Display device
A technology of display device and display area, applied in static indicators, instruments, nonlinear optics, etc., can solve the problem of increasing the frame area, and achieve the effect of reducing the frame area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
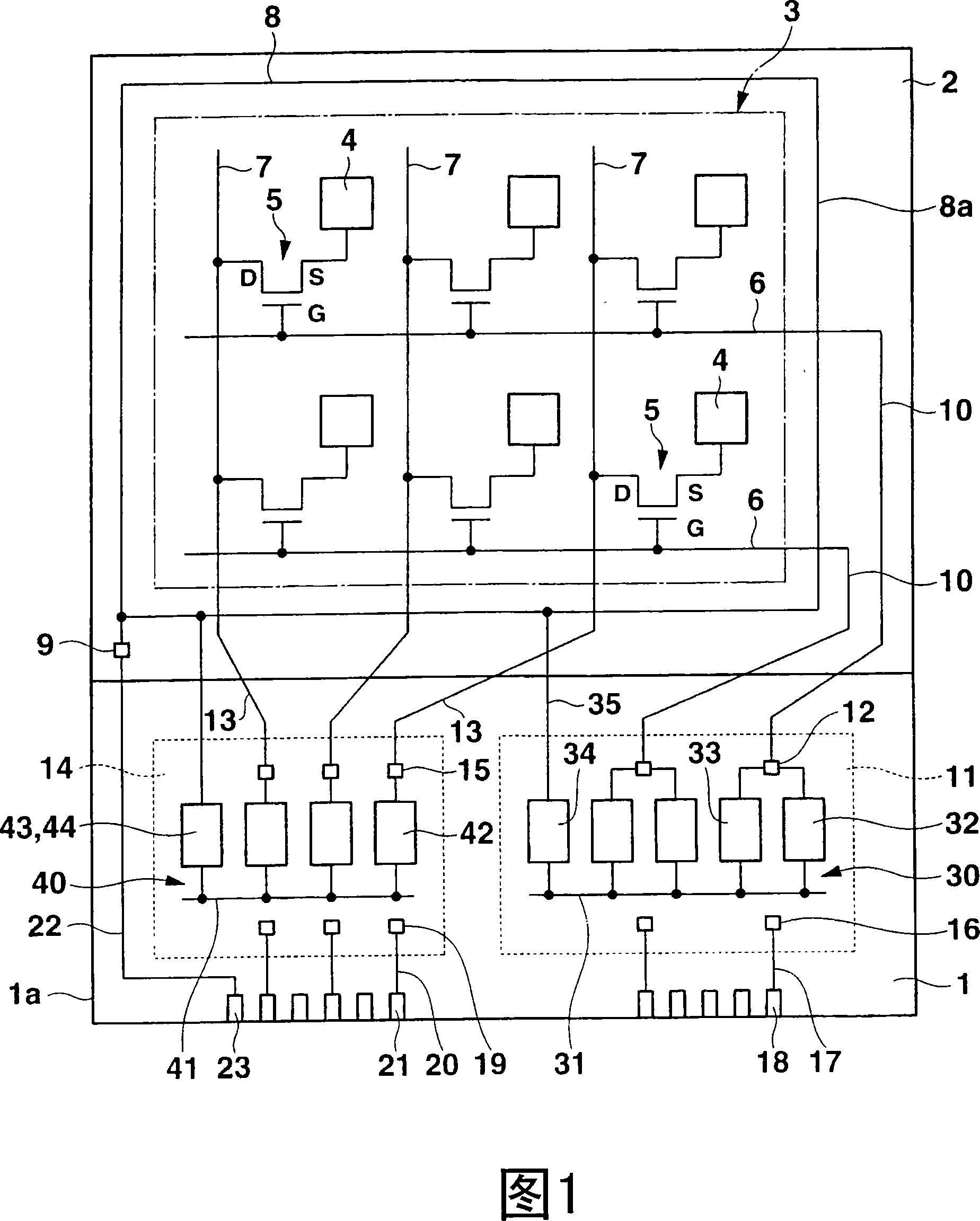
[0022] FIG. 1 is a plan view showing an equivalent circuit of main parts of a liquid crystal display device according to a first embodiment of the present invention. In this liquid crystal display device, the active substrate 1 and the opposite substrate 2 located above the active substrate 1 are bonded together by a substantially square-shaped sealing member (not shown), and the liquid crystal (not shown) is sealed in the sealing Between the two substrates 1 and 2 inside the component. At this time, the lower portion of the active substrate 1 protrudes from the counter substrate 2 . Hereinafter, this protruding portion is referred to as a protruding portion 1a. Moreover, the rectangular area enclosed by the dotted line in FIG. 1 is the display area 3 .
[0023] The display area 3 on the active substrate 1 is provided with: a plurality of pixel electrodes 4 arranged in a matrix, nMOS switching thin film transistors 5 having source electrodes S connected to each pixel electro...
no. 2 approach
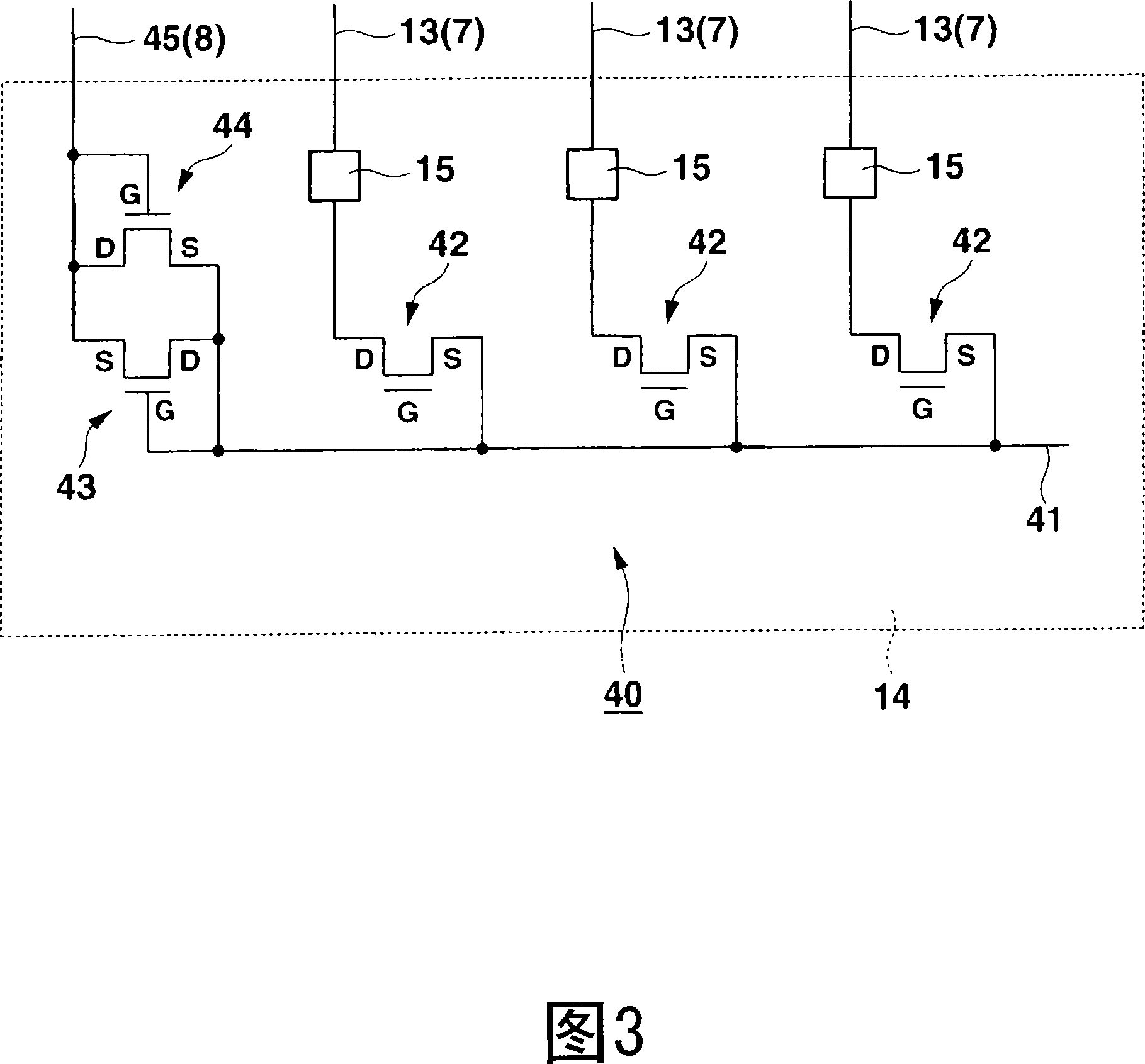
[0067] FIG. 9 is a cross-sectional view similar to FIG. 7 of a liquid crystal display device according to a second embodiment of the present invention. In this liquid crystal display device, the source electrode S of the data line electrostatic protection thin film transistor 42 is connected to the data line electrostatic protection line 41 provided on the upper surface of the gate insulating film 51 . Therefore, the contact hole 63 shown in FIG. 7 becomes unnecessary, and the interlayer contact portion can be further reduced.
[0068] In addition, in the liquid crystal display device of the second embodiment, as shown in FIG. 10 which is the same cross-sectional view as FIG. The source electrode S of the first connecting thin film transistor 43 and the drain electrode D of the second connecting thin film transistor 44 are connected to the contact hole 64 on the common lead 45, and the electrostatic protection line 41 is used to connect the data line to the second contact hole...
no. 3 approach
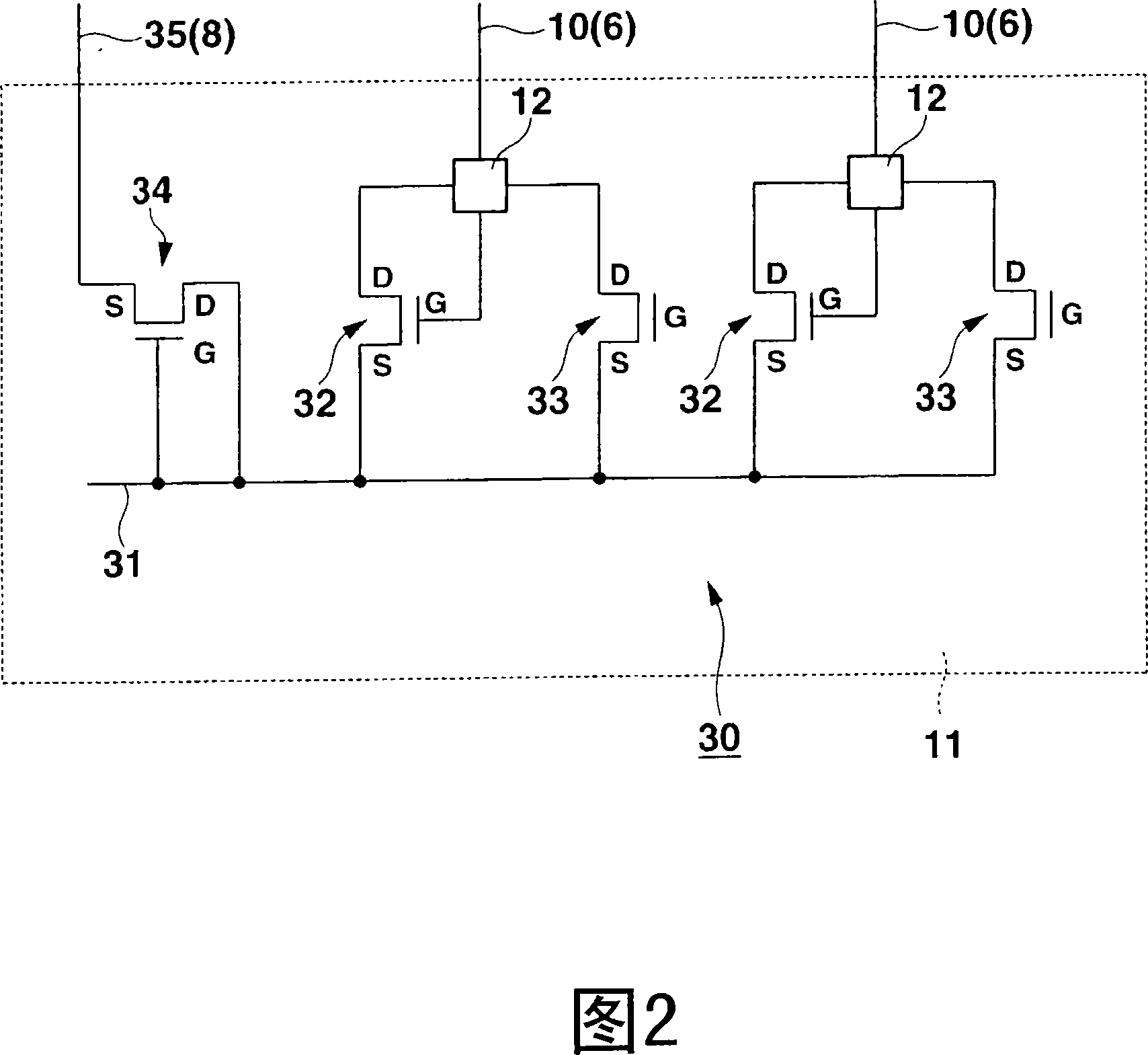
[0070] FIG. 11 is a plan view of an equivalent circuit similar to FIG. 2 of a liquid crystal display device according to a third embodiment of the present invention. In this liquid crystal display device, the difference from the structure shown in FIG. 2 is that the thin-film transistor 33 for static electricity protection for the second scanning line is omitted, and the source electrode S of the thin-film transistor 34 for connection is connected to the thin-film transistor 33 for driving the scanning line. On the Vgl terminal 71 in the driver mounting area 11.
[0071] At this time, a negative voltage (for example, Vgl=-20 to -15V) applied to the scanning line 6 in the non-selected state is supplied to the Vgl terminal 71 . The potential Vgl (-20 to -15V) of the scanning line 6 in the non-selected state is lower than the potential of the common line 8 (for example, Vcom=-5 to +5V). Therefore, a current flows from the electrostatic protection line 31 for scanning lines to th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com