A method for producing an l-amino acid using a bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family having a pathway of glycogen biosynthesis disrupted
A biosynthetic, Enterobacteriaceae technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, botanical equipment and methods, bacteria, etc., and can solve problems such as inactivation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0128] Example 1 Construction of a bacterial strain with an inactivated glgC gene
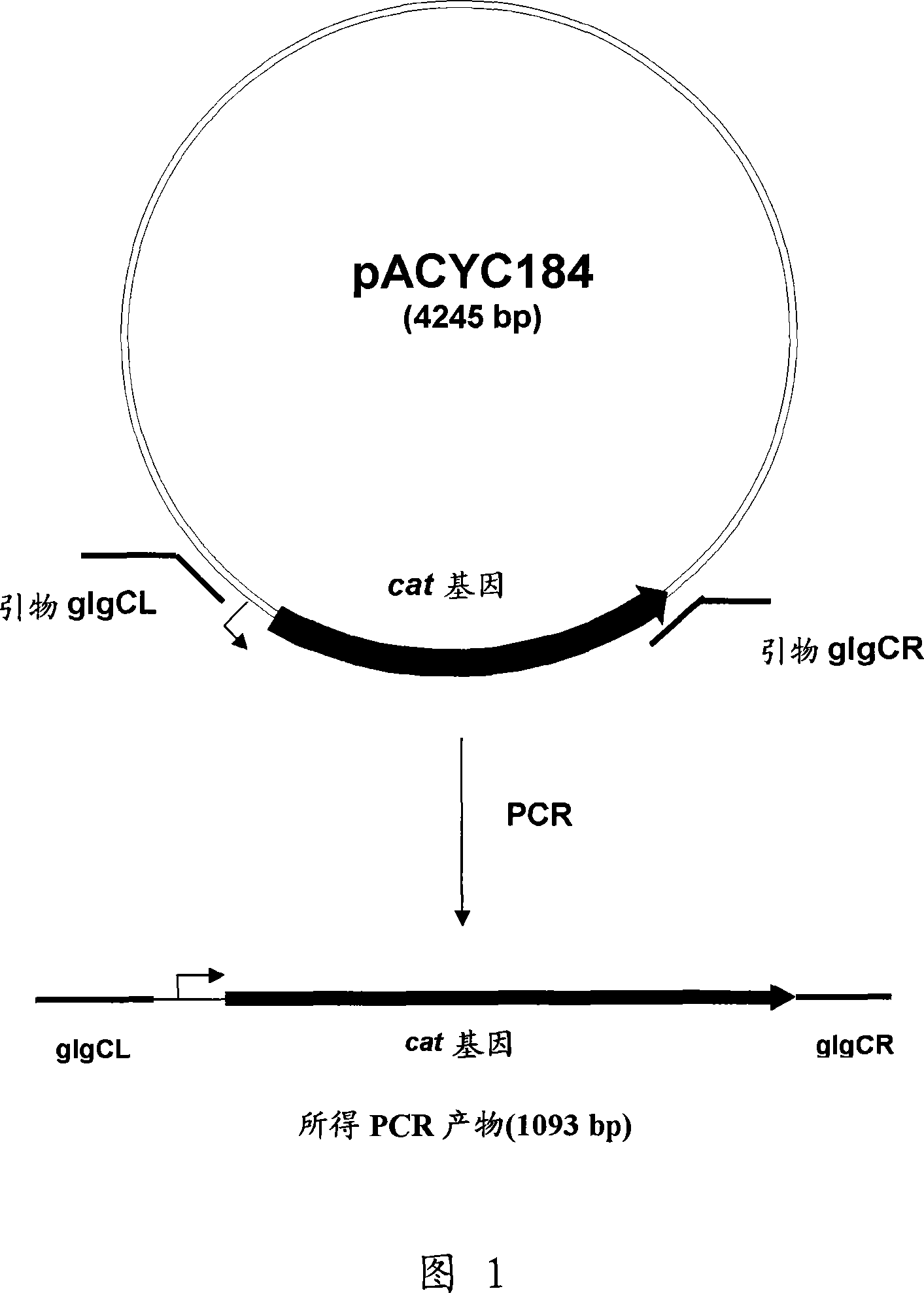
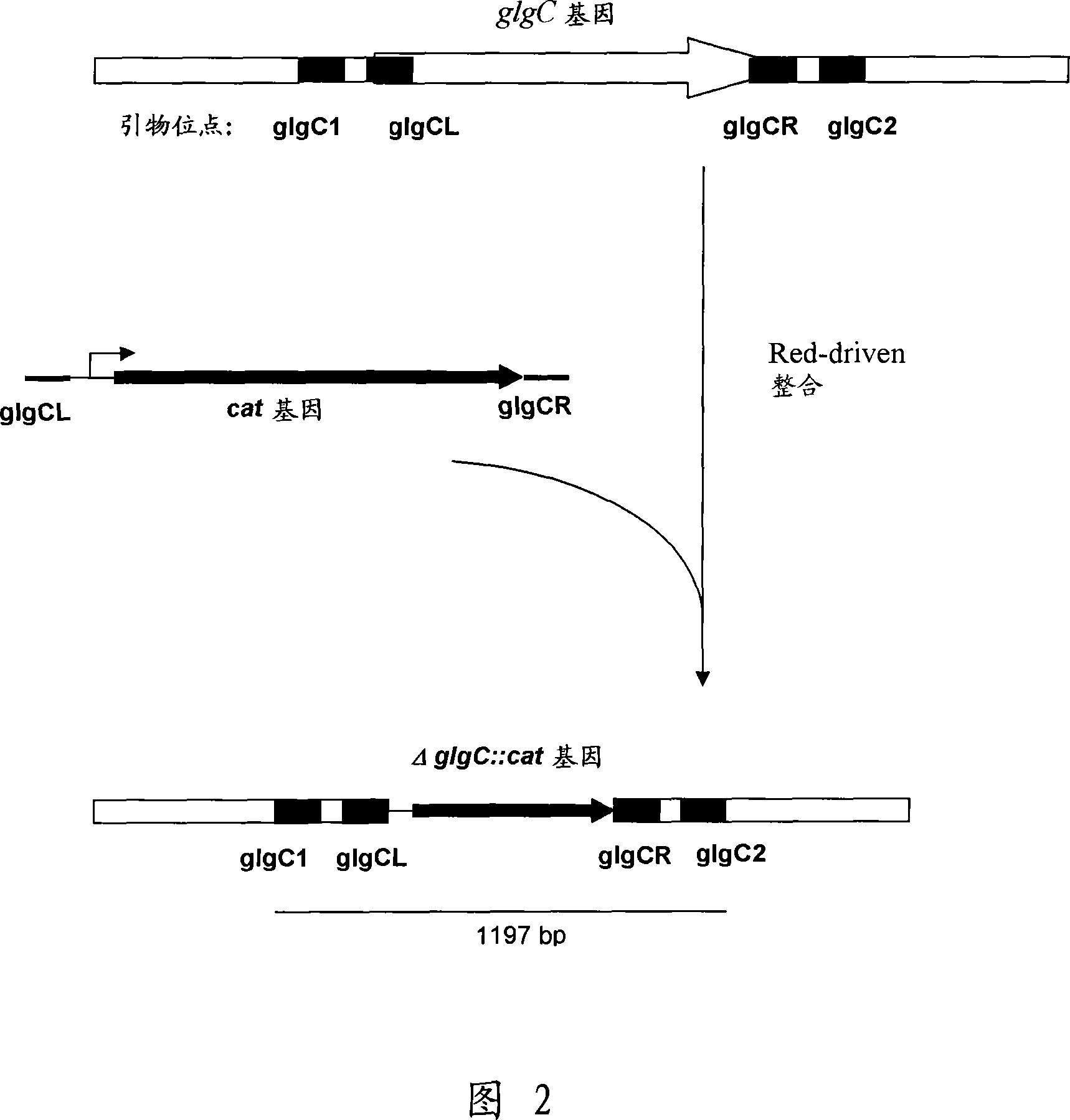
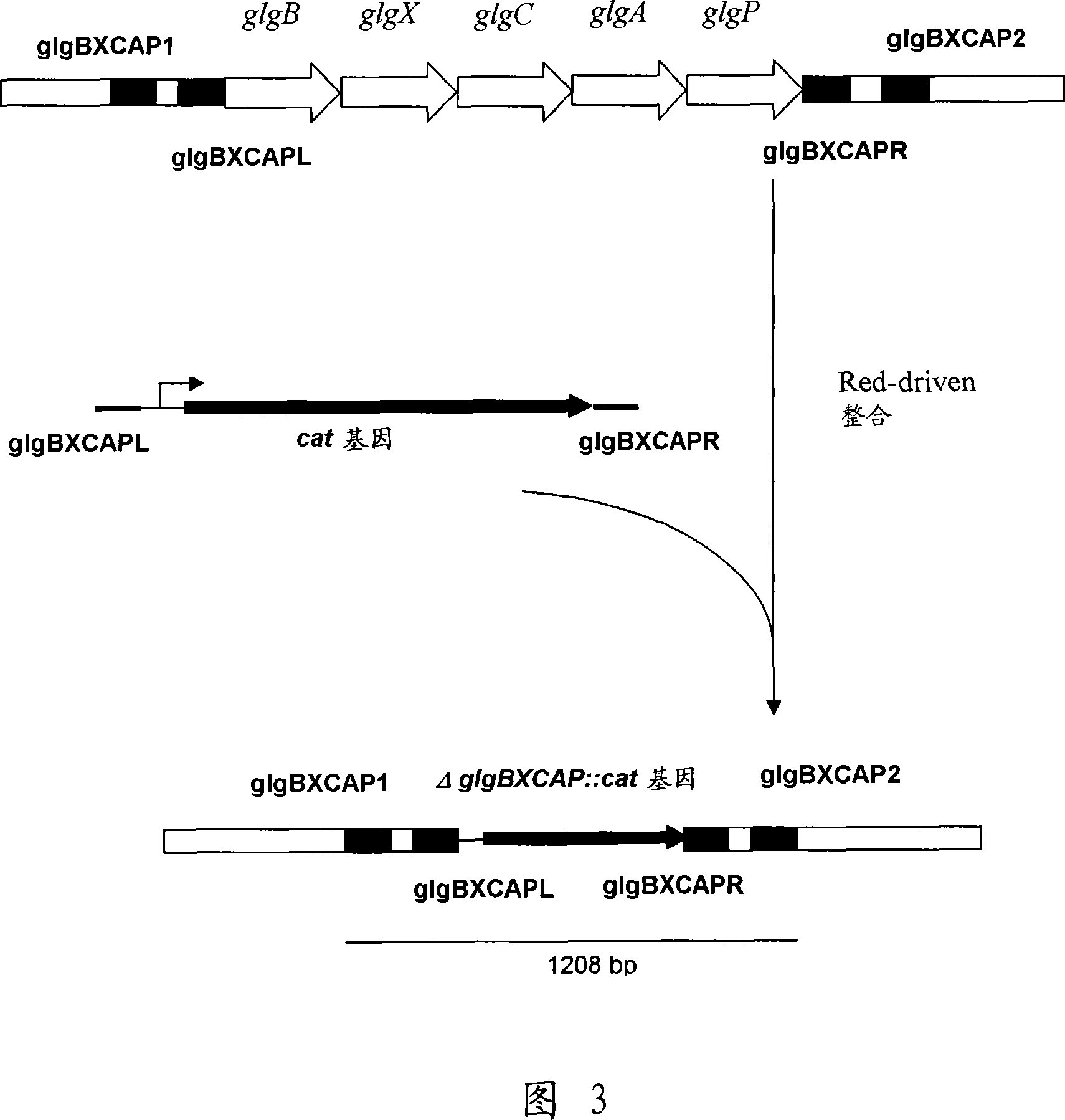
[0129] 1. Deletion of the glgC gene
[0130]The deletion of glgC can be constructed by a method called "Red-driven integration" originally developed by Datsenko, K.A. and Wanner, B.L. (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2000, 97(12), 6640-6645) Genetic strains. According to this method, PCR primers glgCL (SEQ ID NO: 3) and glgCR (SEQ ID NO: 4) complementary to both the region adjacent to the glgC gene in the template plasmid and the antibiotic resistance-conferring gene can be constructed. Plasmid pACYC184 (NBL Gene Sciences Ltd., UK) (GenBank / EMBL Accession No. X06403) can be used as a template for PCR reactions. The conditions of PCR can be as follows: denaturation step at 95°C for 3 minutes; profile of the first two cycles: 95°C for 1 minute, 50°C for 30 seconds, 72°C for 40 seconds; profile of the last 25 cycles: 95°C for 30 seconds, 54°C 30 seconds at 72°C, 40 seconds at 72°C; final step: 5 mi...
Embodiment 2
[0135] Embodiment 2 by Escherichia coli VL334thrC + -ΔglgC produces L-glutamate
[0136] Escherichia coli strain VL334thrC producing L-glutamic acid + (EP 1172433) Deletion of the glgC gene on the chromosome can be performed by conventional well-known methods, for example, from the MG1655 ΔglgC::cat strain by P1 transduction to obtain strain VL334thrC + ΔglgC. strain VL334thrC + Deposited at the Russian National Collection of Industrial Microorganisms (VKPM) (Russia, 117545 Moscow, 1 Dorozhny proezd, 1) on December 6, 2004 under the accession number VKPM B-8961, and then transferred to Budapest on December 8, 2004 Deposit of treaties.
[0137] Two strains, VL334thrC + and VL334thrC + - ΔglgC, all able to grow on L-agar plates at 37°C for 18-24 hours. One ring of cells can then be transferred to a tube containing 2 ml of fermentation medium. The fermentation medium (pH7.2) should contain glucose (60g / l), ammonium sulfate (25g / l), KH 2 PO 4 (2g / l), MgSO 4 (1g / l), thia...
Embodiment 3
[0138] Example 3 Production of L-proline by Escherichia coli 702ilvA-ΔglgC
[0139] Deletion of the glgC gene on the chromosome of the L-proline-producing Escherichia coli strain 702ilvA (VKPM B-8012, Russian Patent Application 2000124295, EP1172433) can be performed by conventional well-known methods as described above to obtain the strain 702ilvA-ΔglgC. The strain 702ilvA has been deposited with the Russian National Collection of Industrial Microorganisms (VKPM) (Russia, 117545 Moscow, 1 Dorozhny proezd, 1) on July 18, 2000 under the accession number VKPM B-8012.
[0140] Both E. coli strains, 702ilvA and 702ilvA-ΔglgC, were able to grow on L-agar plates at 37°C for 18-24 hours. These strains can then be cultured under the same conditions as described above.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com