Illuminating apparatus, illuminating method and display apparatus
A technology for lighting equipment and lighting direction, which is applied to lighting and heating equipment, mechanical equipment, lighting devices, etc. to achieve the effect of suppressing uneven brightness and reducing thickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
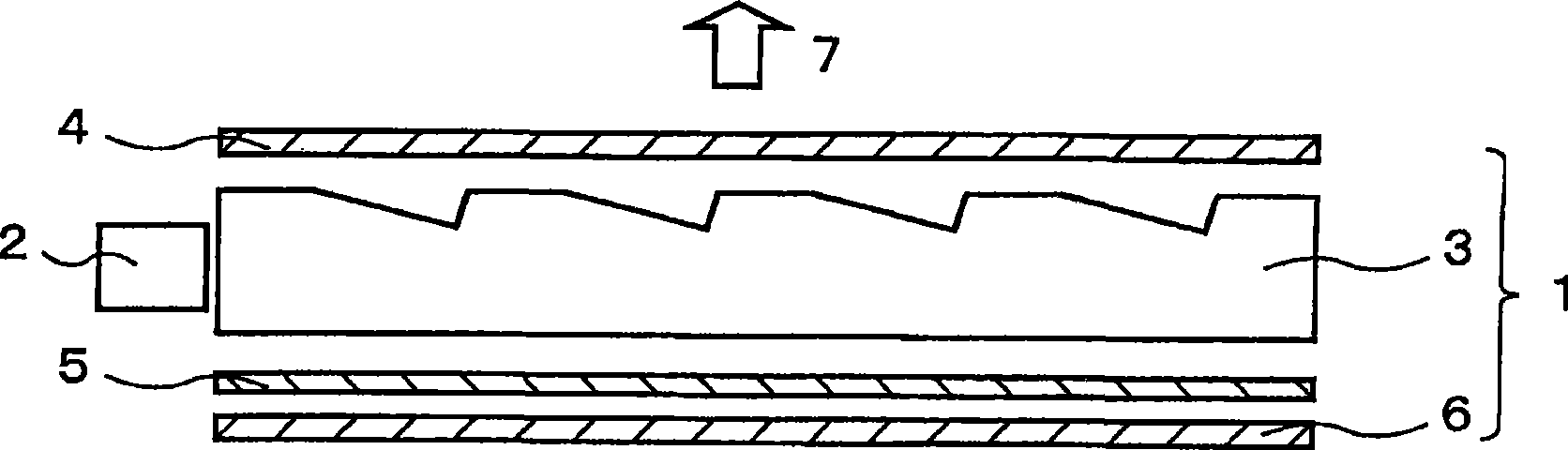
[0141] The beam direction adjuster having a transparent layer width L2 = 0.085 mm, a transparent layer refractive index n = 1.60, a light absorbing layer width L3 = 0.015 mm and a thickness D2 = 0.129 mm was manufactured, wherein the A1 reflective plate was Vapor deposition is on one side thereof and the light absorbing layer extends parallel to the light guiding direction of the light guiding plate. The beam direction adjuster, the linear light source, the light guide plate and the PNLC device were combined to manufacture the lighting device of the present invention as shown in FIG. 23 . In Figure 23, pairs with figure 1 and image 3 The same components are given the same reference numerals, and their detailed descriptions are omitted. results, such as Figure 24 As shown in , a distribution with a maximum exit light angle of 31° in the exit light angle control direction (direction perpendicular to the light guiding direction) is obtained for the transmission state of the...
example 2
[0143] The beam direction adjuster of Example 1, such as Figure 25A The shown light guide plate (inclination of outgoing light in the light guiding direction: β is approximately 43°), beam direction adjuster with a prism surface with an apex angle of 50° ( Figure 25B ), linear light source and PNLC device combination, to manufacture the lighting equipment of the present invention ( Figure 25C ). Figure 25C is similar to Figure 15 A modified configuration of the first exemplary embodiment shown in . As a result, for Figure 26 In the transmission state of the PNLC shown in , a distribution with a maximum outgoing light angle of 31.5° can be obtained in the outgoing light angle control direction (direction perpendicular to the light guiding direction) (the outgoing light angle distribution width M2=63°). Furthermore, when the liquid crystal display panel was attached to the lighting device of this embodiment, it was visually confirmed that there was no Murray effect / une...
example 3
[0145] The beam direction adjuster (second beam direction adjuster) of Comparative Example 1 is disposed between the beam direction adjuster and the PNLC device of the lighting device of Example 2, so that the light absorbing layer extends perpendicularly to the light guiding direction of the light guide plate, to manufacture lighting device( Figure 27 ). As a result, for the transmissive state of the PNLC as shown in FIG. Figure 28A ) in the direction of the maximum exit light angle 29 ° (-29 ° to +29 °) distribution, in the parallel direction ( Figure 28B ) with a distribution with a maximum exit light angle of 29° (-29° to +23°). Figure 27 The construction shown in the Figure 21B The configuration of the second exemplary embodiment shown in is the same.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com