related AACT labeling technol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com