Energy-saving medium access control method in underwater acoustic network
A medium access control, underwater acoustic network technology, applied in the direction of reducing energy consumption, ultrasonic/acoustic wave/infrasonic wave transmission system, transmission system, etc., can solve the problem of battery energy consumption of sensor nodes, large data packet propagation delay, and data packet collision rate Advanced problems, to achieve the effect of saving energy consumption, reducing the number of retransmissions, and reducing the collision rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The technical solutions of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the drawings and embodiments.
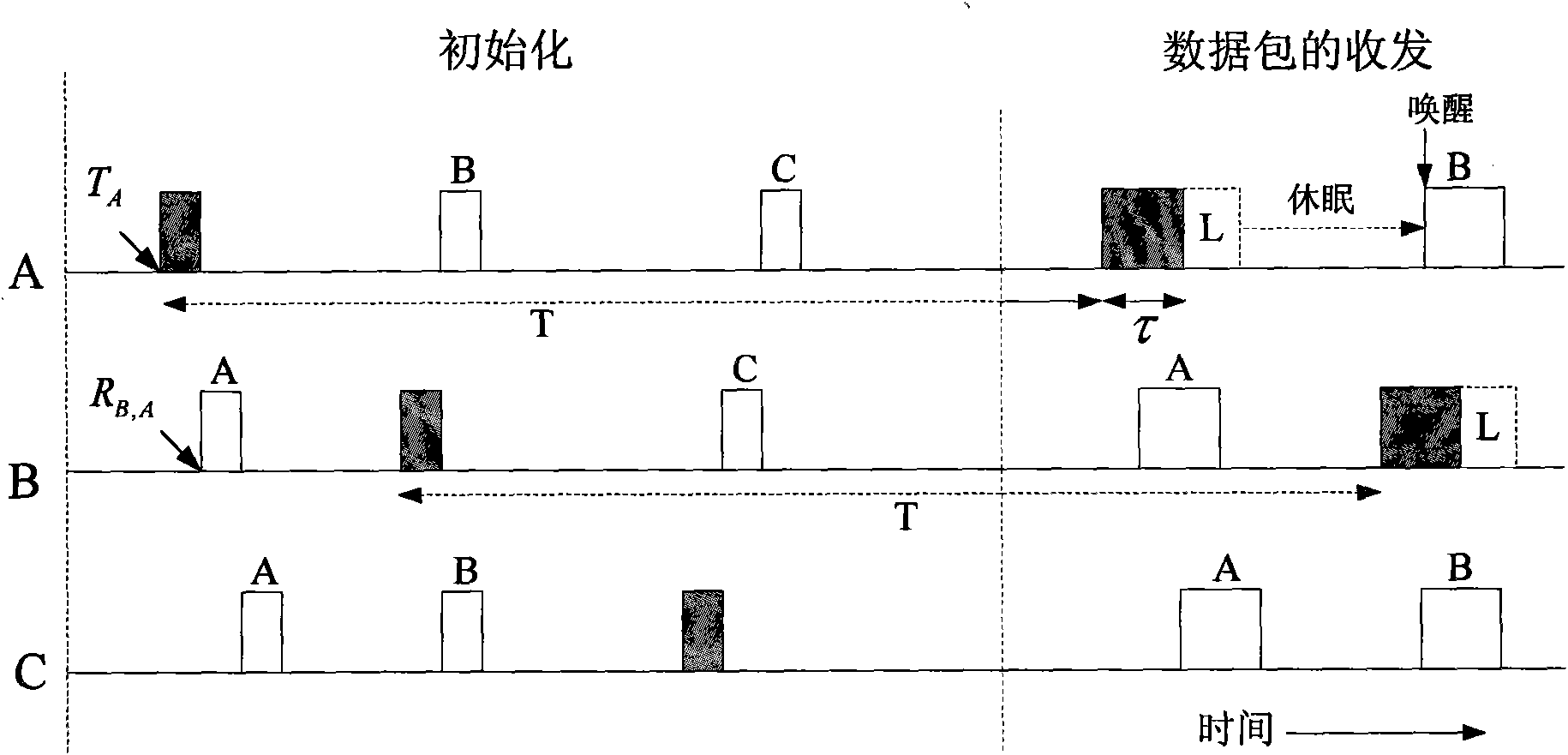
[0030] figure 1 is a network topology instance. exist figure 1 In , the nodes within the sending range of each node become its neighbor nodes. There are five nodes A, B, C, D, and E in the initial setting, and the solid circle represents the sending range of each node. It can be seen from the figure that the neighbor nodes of A are B, C and D; the neighbor nodes of B are A, C, D and E; the neighbor nodes of C are A and B; the neighbor nodes of D are A and B; The neighbor node is B. F is a newly added node after a period of time. In order to distinguish it from the existing nodes in the initial network, its sending range is represented by a dotted circle. After joining the network, its neighbor nodes are B and E. Each node establishes and maintains a wake-up time table, which includes the following items: the sending time of the data p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com