Method, system and base station for adjacent zone
A technology of neighbor cell detection and base station, applied in electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve the problems of unrealistic neighbor relationship, complicated configuration, and inability to accurately configure neighbor relationship, and achieve automatic update and simplified configuration method. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for detecting adjacent cells of HNBs. An information detection mechanism is implemented between HNBs, and the adjacent cells of HNBs will be automatically detected and saved by the HNBs.
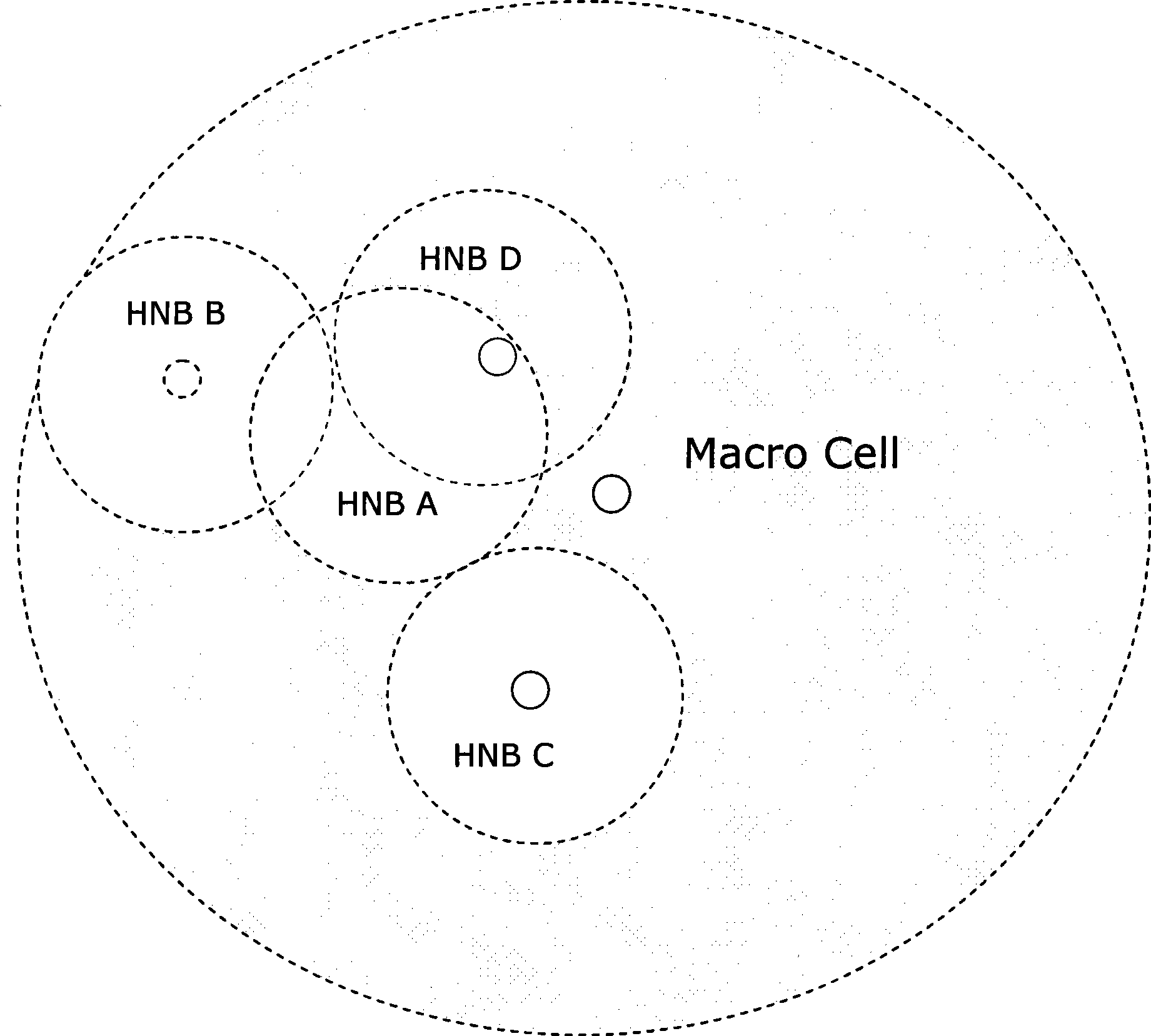
[0030] Such as figure 1 As shown, four HNB A, B, C, and D base stations are deployed within the coverage of a macro cell (Macro Cell). The signal coverage areas of these four base stations are called HNB A, B, C, and D cells respectively. In actual situations, the coverage of the macro cell is much larger than that of the HNB, and the circles in the figure are not proportional.
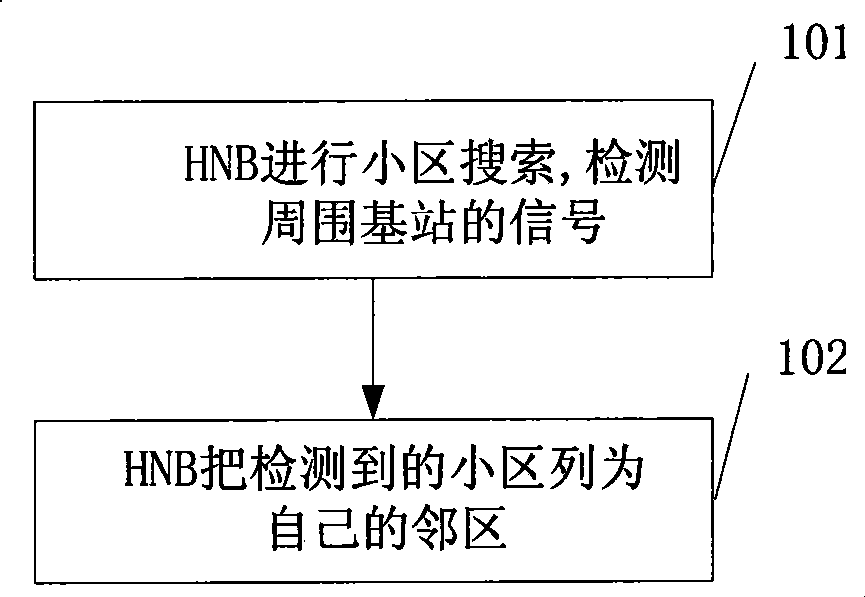
[0031] Attached below figure 1 , taking HNB A as the detection base station as an example to illustrate how HNB A detects neighboring cells. Such as image 3 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0032] Step 101: HNB A detects signals sent by surrounding base stations.
[0033] HNB A conducts cell search and detects signals of surroundin...
Embodiment 2
[0051] by figure 1The working scenario shown is taken as an example. According to the technical solution in Embodiment 1, HNB A can first detect the signal from the macro cell, so HNB A regards the macro cell as a neighboring cell. For the cells corresponding to other HNBs, although the HNB B signal coverage area partially overlaps with the HNB A signal coverage area, the HNB B signal cannot reach the location of HNB A, so HNB A cannot use HNB B as a neighboring cell; similarly, Although HNB C is tangent to HNB A, the signal of HNB C cannot reach the location of HNB A, and HNB A cannot use HNB C as a neighboring cell; while the signal of HNB D can reach the location of HNB A, therefore, HNB A will HNB D acts as a neighboring cell.
[0052] It can be seen that, for HNB A, from the perspective of network deployment, macro cells, HNBs B, C, and D are its neighboring cells. From the perspective of the actual detection process, the neighboring cells that HNB A can detect are: the...
Embodiment 3
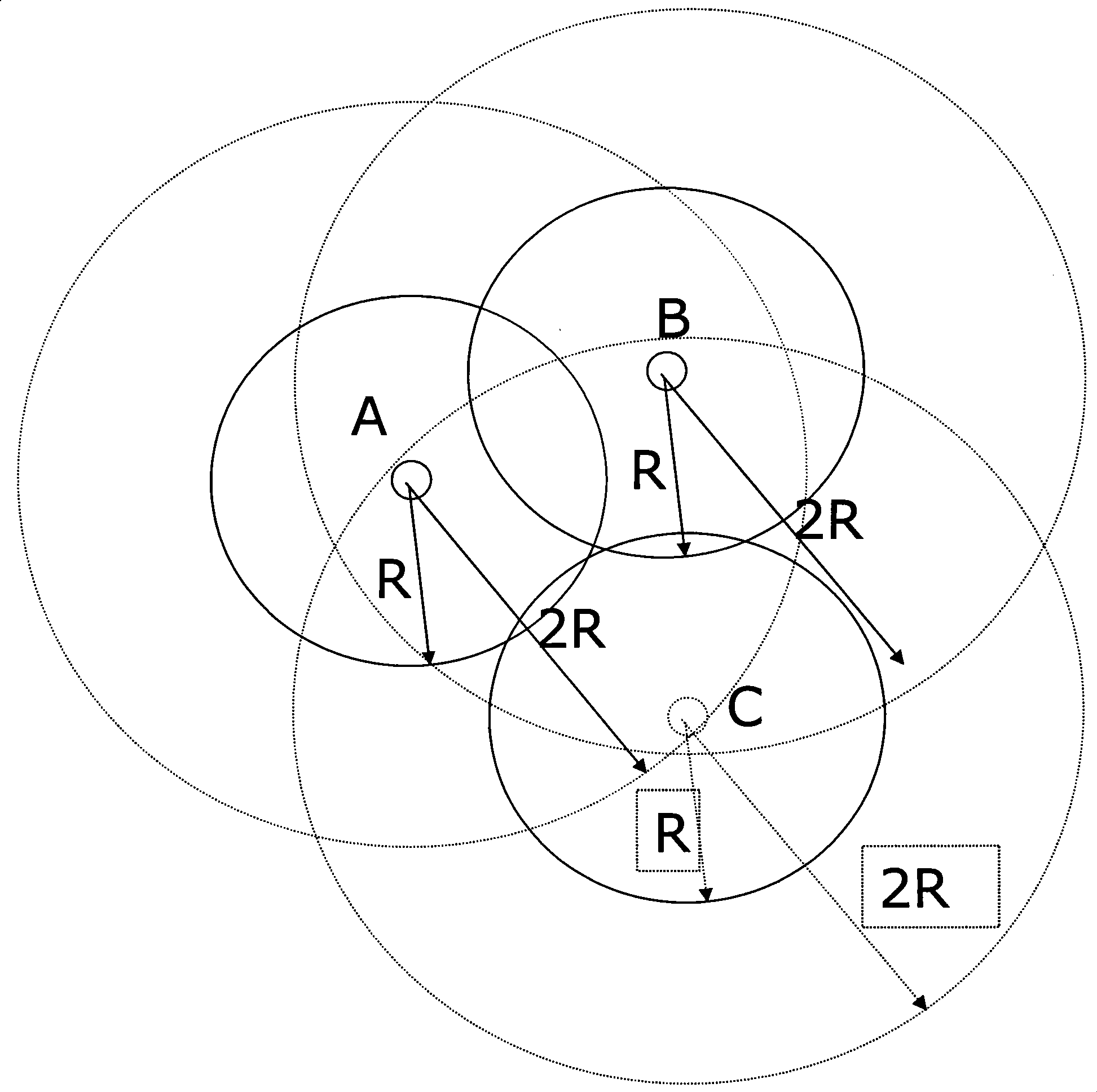
[0065] In some cases, because the coverages of two base stations (HNB and macro cell, HNB and HNB) are not equal. For example: one HNB or NodeB has a large coverage area, and the other has a small coverage area. The coverage of one HNB or NodeB can cover other HNBs; however, even if other HNBs increase their power and coverage, they still cannot cover this HNB or NodeB. In this way, a base station with a small coverage area can receive signals from a base station with a large coverage area, but a base station with a large coverage area cannot receive signals from a base station with a small coverage area.
[0066] At this time, in order for the base station with a larger coverage area to know that the base station with a smaller coverage area is its neighbor cell, it is not enough to only rely on the detection signal of the base station with a larger coverage area. Therefore, after the base station detects a neighboring cell, it needs to establish communication with it, and n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com