Electricity saving device and method for sport wrist-watch
A power-saving method and wristwatch technology, applied in the fields of electrical digital data processing, medical science, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems of high power consumption, high use cost, frequent battery replacement, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
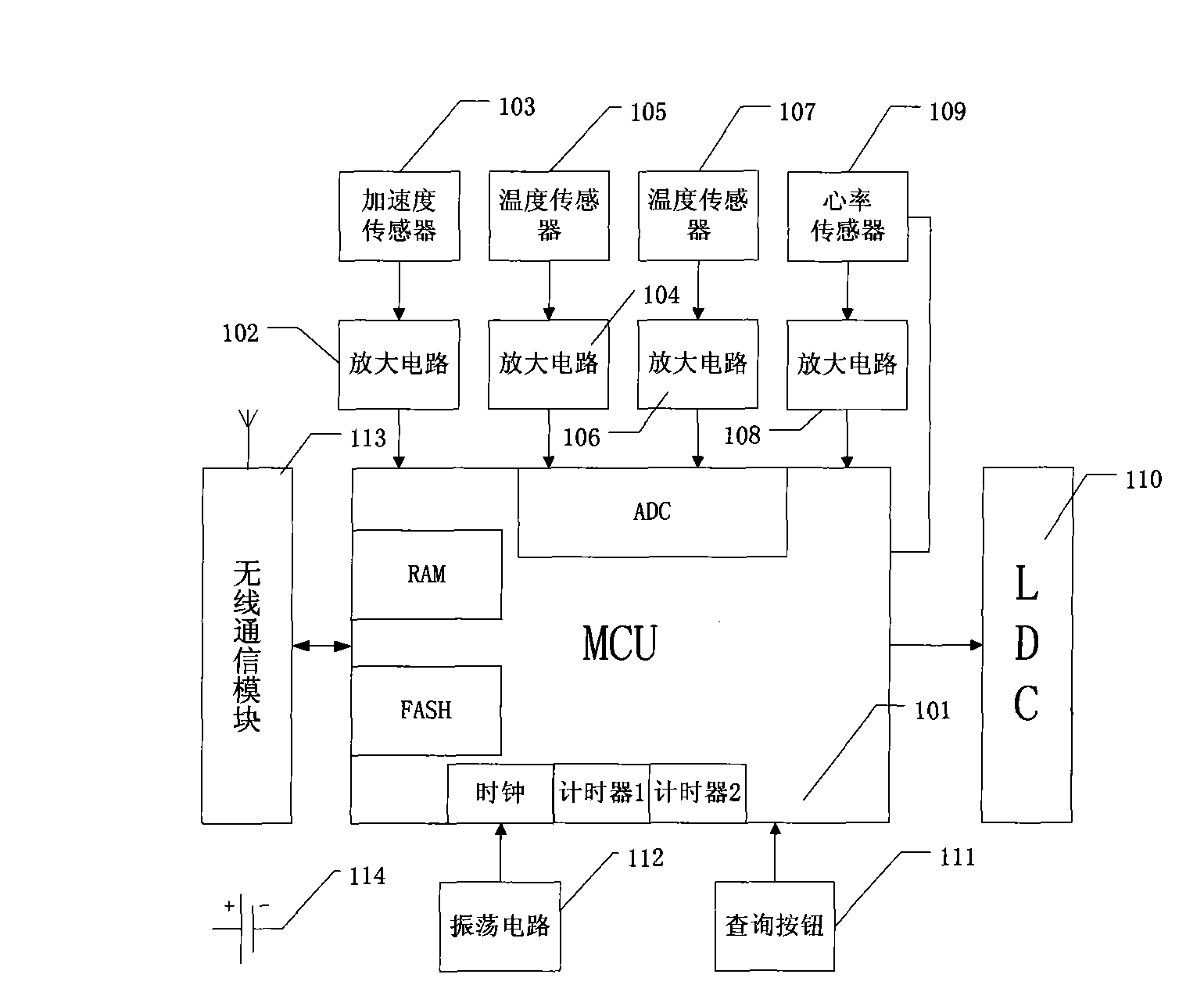
[0023] Embodiment 1: see figure 1 shown. A power-saving device for a sports watch, which includes an MCU, the signal end of the wireless communication module 115 is connected to the signal end of the MCU, the crystal oscillator circuit 104 is connected to the signal end of the clock circuit in the MCU, the signal end of the display 110 is connected to the signal output interface of the MCU, and the The acceleration data acquisition sensor 103 and the heart rate sensor 109 are respectively connected to the I / O port of the MCU through respective amplifying circuits, and the signal input ends of the environmental data acquisition sensor 105 and the body temperature data acquisition sensor 107 are respectively connected to the ADC in the MCU through respective amplifying circuits. Signal terminal connection. The sports watch is provided with an inquiry button 111, and the basic data that can be inquired include exercise prescription, time, amount of exercise completed on the day,...
Embodiment 2
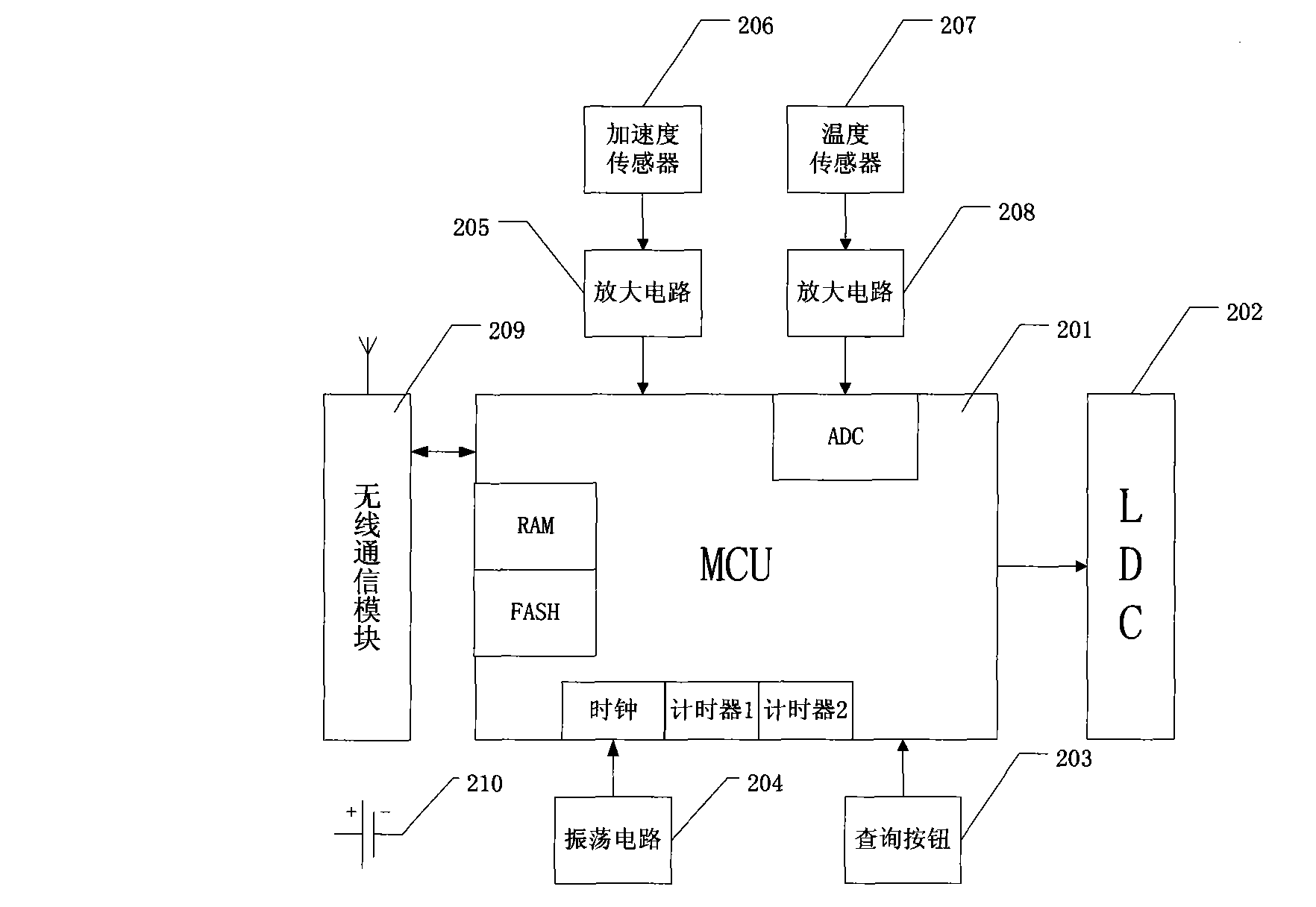
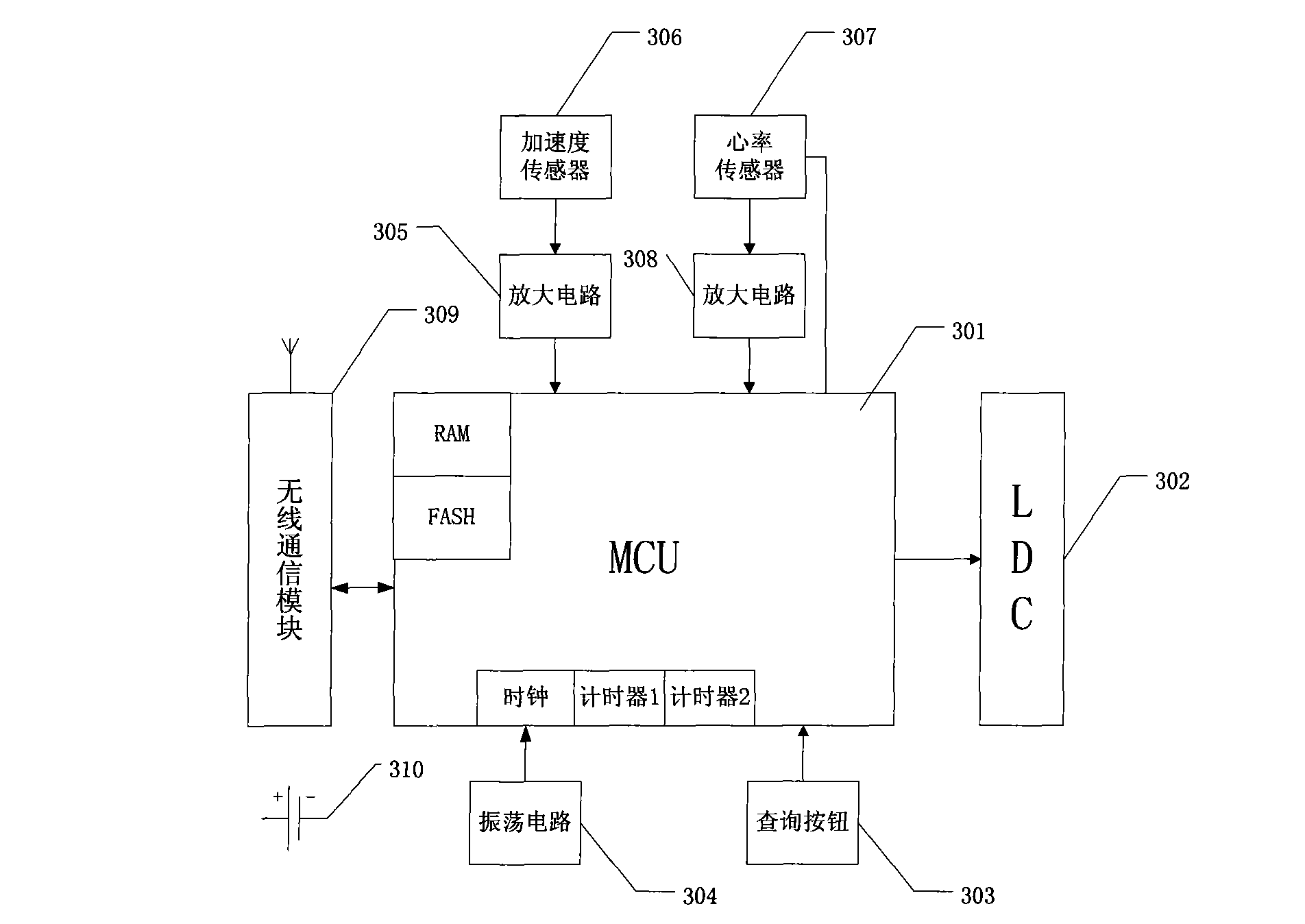
[0033] Embodiment 2 is based on Embodiment 1, reducing the test of an ambient temperature sensor and heart rate, such as figure 2 As shown, the operating mode and power saving mode are basically the same as those in Embodiment 1, but the difference is that there is no need to turn off the ambient temperature sensor and the heart rate test, and the function is different. and image 3 It is to subtract the two temperature sensors, only the heart rate test and the acceleration test, and the heart rate test in the embodiment can be a continuous test or an indirect time test. In terms of power saving function, it is also the same as the embodiment 1 Basically the same, the difference is the difference in function and the reduction in the control scheme. From Figure 4 From the structure, it can be seen that the difference between this and Example 1 is that the heart rate test is reduced, and the actual working mode and power saving mode are still the same as in Example 1, but th...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3: A power-saving method for a sports watch, which includes a sports watch. The sports watch has a built-in clock control program. The sports watch receives the work and rest schedule, time calibration information, and queuing information of the information upload time from the server, and The sleep time or sampling time of the sports watch is automatically set according to the schedule, and the sports watch actively links to the server according to the set sequence to communicate and exchange information. The class time, special exercise time, and sleep time other than physical education class are the sleep time of the sports watch, and the physical education class, recess and non-class, non-sleep time are the interval or continuous sampling time of the sports watch.
[0035] The server is a teaching server and a PC. In the non-sleep state, the acceleration sensor in the sports watch collects data at a set time interval (the interval can be 0.5 seconds, 1.0 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com