Palladium-on-carbon base nano-catalyst for producing hydrogen gas by direct decomposition of methanoic acid and method for producing the same
A nano-catalyst, carbon-supported palladium technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, hydrogen, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of restricting practical application, high operating temperature, potential danger, etc., achieving great application potential, strong resistance to CO Effects of Poisoned Ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
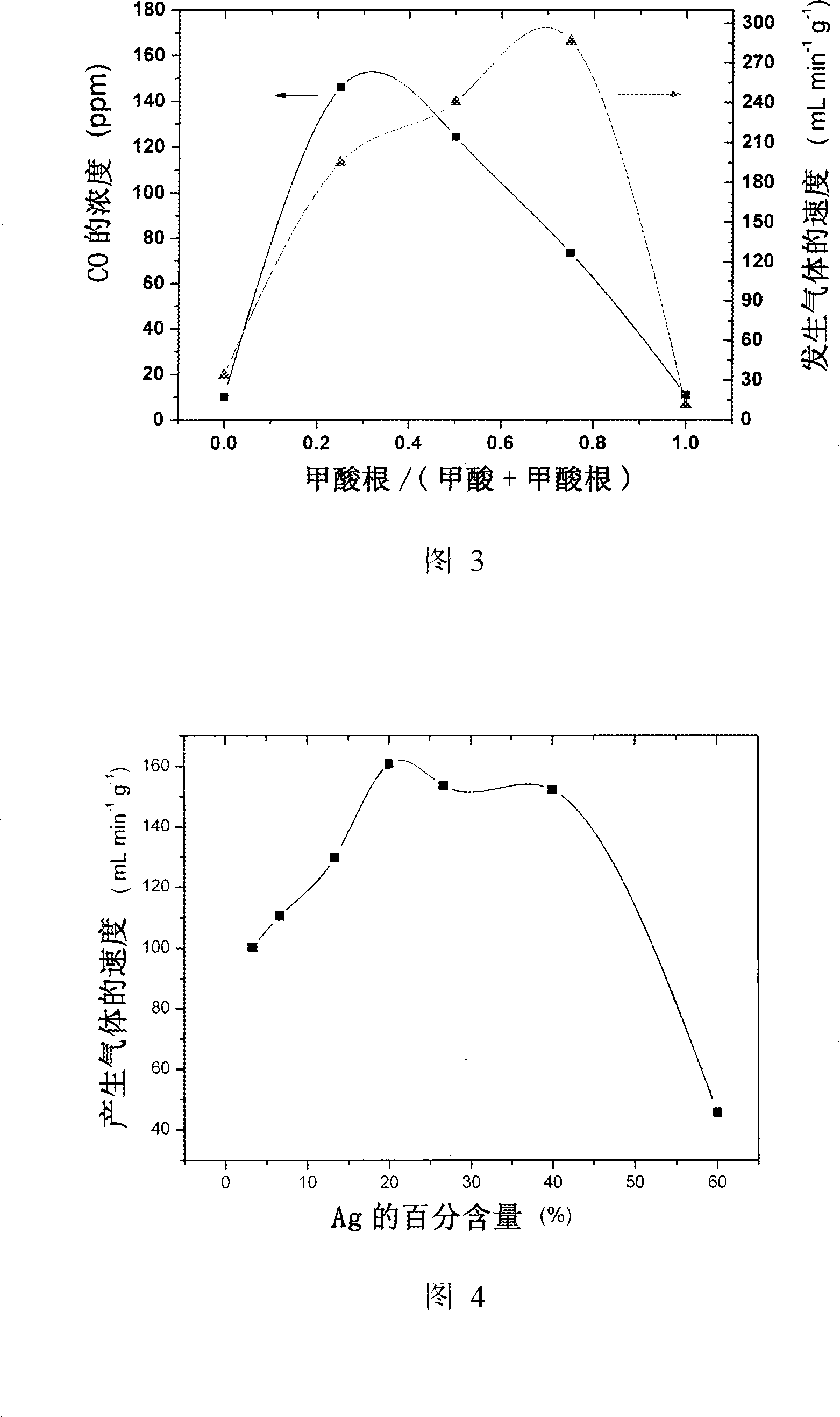
[0034]The catalyzer that above-mentioned obtains is placed in gas generator, at 92 ℃ catalytic decomposition formic acid, used catalyzer is Pd-Au / C, Pd-Ag / C, Pd / C (20wt%Pd, n Pd : n Me =3:1, Me=Ag and Au), the solution used is 5.00ml of aqueous solution containing 9.94mol / L formic acid and 3.33mol / L sodium formate. The rate at which the catalyst catalyzes the decomposition of formic acid is obtained by measuring the gas produced by the reaction. The entire reaction proceeded as shown in Figure 2 within 2 hours.
[0035] It can be seen from the figure that the alloy catalyst containing gold has the highest initial activity and sustained activity, and the activity of the catalyst containing silver is a little weaker than that containing gold, but it is still higher. Catalysts of pure palladium quickly lose their activity for the decomposition of formic acid. Therefore, the addition of gold and silver elements plays a key role in maintaining the activity of the palladium catal...
Embodiment 2
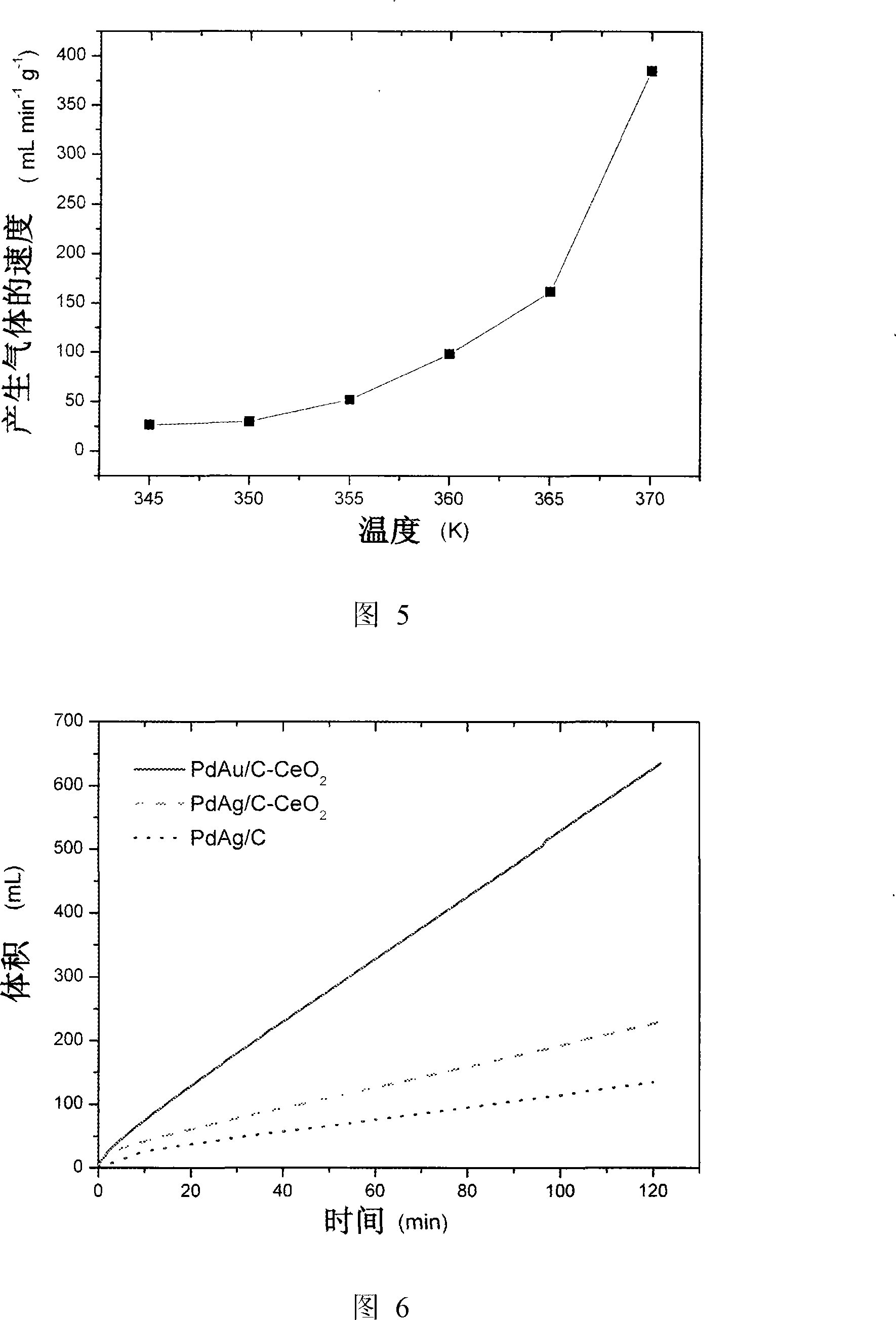
[0037] The effect of the ratio of formate and formic acid on the decomposition rate of formic acid and the concentration of carbon monoxide in reformed gas was investigated. The catalyst used in the experiment is 30mg Pd-Ag / C (20wt%Pd, n Pd : n Ag =3:1), the operating temperature is 92°C. The solution used was 5.00 ml of an aqueous solution containing 9.94 mol / L formic acid and 3.33 mol / L sodium formate. The rate at which the catalyst catalyzes the decomposition of formic acid is obtained by measuring the gas produced by the reaction. The entire reaction proceeded as shown in Figure 3 within 2 hours.
[0038] It can be seen from the figure that the decomposition rate of formic acid and the concentration of carbon monoxide in the reformed gas increase first and then decrease with the increase of formate concentration. It is worth noting that when the decomposition rate of formic acid is at its maximum, the carbon monoxide concentration in the reformed gas has exceeded the m...
Embodiment 3
[0040] The influence of the content of silver in the catalyst on the decomposition rate of formic acid was investigated. The catalyst used in the experiment is 30mg Pd-Ag / C (20wt%Pd, n Pd : n Ag =3:0.5, 3:1, 3:2, 3:3, 3:4, 3:6, 3:9), the operating temperature is 92°C. The solution used was 5.00 ml of an aqueous solution containing 9.94 mol / L formic acid and 3.33 mol / L sodium formate. The rate at which the catalyst catalyzes the decomposition of formic acid is obtained by measuring the gas produced by the reaction. The whole reaction proceeded as shown in Figure 4 within 2 hours.
[0041] It can be seen from the figure that in n Pd : n Ag =3:3, the speed of formic acid decomposition is the largest. Adding too much or too little silver is unfavorable to the activity of the catalyst.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com