Abiotic stress tolerance conferred by J-domain-containing proteins
A technology of structural domains and proteins, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve problems such as the undocumented functional role of DnaJ protein in abiotic stress tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0048] In the present invention, it was found that proteins comprising the conserved J-domain motif of DnaJ can successfully confer tolerance to stress factors such as salinity, low osmotic potential and dehydration in plant cells and plants. Plants and plant cells exhibit this tolerance by means of transgenic modification to contain an expression system that produces this protein. Rice and Arabidopsis plants are exemplified below, but are by no means limited to these examples. Any higher plant or cell of a higher plant is a suitable subject for the methods and materials of the invention.
[0049] The method of the present invention is applicable to any plant, preferably higher plants belonging to the class Angiosperms and Gymnosperms. Plants of the subclass Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous are particularly suitable. Bileaved plants include the following orders: Magnoliales, Illiciales, Laurales, Piperales, Aristochiales, Nymphaeales, Ranunculales ), Papeverales, Sarrace...
Embodiment 1
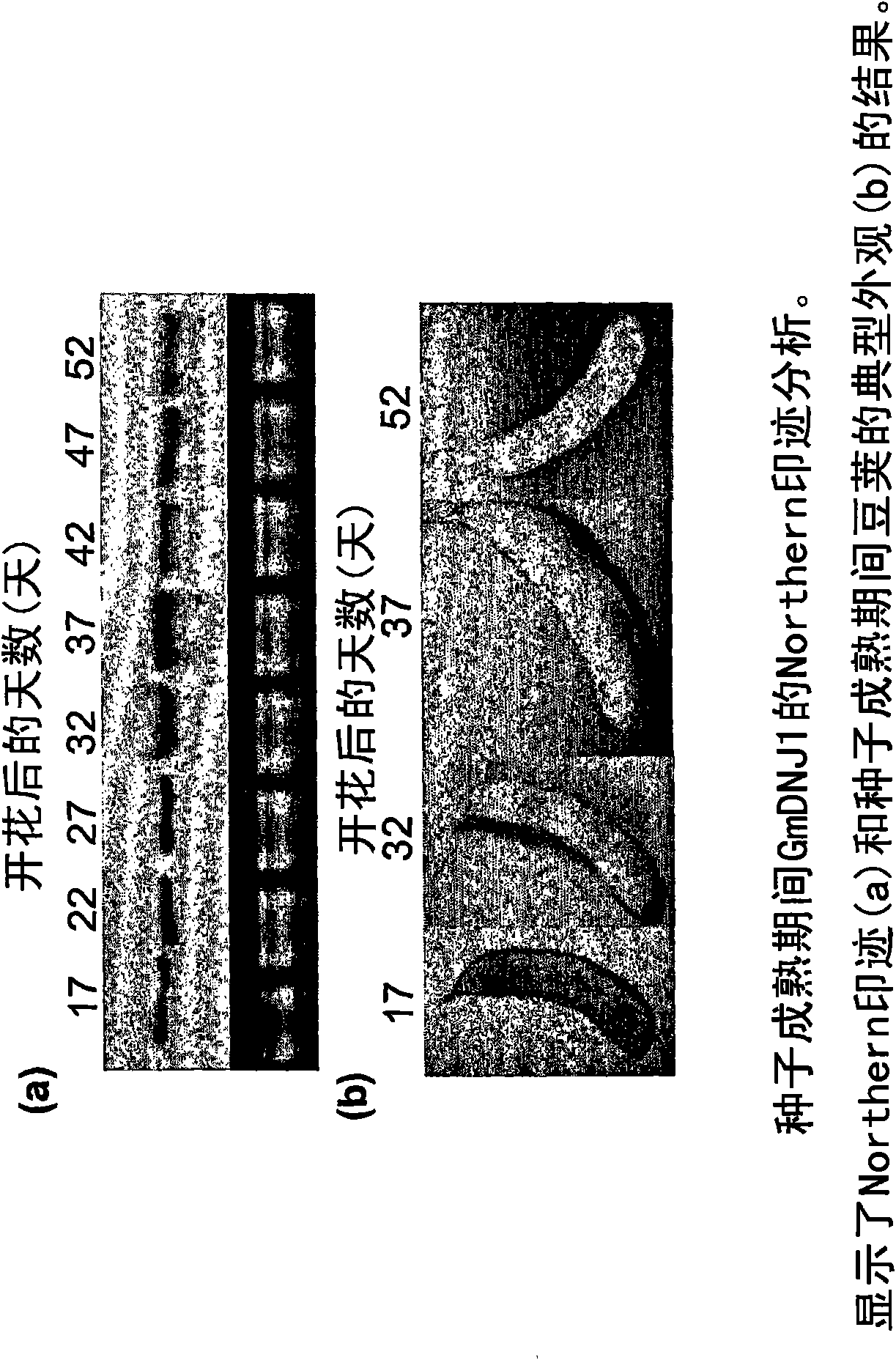
[0065] Expression of GmDNJ1 in response to salinity and dehydration stress
[0066] In this example, expression of GmDNJ1 in leaves and roots of two soybean cultivars in response to salinity stress was investigated. With modified Hoagland's solution (4.5mM KNO 3 , 3.6mM Ca(NO 3 ) 2 , 1.2mM NH 4 NO 3 , 3.0 mM MgSO 4 , 1.2mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 0.25mM KH 2 PO 4 , 4.5 μM nSO 4 , 4.5 μM ZnSO 4 , 1.5 μM CuSO 4 , 0.4μM (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 , 0.09 mM Fe-EDTA and 1.5 μM H 3 BO 3 ) were irrigated with two soybean germplasms, Wenfeng7 (salt tolerant) and Union (salt sensitive), treated with 125 mM NaCl. Leaf and root samples were collected 0-144 hours after treatment.
[0067] As previously described (Sambrook, J. et al., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manuals (Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual), 3rd Edition, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, NY, (2001)) Root and leaf extracts were subjected to Northern blot analysis. Antisense single-stranded DNA...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Transgenic Arabidopsis
[0073] Using the vacuum infiltration protocol (Bechtold, N. et al., Arabidopsis Protocols, Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ, (1993) 259-266), The recombinant nucleic acid containing GmDNJ1 under the control of the constitutive cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter was cloned into a binary vector (Brears, T. et al., Plant Physiol. (1993) 103:1285-1290), introduced into Agrobacterium and transformed into Arabidopsis. After selection of transformants with antibiotic-containing media, individuals with successful integration of the transgene into the genome were verified by PCR using gene-specific primers; Northern blot analysis was performed to confirm transgene expression in the transgenic plant lines. A T containing a single insert was obtained 3 Seeds of homozygous lines were used for subsequent physiological studies. Four homozygous transgenic lines of Arabidopsis thaliana GmDNJ1 were constructed. A-3-4 and M-3-1 with higher expression levels...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com