Method for screening catalysis non-aqueous phase system transesterification enzyme by fluorospectrophotometry
A fluorescence spectrophotometry, non-aqueous phase technology, used in fluorescence/phosphorescence, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of inability to perform measurement, limit the application of fluorescence spectrophotometry, and achieve the effect of simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
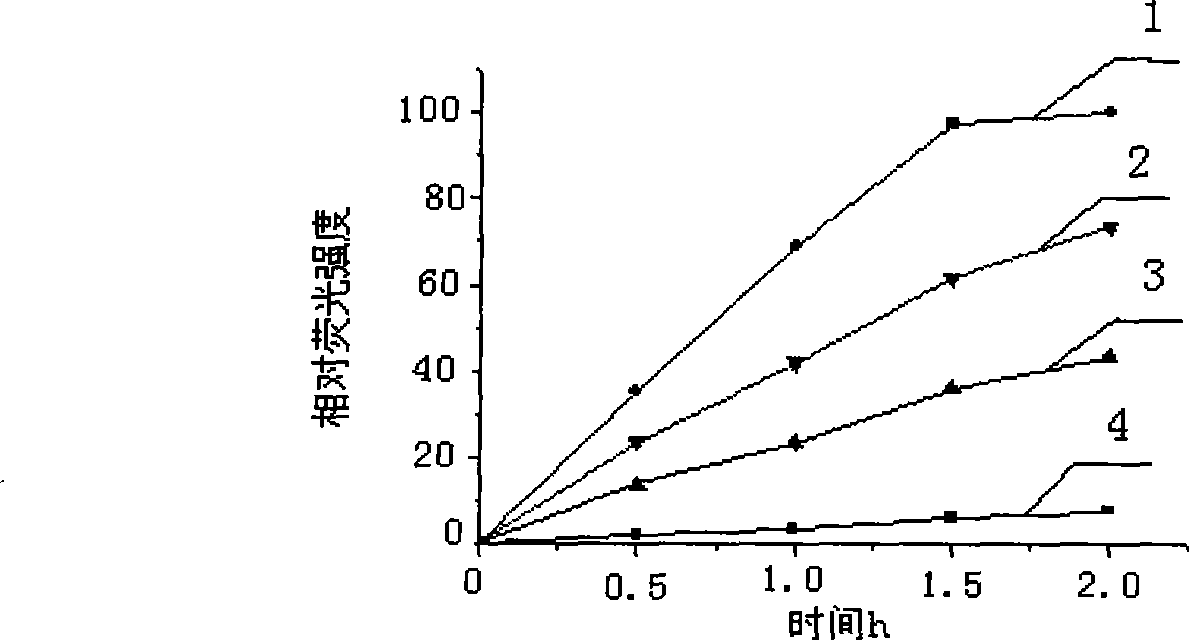
[0026] Embodiment 1: the ability of different reference enzymes to catalyze the transesterification reaction
[0027] The enzymes used in the experiment were all commercial enzyme preparations. Protease bacillolysin (optimum temperature 37°C, optimum pH 7.5) was purchased from Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., Japan, and lipase LPL-3 (optimum temperature 50°C, optimum pH 7.5). 0) Purchased from Japan Amano Enzyme Co., Ltd., protease subtilisin Carlbergs (optimum temperature 37°C, optimum pH 7.5) was purchased from Sigma Company, protease Alcalase 3.0T (optimum temperature 50°C, optimum pH 8.5) was purchased from from Novozymes. NBD-H.NH 2 NH 2 Purchased from Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., chromatographically pure. Vinyl laurate (chromatographically pure) was purchased from Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., Japan. Vinyl propionate (chromatographic grade) was purchased from Sigma. The 1420 multilabel counter multifunctional resolution fluorometer used in the fluoresce...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2: Study the impact of different transesterification ester substrates on the reaction
[0031]Vinyl propionate and vinyl laurate, which have the same alcohol moiety structure and different carboxylic acid moiety carbon chain lengths, were used as substrates for the enzyme-catalyzed transesterification reaction, and the effects of ester substrates with different molecular sizes on the reaction were studied. The abilities of the four enzymes used in the experiment to catalyze the reaction of vinyl propionate and n-propanol were greater than those of vinyl laurate and n-propanol, indicating that the small molecule ester substrate is beneficial to the enzyme action.
Embodiment 3
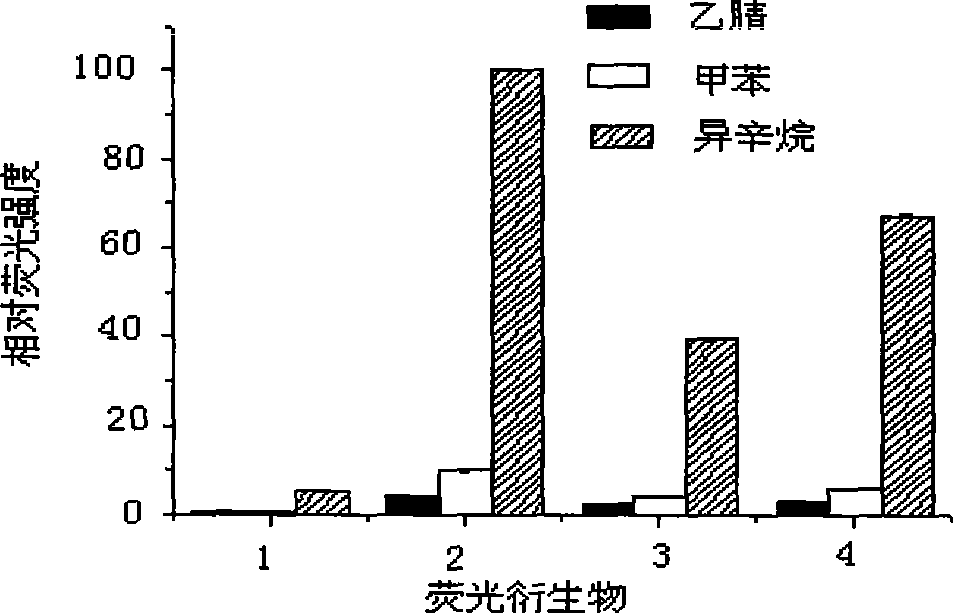
[0032] Embodiment 3: Study the influence of different organic solvents on reaction
[0033] Using vinyl propionate and n-propanol as substrates, compare the effects of different hydrophobic organic solvents: isooctane (logP=4.5), toluene (logP=2.5), acetonitrile (logP=-0.33) on the catalytic ability of enzymes . The catalytic abilities of these four enzymes showed a consistent trend in the isooctane, toluene, and acetonitrile systems, but as the hydrophobicity of organic solvents decreased, the catalytic activities of these four enzymes decreased rapidly: protease bacillolysin, lipase LPL- 3. The catalytic ability of protease subtilisin Carlsberg and protease Alcalase 3.0T in toluene is only 11.5%, 10.1%, 10.8% and 8.8% in isooctane respectively; the catalytic ability in acetonitrile is only 1% in isooctane 5.7%, 4.1%, 5.3%, and 4.7%. Compared with toluene and acetonitrile, isooctane with stronger hydrophobicity is more suitable as a solvent for enzyme-catalyzed transesterif...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com