Projection optical system and projection image display
一种投影光学系统、光学系统的技术,应用在投影光学系统和投影图像显示装置领域,能够解决不能同时减小深度等问题,达到低失真、高分辨率、稳定光学性能的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
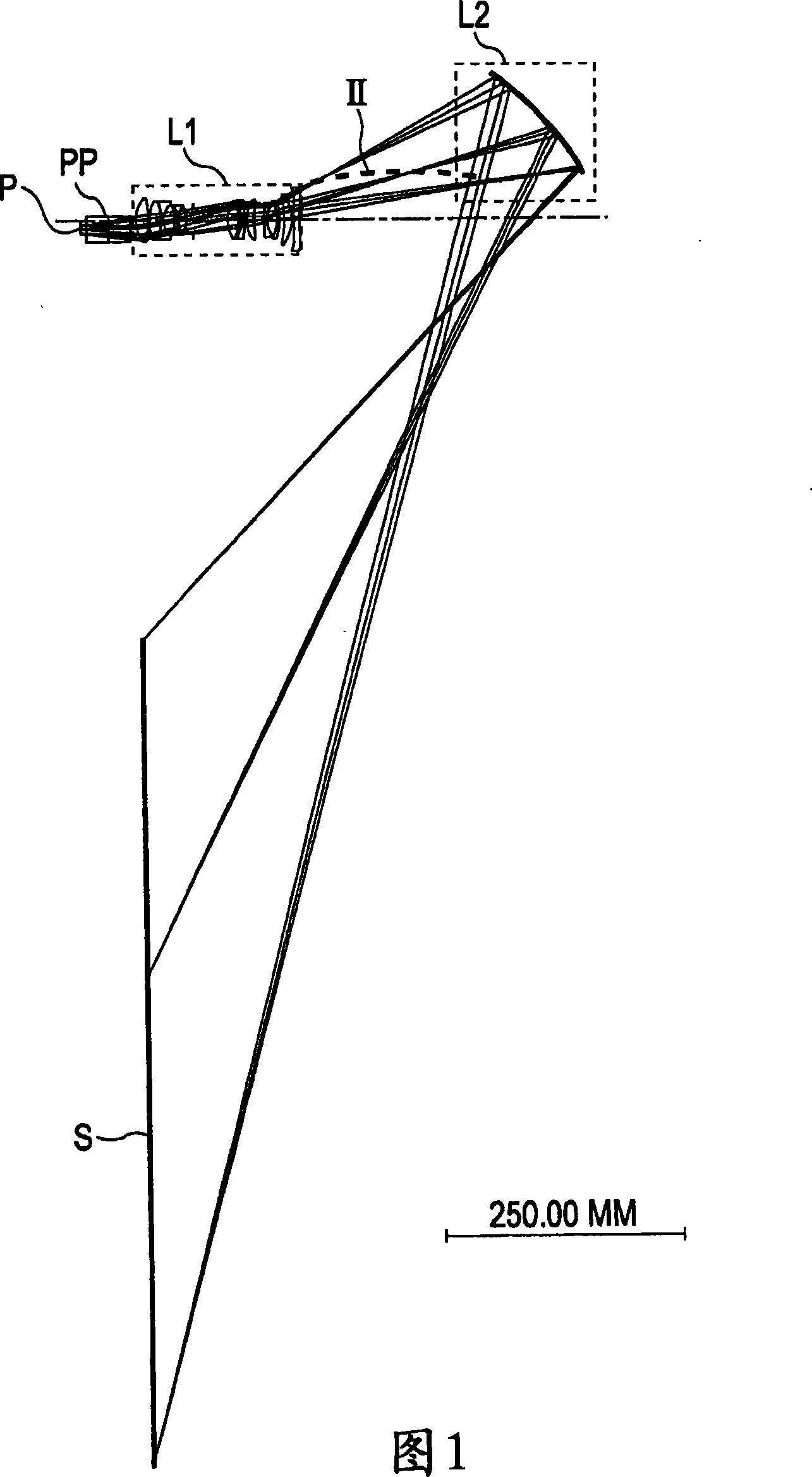
[0192] Fig. 1 illustrates an optical path according to a first embodiment. The image display element P functions as a modulation unit. Light emitted from a light source (not shown) is modulated by the image display element P according to a video signal. In this way, a primary imaging plane is formed. A reflective or transmissive dot-matrix liquid crystal display panel or a digital micromirror device (DMD) may be used for the image display element P. Referring to FIG. Reference numeral PP denotes a polarizing beam splitter (PBS), a color combining prism combining video signals of red, green and blue, or a total internal reflection (TIR) prism.
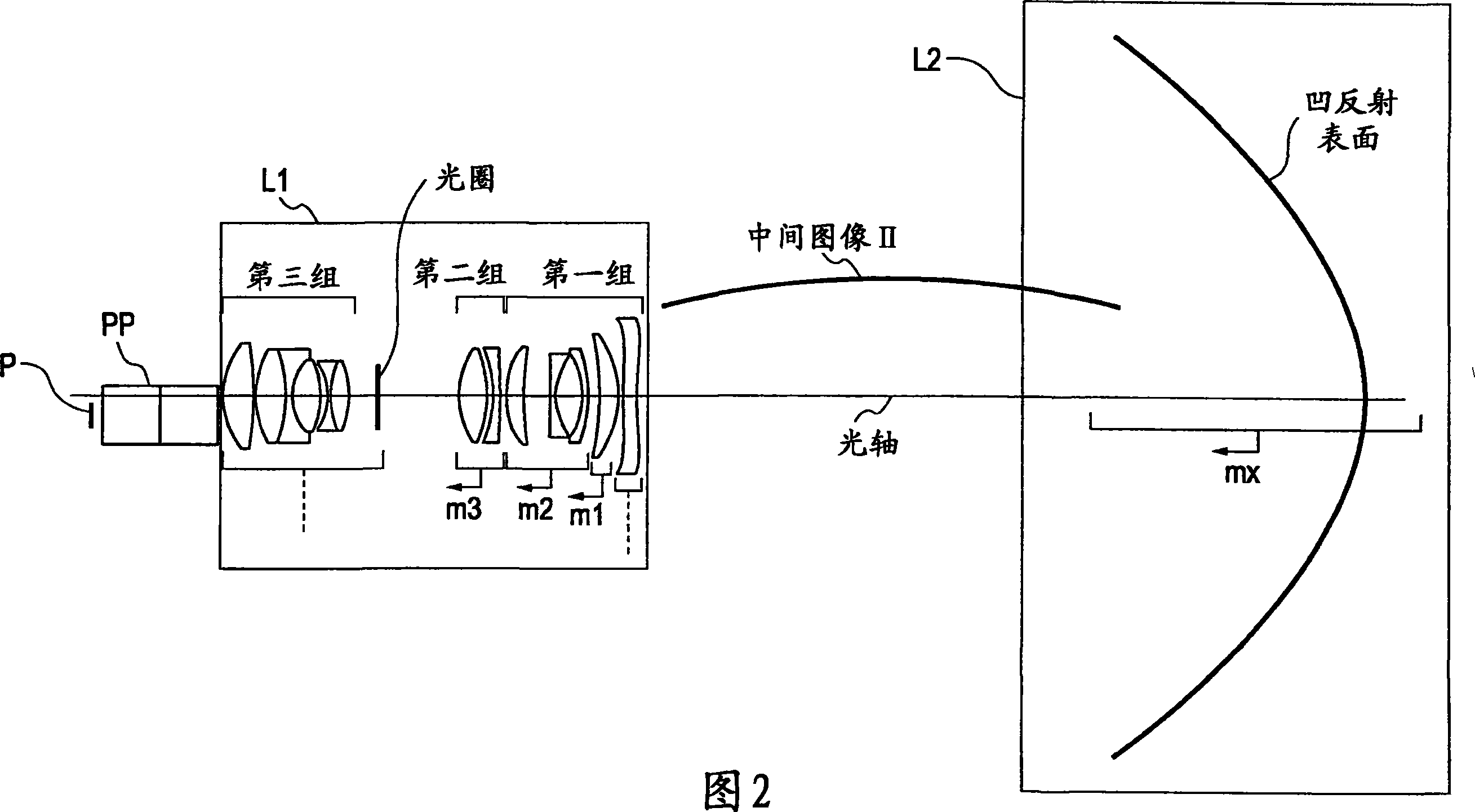
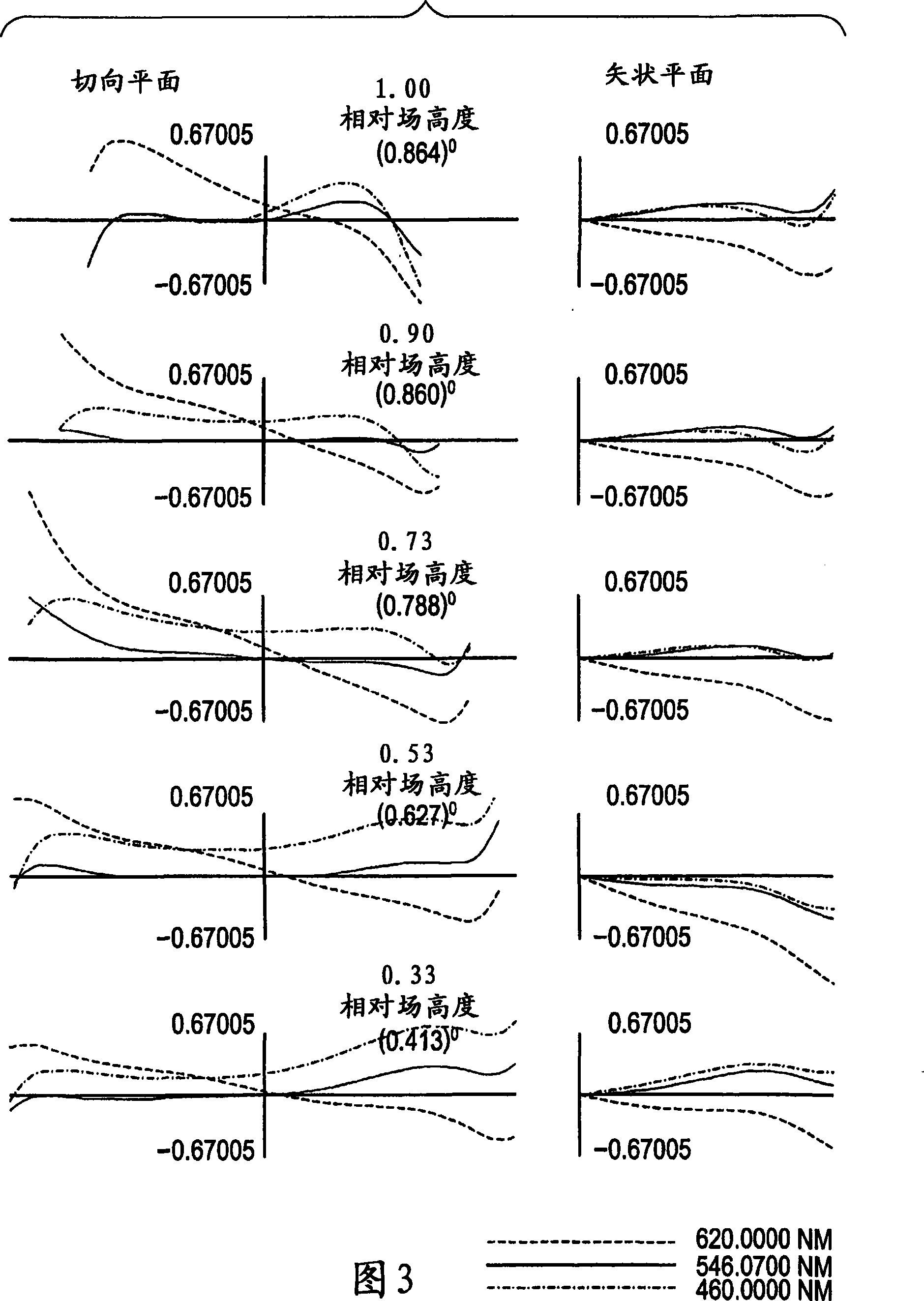
[0193] FIG. 2 illustrates a portion of the projection optical system shown in FIG. 1 in detail. The first optical system L1 includes a first group with negative refractive power, a second group with positive refractive power, a diaphragm, and a third group with positive refractive power in the following order from the secondary ima...
no. 2 example
[0216] Fig. 12 illustrates an optical path according to the second embodiment. The image display element P functions as a modulation unit. Light emitted from a light source (not shown) is modulated by the image display element P according to a video signal. In this way, a primary imaging plane is formed. For the image display element P, a reflective or transmissive dot-matrix liquid crystal display panel or a digital micromirror device (DMD) may be used. Reference numeral PP denotes a polarizing beam splitter (PBS), a color combining prism combining video signals of red, green and blue, or a total internal reflection (TIR) prism.
[0217] FIG. 13 illustrates a portion of the projection optical system shown in FIG. 12 in detail. The first optical system L1 includes a first group with negative refractive power, a second group with positive refractive power, a diaphragm, and a third group with positive refractive power in the following order from the secondary imaging plane ...
no. 3 example
[0238] Fig. 20 illustrates an optical path according to the third embodiment. The image display element P functions as a modulation unit. Light emitted from a light source (not shown) is modulated by the image display element P according to a video signal. In this way, a primary imaging plane is formed. For the image display element P, a reflective or transmissive dot-matrix liquid crystal display panel or a digital micromirror device (DMD) may be used. Reference numeral PP denotes a polarizing beam splitter (PBS), a color combining prism combining video signals of red, green and blue, or a total internal reflection (TIR) prism.
[0239] FIG. 21 illustrates a portion of the projection optical system shown in FIG. 20 in detail. The first optical system L1 includes a first group with negative refractive power, a second group with positive refractive power, a diaphragm, and a third group with positive refractive power in the following order from the secondary imaging plane s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com