Large temperature rise compression heat pump units
A compression heat pump and compressor technology, applied in heat pumps, refrigerators, refrigeration components, etc., can solve problems such as the reduction of cold water outlet temperature, the reduction of system performance coefficient, and the reduction of energy utilization efficiency, so as to reduce heat transfer temperature difference, The effect of improving the coefficient of performance and reducing the temperature difference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
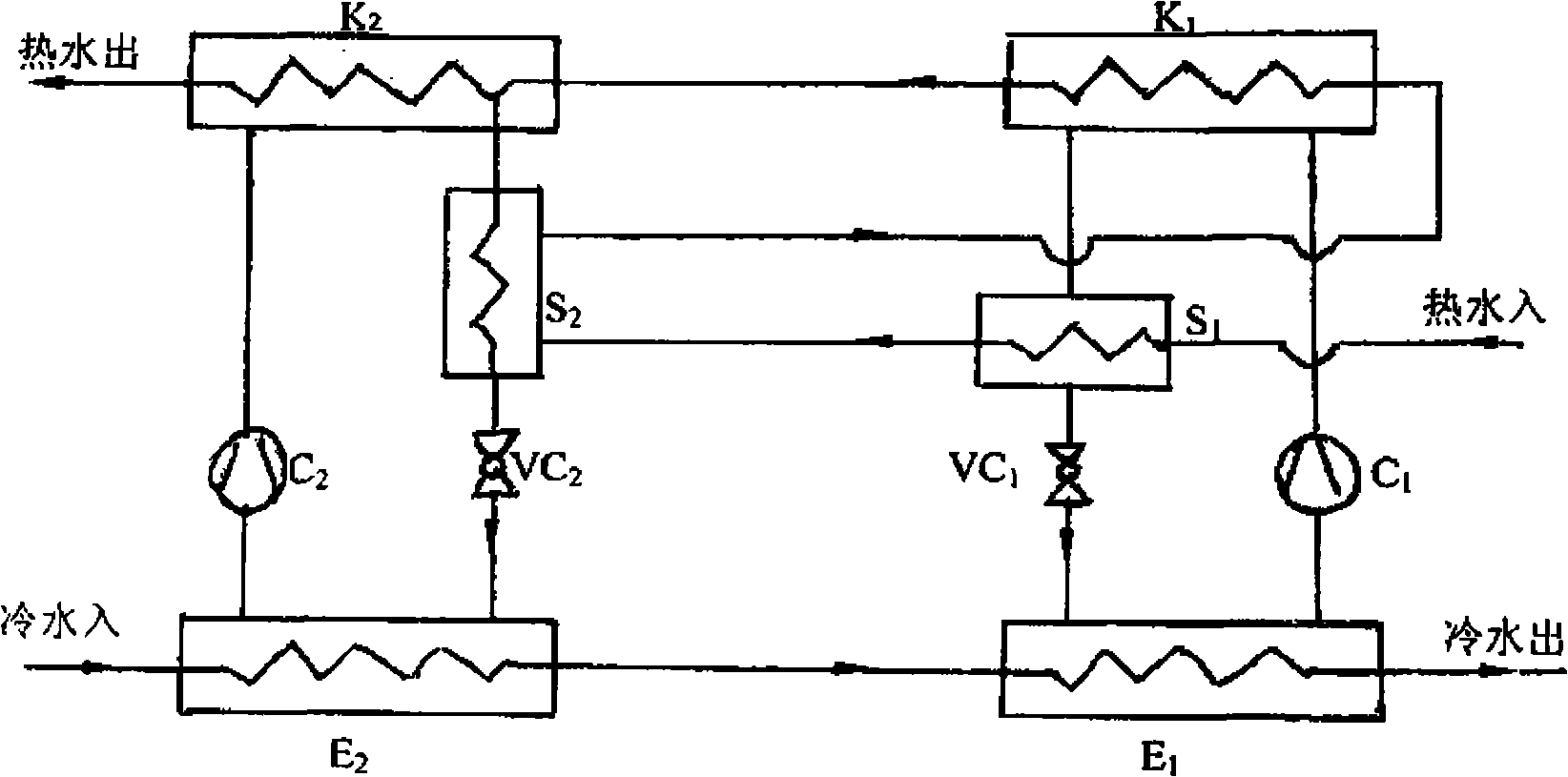
[0013] Embodiment 1 Two-stage series-connected compression heat pump unit with subcooling
[0014] As shown in Figure 1(a), the compressor C1 is connected between the first-stage condenser K1 and the evaporator E1, and the subcooler S1 and the throttling device VC1 are connected in parallel with the compressor C1 after being connected in series, and the second-stage condenser K2 The compressor C2 is connected with the evaporator E2, and the subcooler S2 and the throttling device VC2 are connected in parallel with the compressor C2 after being connected in series; 40 ℃ hot water return water enters the subcooler S1 from the hot water inlet of the subcooler S1, It flows through the cooler S1, the subcooler S2, the condenser K1 and the condenser K2 in sequence, and after being heated by the two-stage condenser, the high temperature hot water is output from the hot water outlet of the condenser K2, and the temperature of the hot water is 50-55°C. The return water of 25°C cold wate...
Embodiment 2
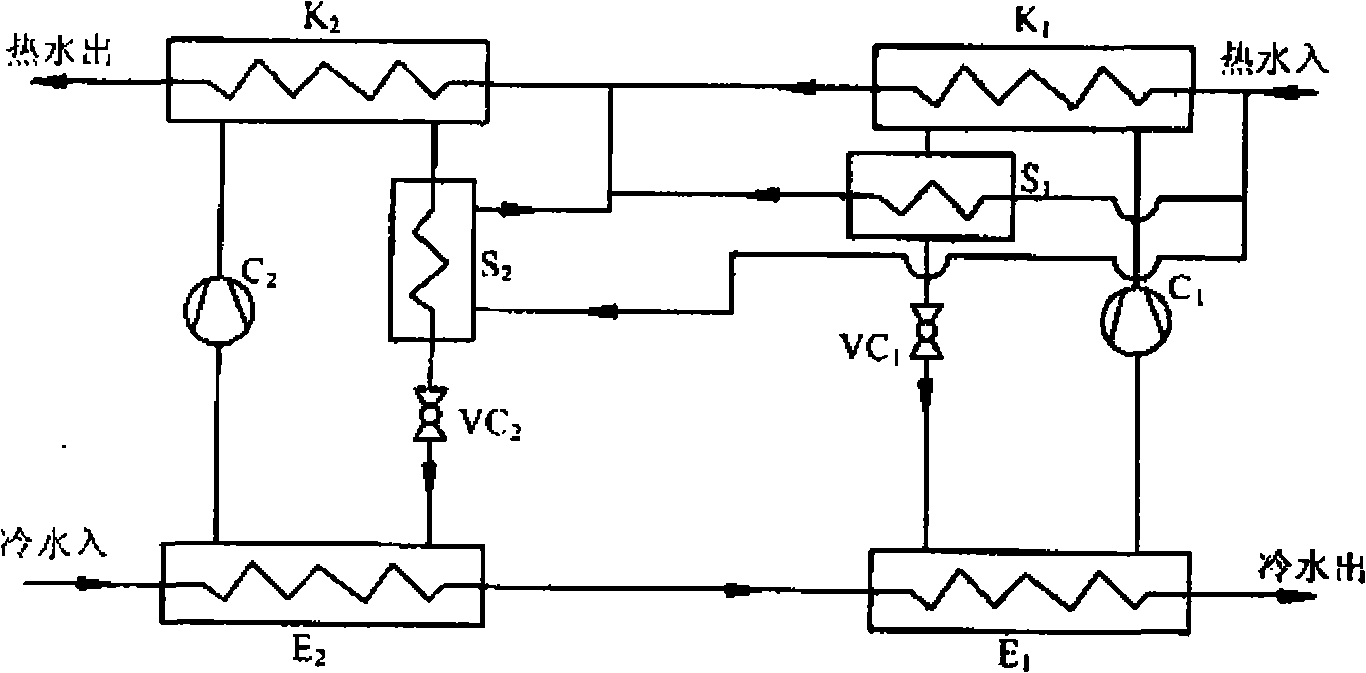
[0015] Embodiment 2 Compression heat pump unit with two stages in series and subcooling
[0016] As shown in Figure 1(b), the basic structure of the heat pump unit is the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is that the hot water pipeline is a subcooler S1, a subcooler S2, and the first stage condenser K1 are connected in parallel and then connected to the second The stage condenser K2 is connected in series. The return water of 40°C hot water passes through the parallel circuit of subcooler S1, subcooler S2, and first-stage condenser K1, and then passes through the second-stage condenser K2. After heating, it outputs hot water with a higher temperature. At 50-55°C. The return water of 25°C cold water flows through evaporator E2 and evaporator E1 successively, and then the temperature is lowered step by step, and then 10°C cold water is output. The hot water is heated up in steps, and the cold water is cooled in steps in the two-stage evaporator. The condensation pre...
Embodiment 3
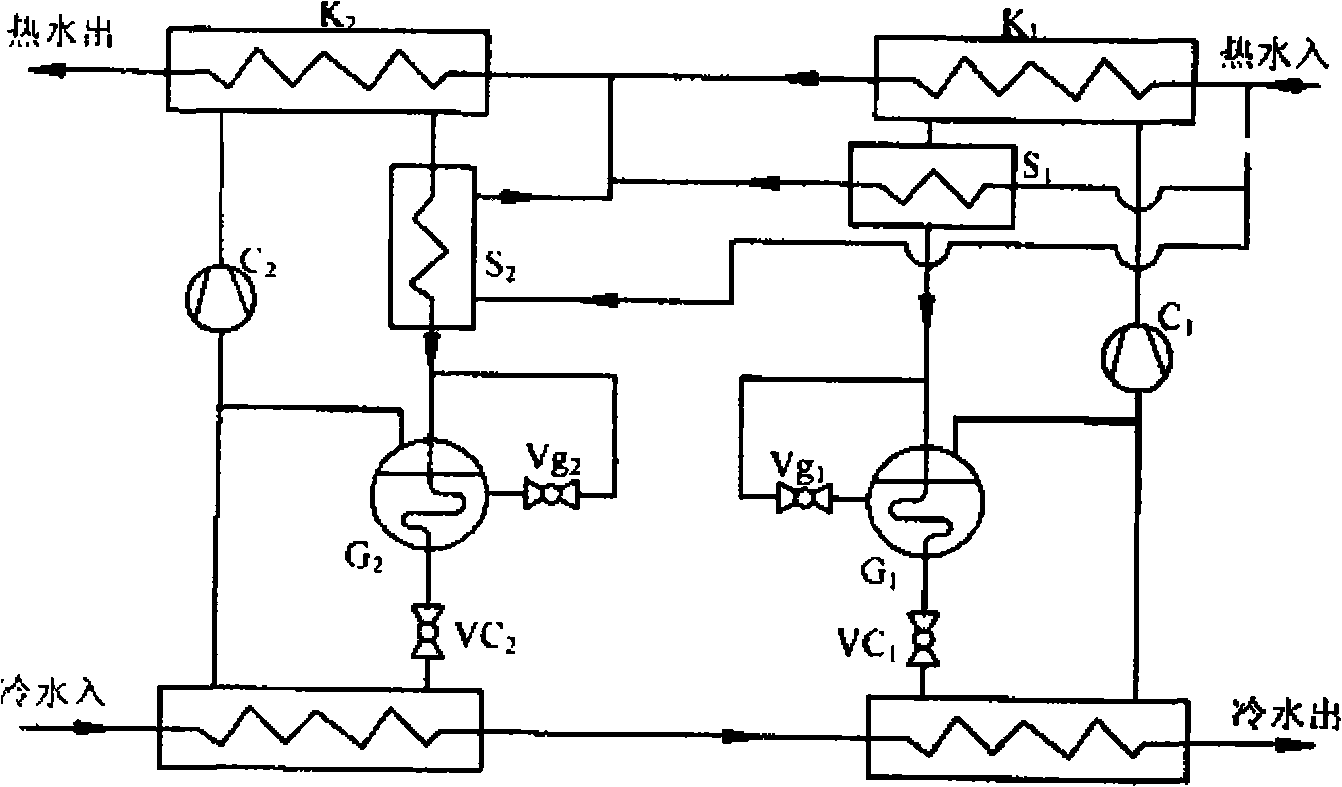
[0017] Embodiment 3 Two-stage series connection plus subcooling and economizer compression heat pump unit
[0018] In order to further improve the coefficient of performance of the compression heat pump unit, such as figure 2 As shown, the heat pump unit is composed of two heat pump units, and its basic structure is the same as that of Embodiment 2, the difference is that an economizer G1 is connected in series between the subcooler S1 and the throttling device VC1; An economizer G2 is connected in series between the throttling device VC2. The return water of 40°C hot water passes through the parallel circuit of subcooler S1, subcooler S2, and first-stage condenser K1, and then passes through the second-stage condenser K2 After being heated, it outputs hot water with a higher temperature, and the temperature of the hot water is 50-55°C. The return water of 25°C cold water flows through evaporator E2 and evaporator E1 successively, and then the temperature is lowered step by s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com