Vehicle control device and data rewriting system
A technology for vehicle control devices and rewriting systems, which is applied to program control devices, transmission systems, vehicle components, etc., and can solve problems such as unexpected changes in vehicle control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 3 example
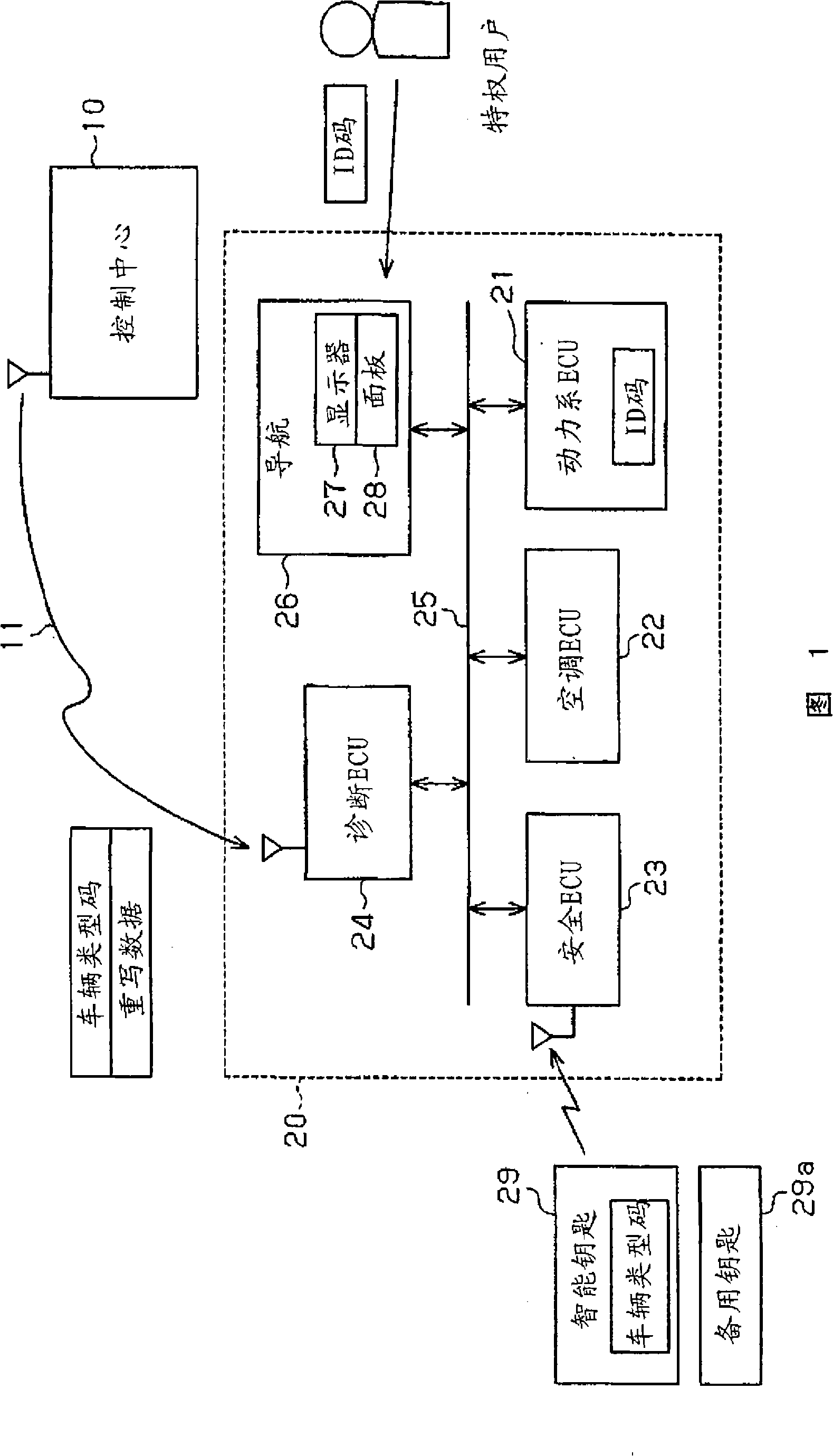
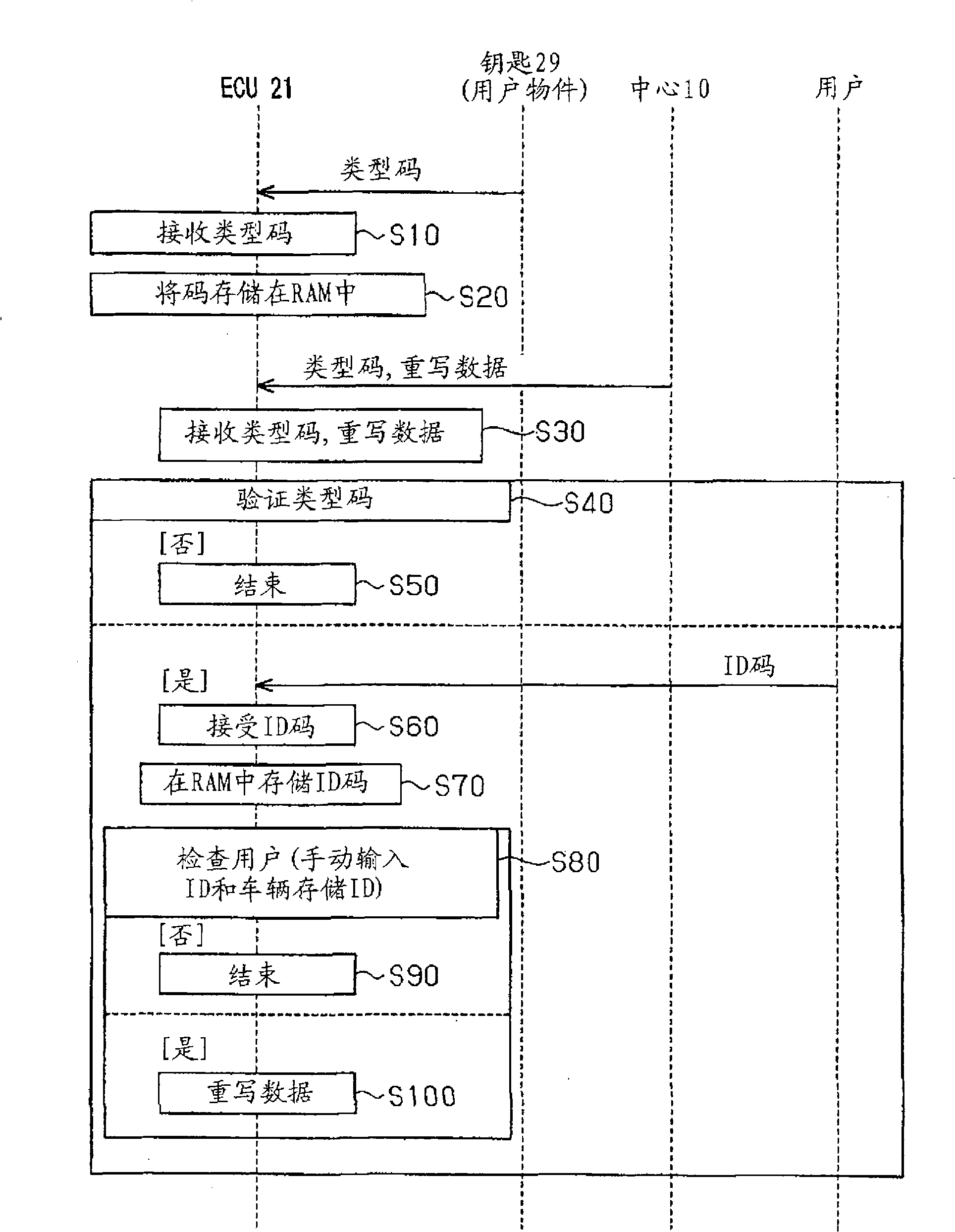
[0086] In the second embodiment, when the ID code (manually input value) manually input by the user, the ID code (user item collection value) obtained from the ETC card 41 of the user item, and the ID code (vehicle item collection value) pre-stored in the vehicle 20 stored value) match each other, the user is identified as a privileged user. That is to say, only one user ID code is stored in the vehicle 20, and by using this single ID code, a manual input ID code (manual input value) and an ID code acquired from a user item (user item collection) are performed. value) validation of both. In this case, if someone deciphers the data stored in the user item to illegally acquire the ID code stored in the user item, the person will know the ID code to be manually input.
[0087] In order to prevent a person from rewriting data without permission by using the ID code illegally obtained in this way, it is preferable to set the ID code manually input and the ID code stored in the use...
no. 4 example
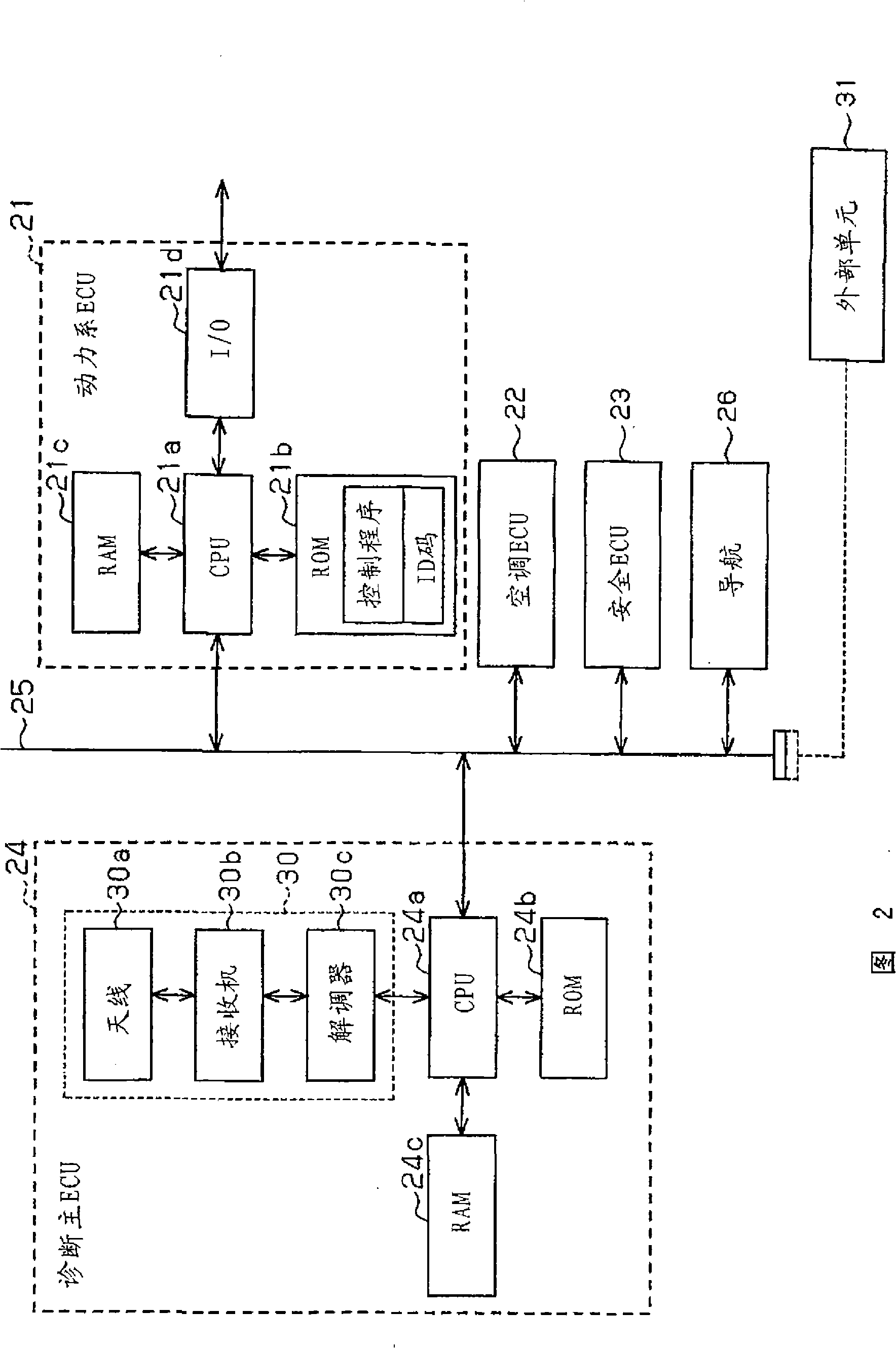
[0090] In each of the above embodiments, if in the verification process S40( Figure 5 ) to identify that the distributed data is for the vehicle (S403: YES), the GUI for manual input will be displayed on the display 27 of the navigation unit 26 (S406). In the fourth embodiment, the GUI is allowed to be displayed only when the user enters the vehicle using the master key 29 . That is, when the user enters the vehicle by using a key (spare key) 29a different from the master key 29, the user is prohibited from manually inputting the ID code. In this case, even if someone knows the ID code that needs to be entered manually, if he does not have the master key, that person cannot cause the process of rewriting the data to proceed. Therefore, this makes it more difficult to illegally rewrite data.
[0091] As shown in FIG. 14, the navigation unit 26 executes a process of displaying a GUI for manual input of an ID code. The navigation unit 26 repeatedly executes this process at re...
no. 6 example
[0102] In the sixth embodiment, a method for more strictly performing the user identification check in the above-described embodiments is implemented. The user identification check in the above-described embodiment is performed only by ID code authentication. By adding a user authentication method other than ID code authentication, user identification checks can be performed more strictly. The following two methods can be implemented as user authentication methods other than ID code authentication.
[0103] (A) User identification via biometric identification verification
[0104] Biometric identification verification is a method for identifying individual human beings by using biometric information that differs among individual human beings, such as fingerprint patterns and retinal patterns. For example, a device for reading a fingerprint pattern is equipped in the vehicle 20, and the device checks whether the user's fingerprint pattern read by itself matches the fingerprin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com