Organic electroluminescent device capable of emitting white light and method for fabricating the same
An electroluminescence and white light technology, applied in the fields of electro-solid devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to repeat device performance, high manufacturing costs, affecting industrialization, etc. , the effect of fast response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
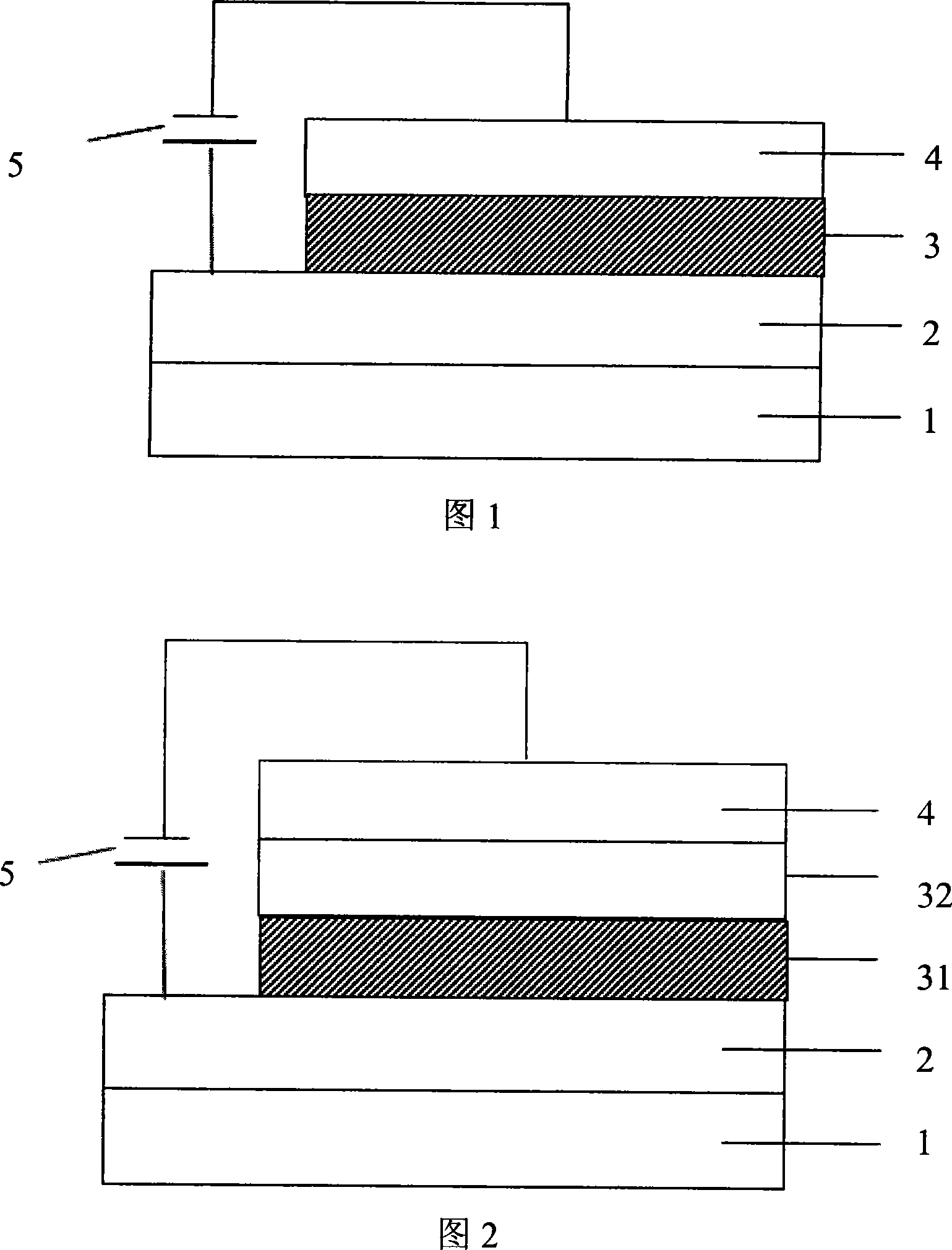
[0061] As shown in FIG. 1 , the hole transport layer in the structure of the device doubles as the white light emitting layer 3 .
[0062] The material of the hole transport layer of the device and also as the white light-emitting layer is PVK:NPB, and the cathode layer is made of Mg:Ag alloy. The entire device structure is described as:
[0063] Glass substrate / ITO / PVK:NPB(80nm) / Mg:Ag(200nm)
[0064] The preparation method is as follows:
[0065] ①Use detergent, ethanol solution, acetone solution and deionized water to ultrasonically clean the conductive substrate ITO glass, and dry it with dry nitrogen after cleaning. Wherein the ITO film on the glass substrate is used as the anode layer of the device, the square resistance of the ITO film is 10Ω / □, and the film thickness is 180nm.
[0066] ② Move the dried substrate into a vacuum chamber, and pretreat the ITO glass with low-energy oxygen plasma for 10 minutes under an oxygen pressure environment with an air pressure of 2...
Embodiment 2
[0073] As shown in FIG. 2 , the organic layer 3 in the structure of the device includes a hole transport layer also serving as a white light emitting layer 31 , and a hole blocking layer also serving as an electron transport layer 32 .
[0074] The hole transport layer of the device also serves as the white light-emitting layer material is PVK:NPB, the hole blocking layer also serves as the electron transport material BCP, and the cathode layer uses Mg:Ag alloy. The entire device structure is described as:
[0075] Glass substrate / ITO / PVK:NPB(80nm) / BCP(20nm) / Mg:Ag(100nm)
[0076] The fabrication process of the device is similar to that of Example 1.
Embodiment 3
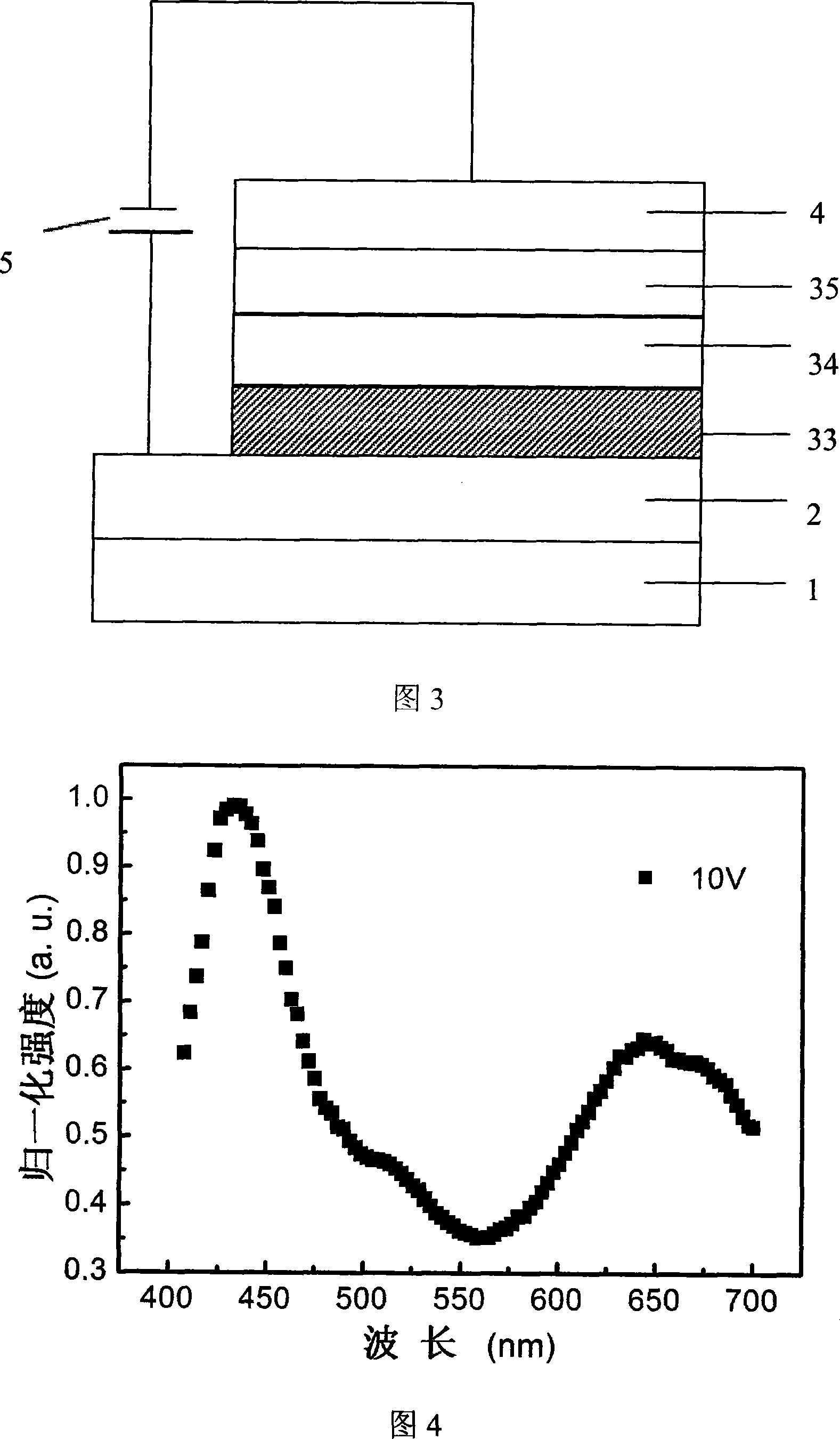
[0078] As shown in FIG. 3 , the organic layer 3 in the structure of the device includes a hole transport layer also serving as a white light emitting layer 33 , a hole blocking layer 34 and an electron transport layer 35 .
[0079] The material of the hole transport layer and the white light emitting layer of the device is PVK:NPB, the hole blocking material BCP, and the electron transport material Alq 3 , The cathode layer is made of Mg:Ag alloy. The entire device structure is described as:
[0080] Flexible substrate / ITO / PVK:NPB(80nm) / BCP(20nm) / Alq 3 (10nm) / Mg:Ag(100nm)
[0081] The fabrication process of the device is similar to that of Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sheet resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Film thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com