Method for detecting fungal polysaccharide
A technology of fungal polysaccharides and polysaccharides, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to strictly quantify chemical analysis methods, limit the use range of gel electrophoresis methods, and difficult to master operating techniques, and achieve a wide range of molecular weights , mild conditions and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1: The method for detecting fungal polysaccharides specifically includes the following process steps:
[0024] (1) sample preparation
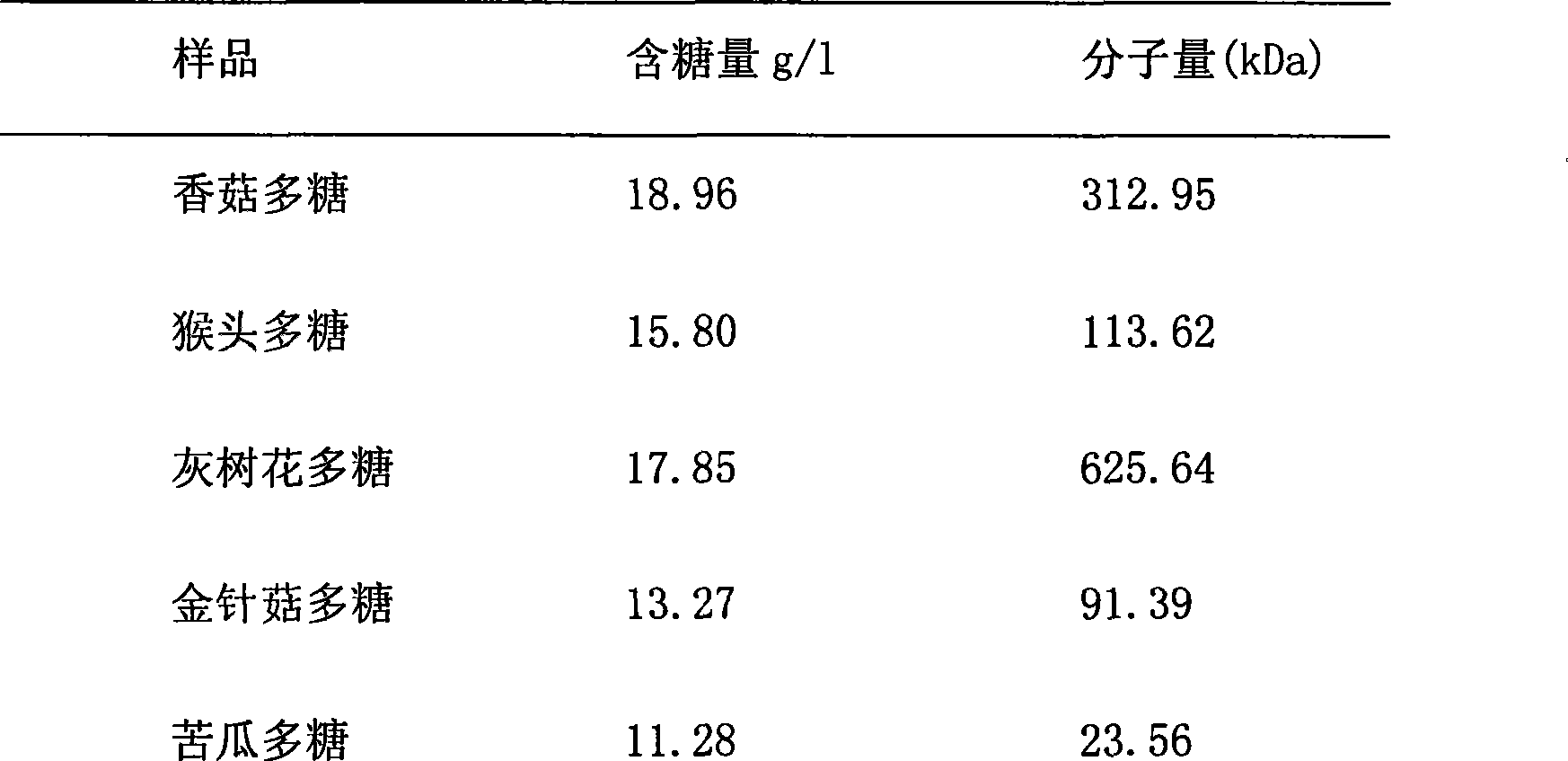
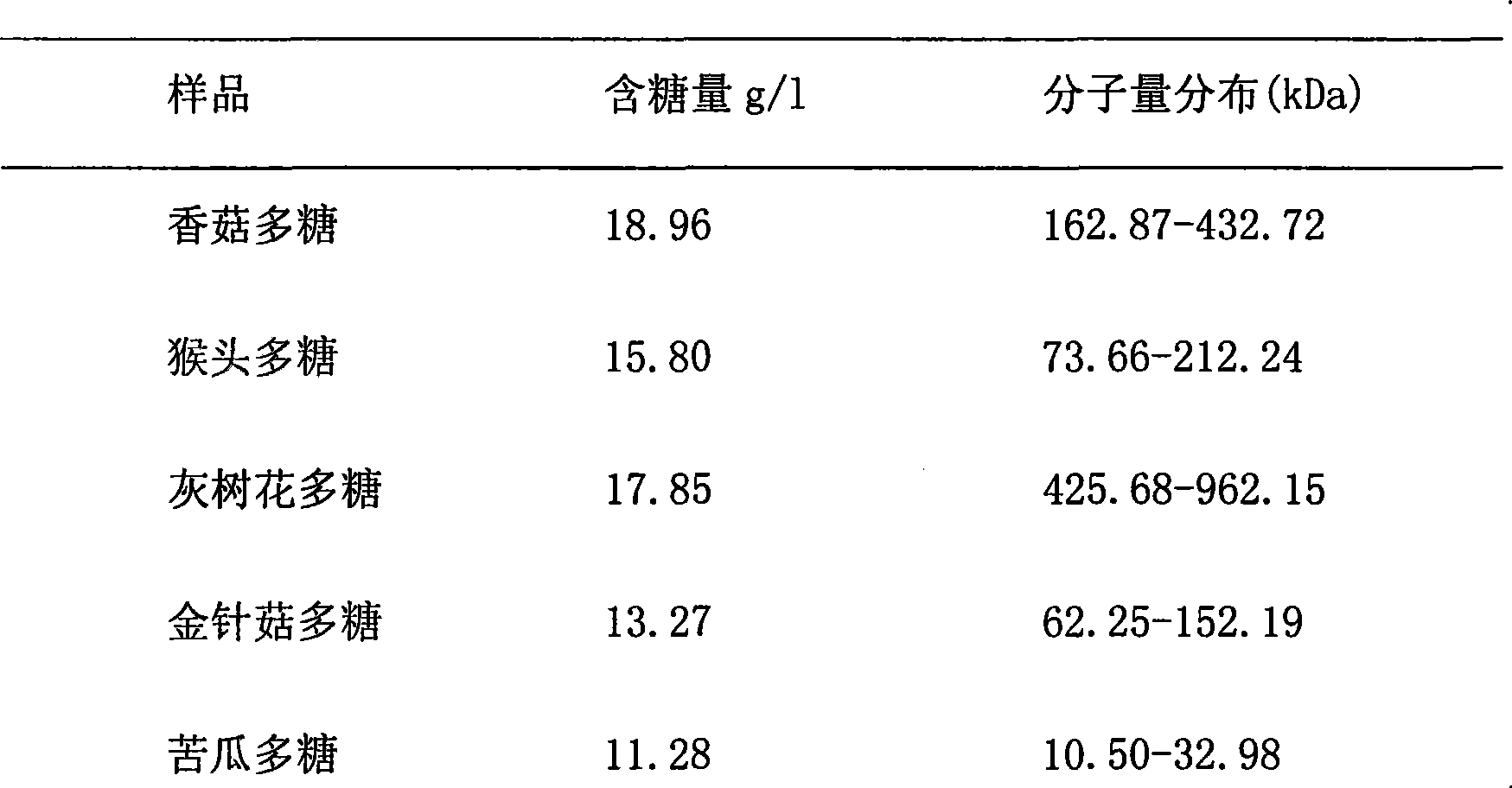
[0025] Weigh a certain amount (20mg) of polysaccharide samples (lentinan, Hericium erinaceus, Grifola frondosa polysaccharide, Flammulina velutipes polysaccharide, bitter gourd polysaccharide) into 5 clean test tubes or small measuring cups, add 5ml of distilled water and stir to dissolve , Store in a low temperature (4°C) refrigerator for later use. The concentration of the sample solution is 0.1mg / ml;
[0026] (2) Preparation of mobile phase
[0027] The above-mentioned solvent used for dissolving polysaccharides is degassed with a degasser and used as a mobile phase;
[0028] (3) Sampling, buffering, focusing balance
[0029] The single-phase chromatography (asymmetric field-flow separation) instrument (The Eclipse AF4), multi-angle static light scattering instrument (MALS, DAWN HELEOS II), dynamic light scattering ins...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2: the same as the steps of Embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0036] 1. Weigh 60mg of polysaccharide samples (lentinan, Hericium erinaceus, Grifola frondosa polysaccharide, Flammulina velutipes polysaccharide, bitter melon polysaccharide) into a clean test tube or small measuring cup, add 30ml of 0.85% sodium chloride solution and stir to dissolve Afterwards, store them in a low-temperature (4°C) refrigerator for later use. The concentration of the sample solution is 0.5mg / ml;
[0037] 2. The operating process conditions are as follows: use a micropipette to draw 60 μL of the prepared polysaccharide sample and an appropriate amount of mobile phase for sample injection, buffer and focus balance. Injection, buffering, focusing balance time is 8min, injection speed: 0.5mL / min; focusing balance time is 3min, channel flow rate: 1.2mL / min, crossflow flow rate: initially run at 5mL / min for 3 minutes, then Decrease to 2.5mL / min and run for 5.5 minutes, then gradua...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3: the same as the steps of Embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0041]1. Weigh 100mg of polysaccharide sample into a clean test tube or small measuring cup, add 60ml of phosphate buffer (7.0mmol / L KH 2 PO 4 , 7.0mmol / L Na 2 HPO 4 , pH=6.8) stirred to dissolve, and stored in a low temperature (4°C) refrigerator for later use. The concentration of the sample solution is 0.95mg / ml;
[0042] 2. The operating process conditions are as follows: use a micropipette to draw 120 μL of the prepared polysaccharide sample and an appropriate amount of mobile phase for sample injection, buffer and focus balance. Injection, buffering, focusing balance time is 10min, injection speed: 0.95mL / min; focusing balance time is 5min, channel flow rate: 2.0mL / min, crossflow flow rate: initially run at 9mL / min for 1 minute, then Reduce to 4mL / min and run for 3 minutes, then gradually reduce to 0ml / min, the total running time is 25 minutes. The flow rate of the sugar sample is: 0.9...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com