Molecule acid and alkaline dissociation constant prediction method based on layered atomic addition model
A technology of dissociation constant and prediction method, which is applied in the direction of testing pharmaceutical preparations, electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, etc., and can solve problems such as low bioavailability, high cost, and poor absorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1. Parameter table construction
[0047] The least squares method is the most commonly used method for fitting the compositional parameters of the traditional group / atom summation model, but for nonlinear models, the least squares method is not suitable for modeling. Adaptive optimization has been proven to be an effective method for dealing with problems without knowledge of the search space (solution space). In this study, the inventors used the genetic algorithm for adaptive parameter estimation, and the specific steps are as follows:
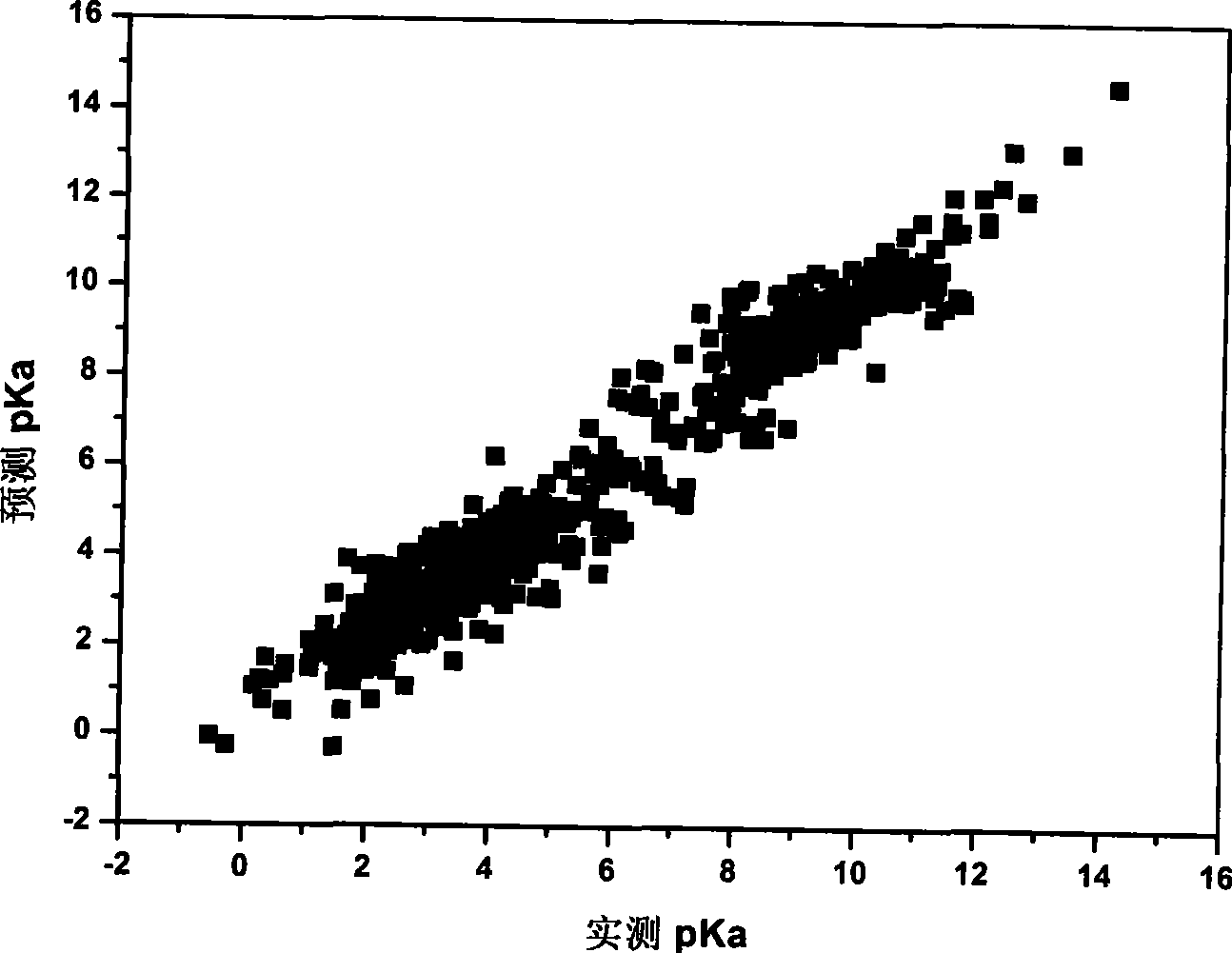
[0048] Data samples are from Lange's Handbook of Chemistry. As a sampling standard, select the pK measured in aqueous solution at 25°C a The experimental values totaled 1300 compounds, covering a wide space of chemical diversity. Among them, the most common 41 kinds of dissociation centers are selected, and their pK a 0 The value is determined by its corresponding simplest organic molecule, such as the pK of the alco...
Embodiment 2
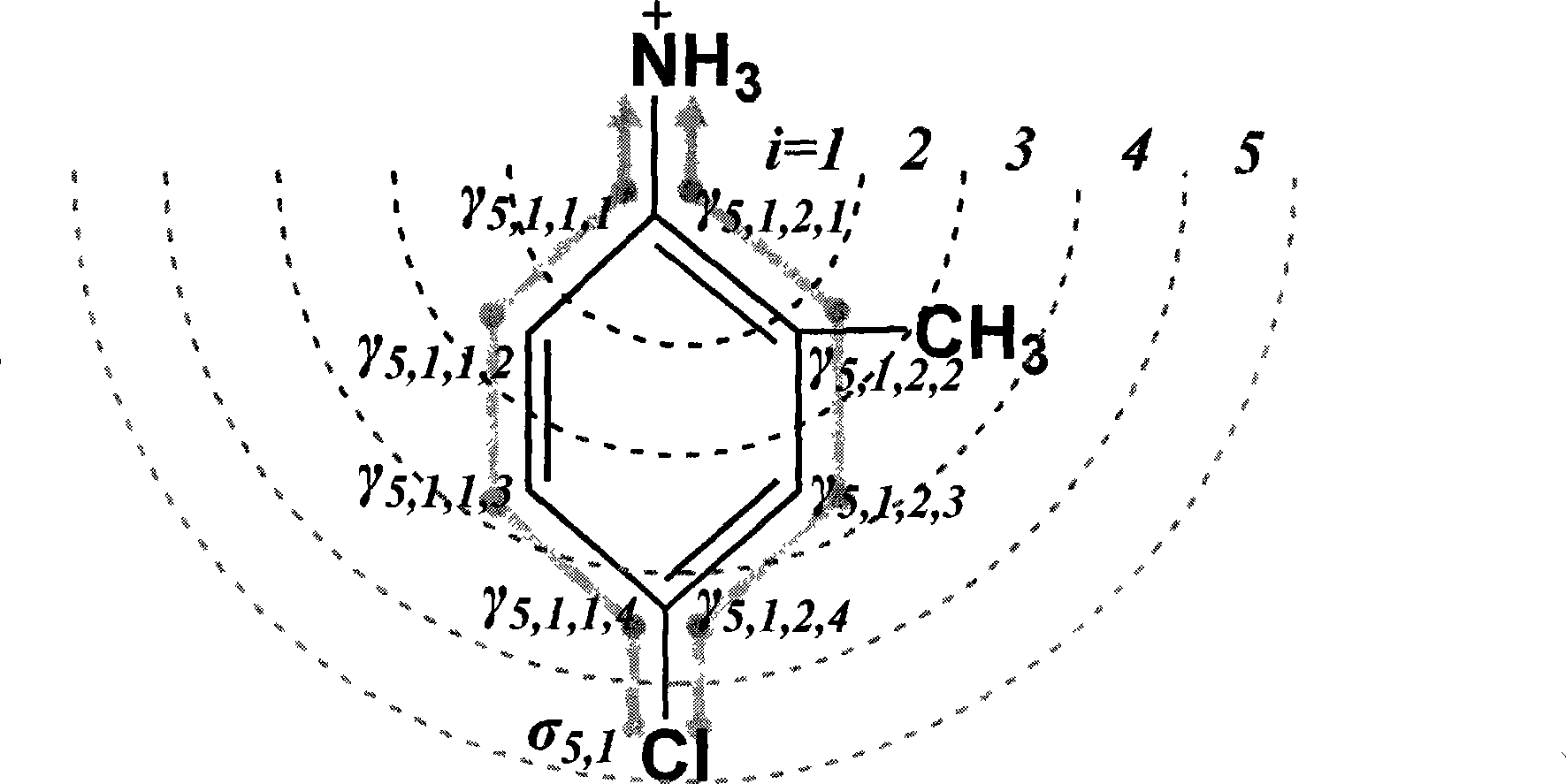
[0080] Take p-chloroaniline as an example ( figure 2 ):
[0081]a. First identify the dissociation center, and use the method based on substructure matching to query NH 3 +, corresponding to the dissociation center aniline (ID: 17) in Table 1, pK a 0 The value is 5.17. build as figure 2 Molecular junction tree shown, dissociation center NH 3 + is the 0th layer (i=0).
[0082] b. According to the electronic effect constant (σ) table and electronic effect transfer parameter (γ) table defined in Tables 2 and 3, use the method based on substructure matching to query and obtain the σ and γ values corresponding to the atomic types of each layer.
[0083] c. To calculate the contribution of the 5th layer (i=5) atoms to the electronic effect of the dissociation center, first determine the atoms in the 5th layer (1 in total, the atom type is chlorine, where i=5, j=1) ; Look up Table 2 to get the electron effect constant σ of the atom 5,1 =6.39 (ID: 26); this atom involves t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com