Process for the preparation of dispersions of cross-linking agents in water
A technology of cross-linking agent and dispersion liquid, applied in textile, coating, fabric and other directions, can solve problems such as difficulty in dispersion of intermediates, and achieve the effect of high cross-linking density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-13
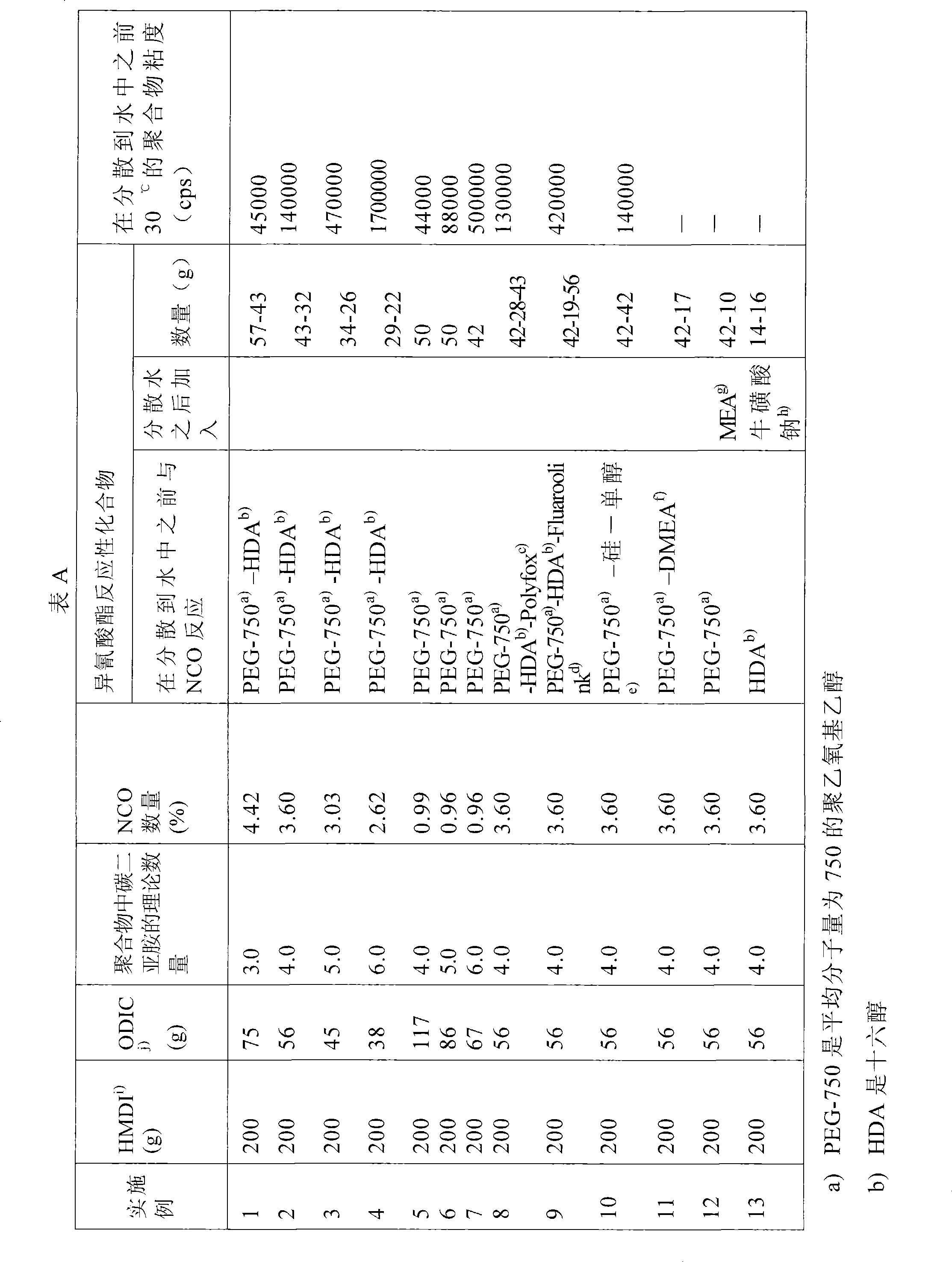
[0040] Examples 1-13 : Preparation of an aqueous dispersion of polycarbodiimide based on dicyclohexylmethane-4,4'-diisocyanate and octadecyl isocyanate.
[0041] Under nitrogen, a mixture of dicyclohexylmethane-4,4'-diisocyanate (hereinafter denoted as HMDI) and octadecyl isocyanate (hereinafter denoted as ODIC) shown in Table A and 2 g of 1- Methylphosphene-1-oxide was heated to 140°C while stirring, and the heating was continued until the isocyanate content in Table A was obtained. The mixture was then cooled to 90-100°C. The reaction time was 8 hours. Compounds adding hydroxyl functionality as indicated in Table A, total equimolar to isocyanate functionality. Dibutyltin lauryl was added as a catalyst in an amount of 0.01% by weight and reacted further at 90-100° C. until the isocyanate signal disappeared in the infrared spectrum, which took about 3 hours. In the case of Example 11, dimethylethanolamine was added after a reaction time of 1 hour. The mixture was cooled t...
Embodiment 14-16
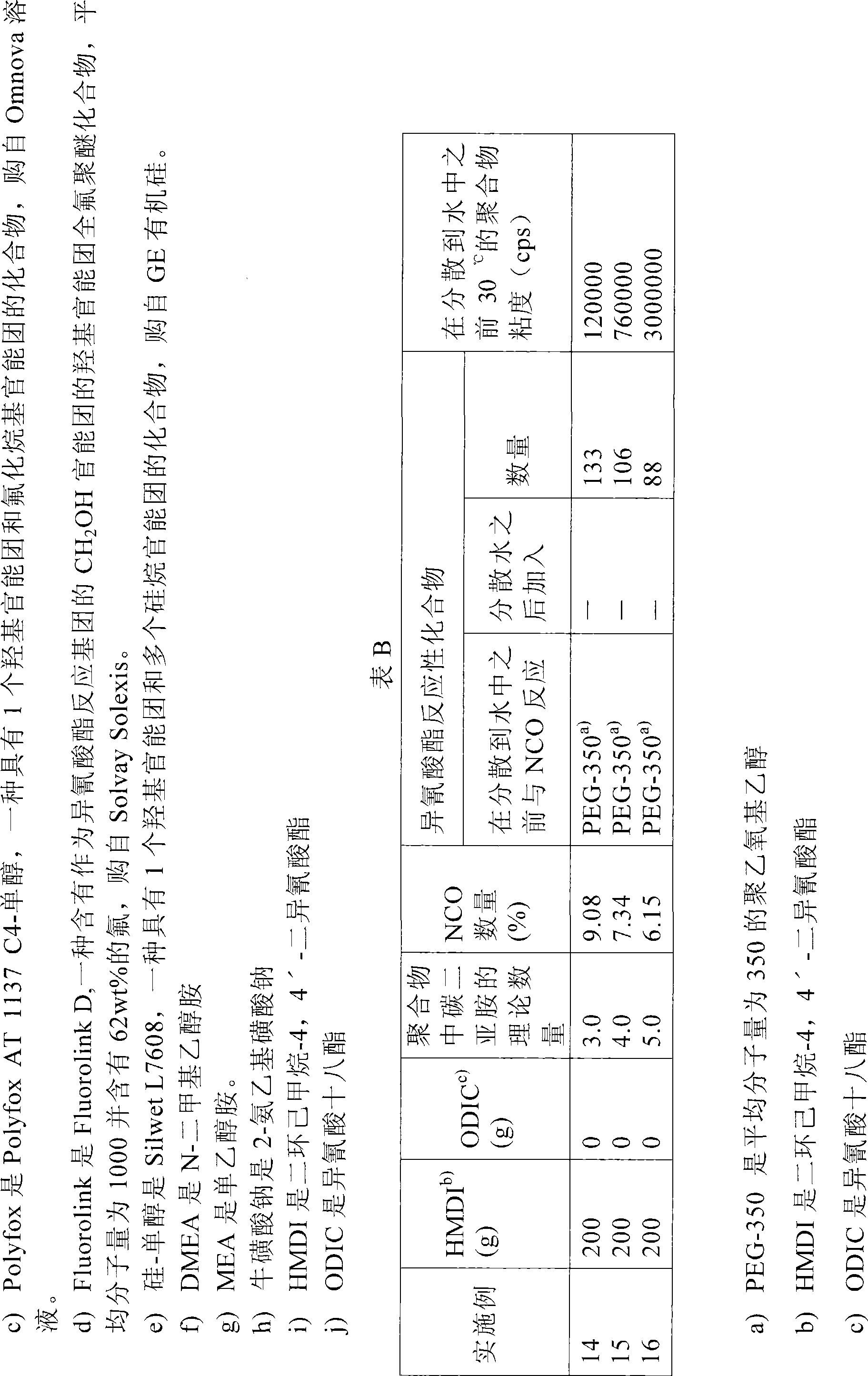
[0044] Examples 14-16: Comparative Example: Preparation of an aqueous dispersion of polycarbodiimide based on dicyclohexylmethane-4,4'-diisocyanate.
[0045] As shown in Table B, dicyclohexyl-4,4'-diisocyanate-based and capped with PEG-350 (polyethoxyethanol with an average molecular weight of 350) was prepared according to the method described in WO 2005 / 003204. Dispersion of polycarbodiimide. These polycarbodiimides do not contain additional hydrophobic groups. The polyethoxylates used in these comparative examples were of lower molecular weight than those used in Examples 1-13 in case the final product would contain too much hydrophilic material.
[0046] When comparing the viscosities in Examples 14, 15 and 16 with those in Examples 1, 2 and 3 and Examples 5 and 6, it appears that the implementation of The viscosities in Examples 1, 2 and 3 and Examples 5 and 6 are much lower than those in Examples 14, 15 and 16.
Embodiment 17-29
[0047] Examples 17-29: Aqueous dispersions of polycarbodiimide were prepared based on HMDI.
[0048] The procedure of Examples 1-13 was repeated except that 0.01 M disodium phosphate buffer was used instead of water. The samples were subjected to a stability test at 50°C. Check the amount of carbodiimide every two weeks. The product is stable at 50°C for at least 8 weeks.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com