Laminated phase-difference film
A retardation film and retardation technology, applied in layered products, optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of poor optical uniformity and increased photoelastic coefficient of laminated films.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0119] (Film A1)
[0120] A polycarbonate resin (manufactured by Teijin Chemicals Co., Ltd., AD-5503) was dissolved in methylene chloride, and cast into a film to obtain a polycarbonate resin cast film having a thickness of 35 μm. At 151° C., the film was uniaxially stretched 1.3 times in the longitudinal direction of the free end to obtain a retardation film A1 having a Re of 262 nm in light of a wavelength of 550 nm and a film thickness of 30 μm. The photoelastic coefficients of the polycarbonate resin casting film and the retardation film A1 used to prepare the retardation film A1 were measured, and it was found that they were 75×10 before and after stretching. -12 Pa -1 .
[0121] (Film B1)
[0122] Next, at 143°C, a ring-opening polymerization type polynorbornene film (manufactured by Zeon Co., Ltd., ZEONOR) with a film thickness of 170 μm was uniaxially stretched 2.0 times in the longitudinal direction of the free end to produce the wavelength of the refractive index....
Embodiment 2 and 3
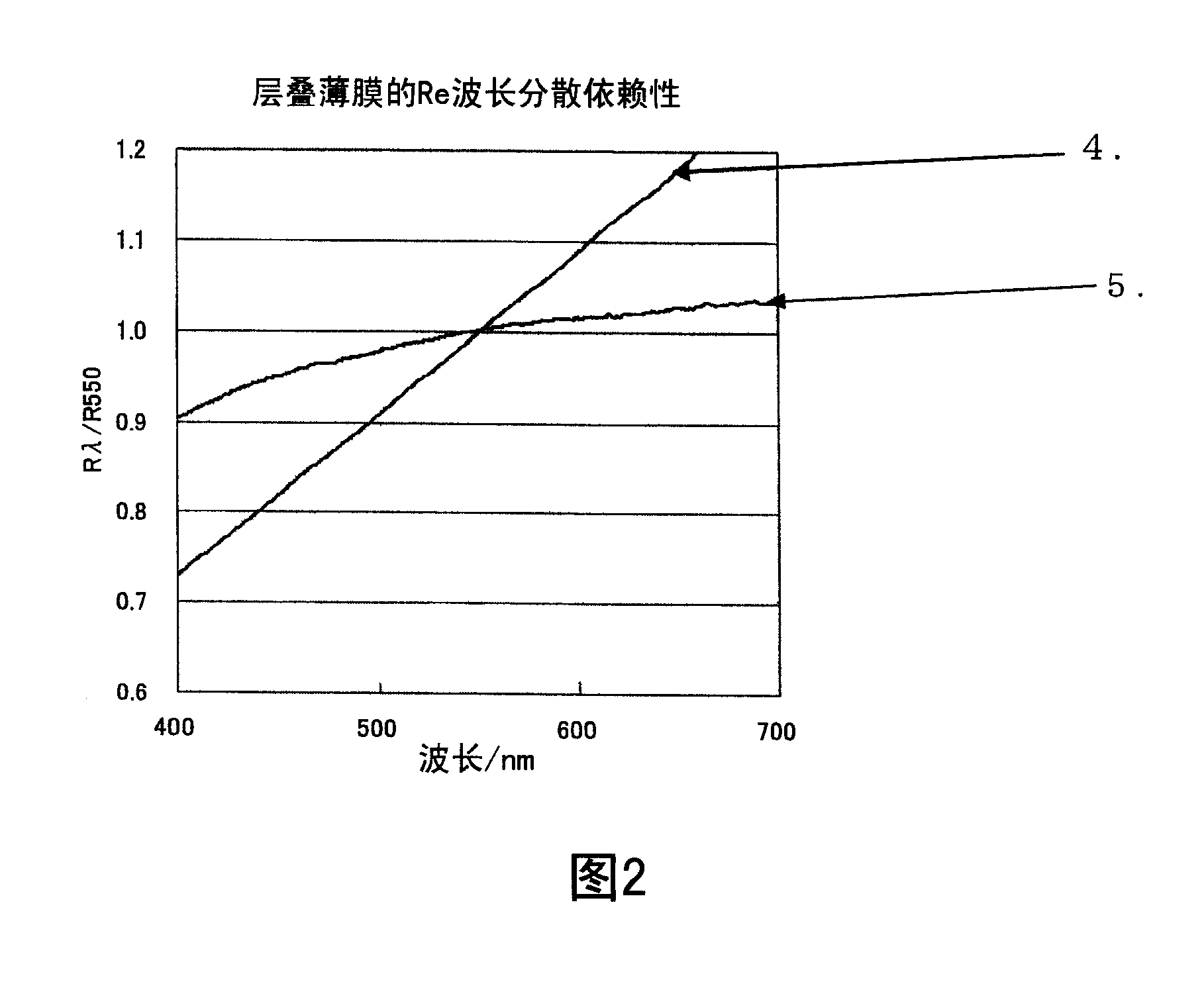
[0126] Using the retardation films shown in Table 1, a laminated retardation film was produced in the same manner as in Example 1. Table 2 shows the properties of the obtained laminated film.
Embodiment 4
[0128] (Film B4)
[0129] At 143°C, a film with a thickness of 170 μm produced by melt-extruding a copolymerized polynorbornene resin (DAICEL Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., TOPAS) was uniaxially stretched 2.0 times in the longitudinal direction of the free end to obtain Retardation film B4 with a Re of 400 nm and a film thickness of 120 μm in light with a wavelength of 550 nm. The photoelastic coefficients of the polynorbornene film used to prepare the retardation film B4 and the retardation film B4 were measured, and it was found that both before and after stretching were -7.8×10 -12 Pa -1 .
[0130] (cascade)
[0131] This retardation film B4 and the aforementioned retardation film A1 were produced in the same manner as in Example 1 to form a laminated retardation film. Table 2 shows the properties of the obtained laminated retardation film.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| photoelasticity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| photoelasticity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| photoelasticity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com