Heat exchanger
A heat exchanger and heat sink technology, applied in heat exchange equipment, heating methods, household heating, etc., can solve the problems of wind flow obstruction, inability to strengthen the heat sink, unable to increase the rigidity of the heat sink, etc., and achieve increased strength , smooth flow effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
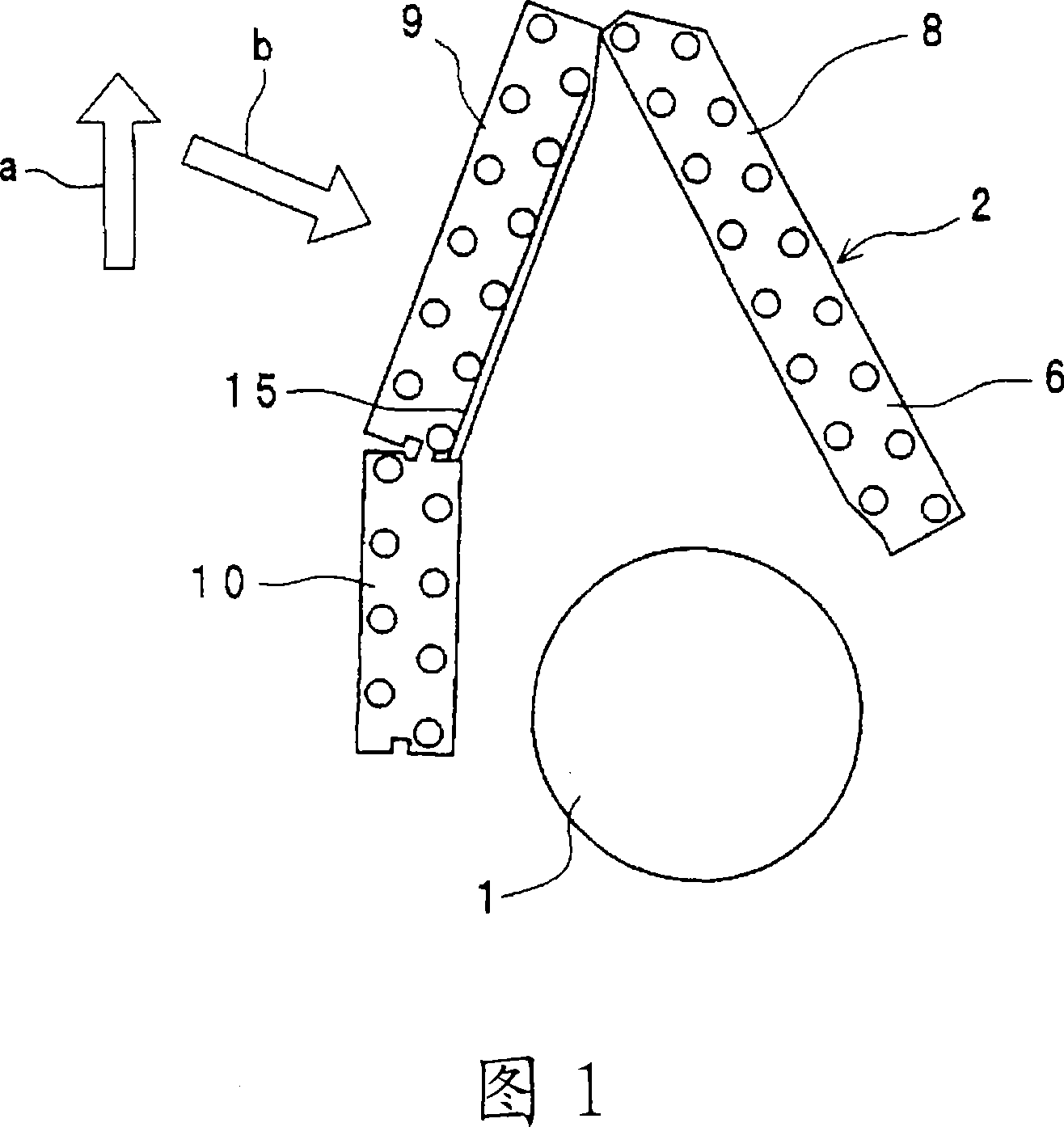
[0051] Fig. 1 is a schematic sectional view of an air conditioner using a heat exchanger according to a first embodiment of the present invention. In Fig. 1, 1 is a blower fan, and 2 is a heat exchanger. In addition, in FIG. 1 , arrow a indicates the vertically upward direction when the heat exchanger is arranged in the air conditioner in use, and arrow b indicates the flow direction of wind as the heat transfer medium. In FIG. 1 , for the sake of brevity, the case for accommodating the blower fan 1 and the heat exchanger 2 and the like are omitted.
[0052] In this air conditioner, the blower fan 1 is rotated, and the air sucked in via the heat exchanger 2 is blown out from an air outlet not shown.
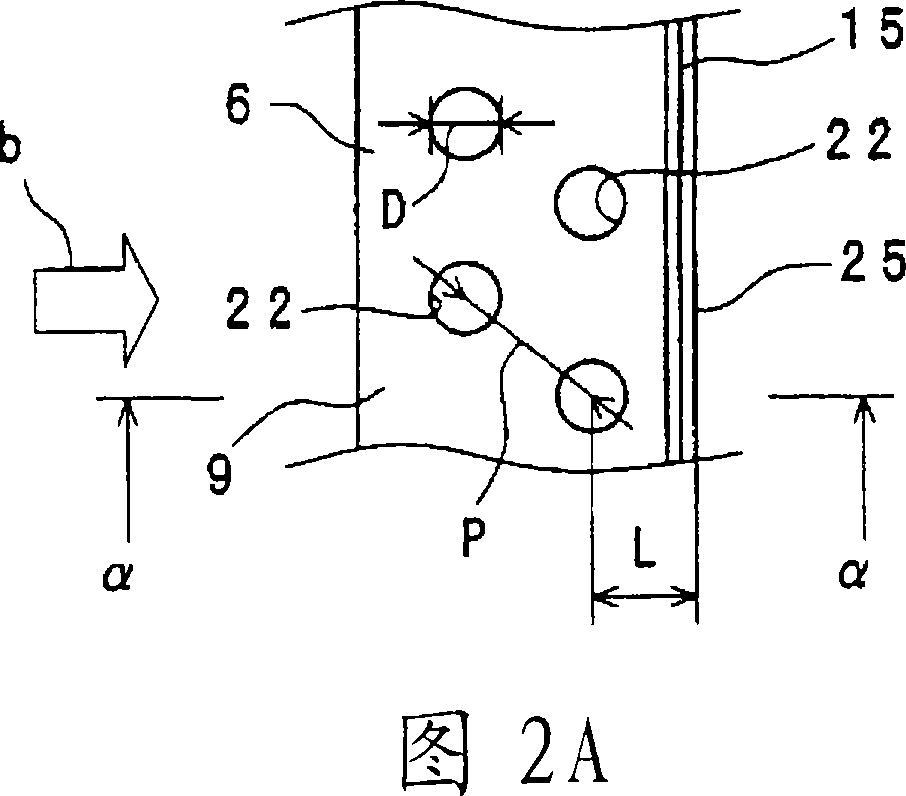
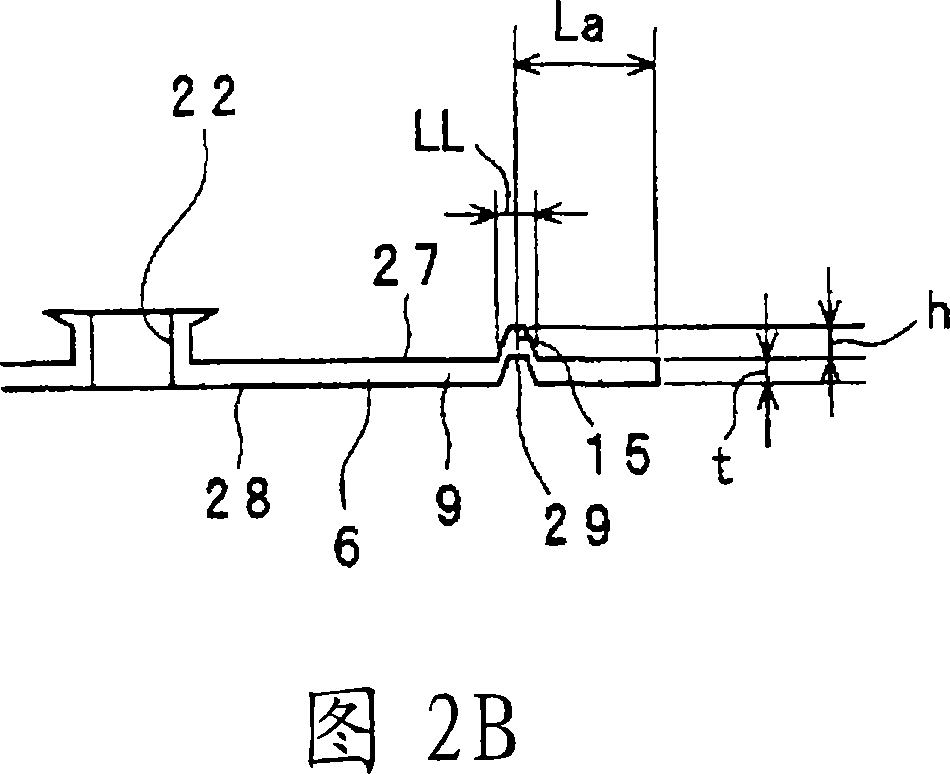
[0053]The heat exchanger 2 has a fan 6 and heat transfer tubes (not shown). The plurality of fans 6 are arranged at predetermined intervals in a direction perpendicular to the paper surface in FIG. 1 . The above-mentioned fan 6 is in the shape of a flat plate. The above-menti...
no. 2 approach
[0088] Fig. 4 is a partial enlarged view of the second portion 79 of the fin 73 included in the heat exchanger of the second embodiment. The heat exchanger of the second embodiment differs from the heat exchanger of the first embodiment only in that, in the second part 79, the row of the insertion holes 72 for the insertion of the heat transfer tubes arranged in a staggered direction in the width direction is different from that of the first embodiment. A second rib 76 is formed therebetween, and the second rib 76 is substantially parallel to the first rib 75 and has substantially the same shape as the first rib 75 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com