Floor and its production method and its uses as ground heat floor
A technology for flooring and slats, applied in manufacturing tools, building structures, floors, etc., can solve the problems of easy cracking, warping and deformation of the surface plate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Floor
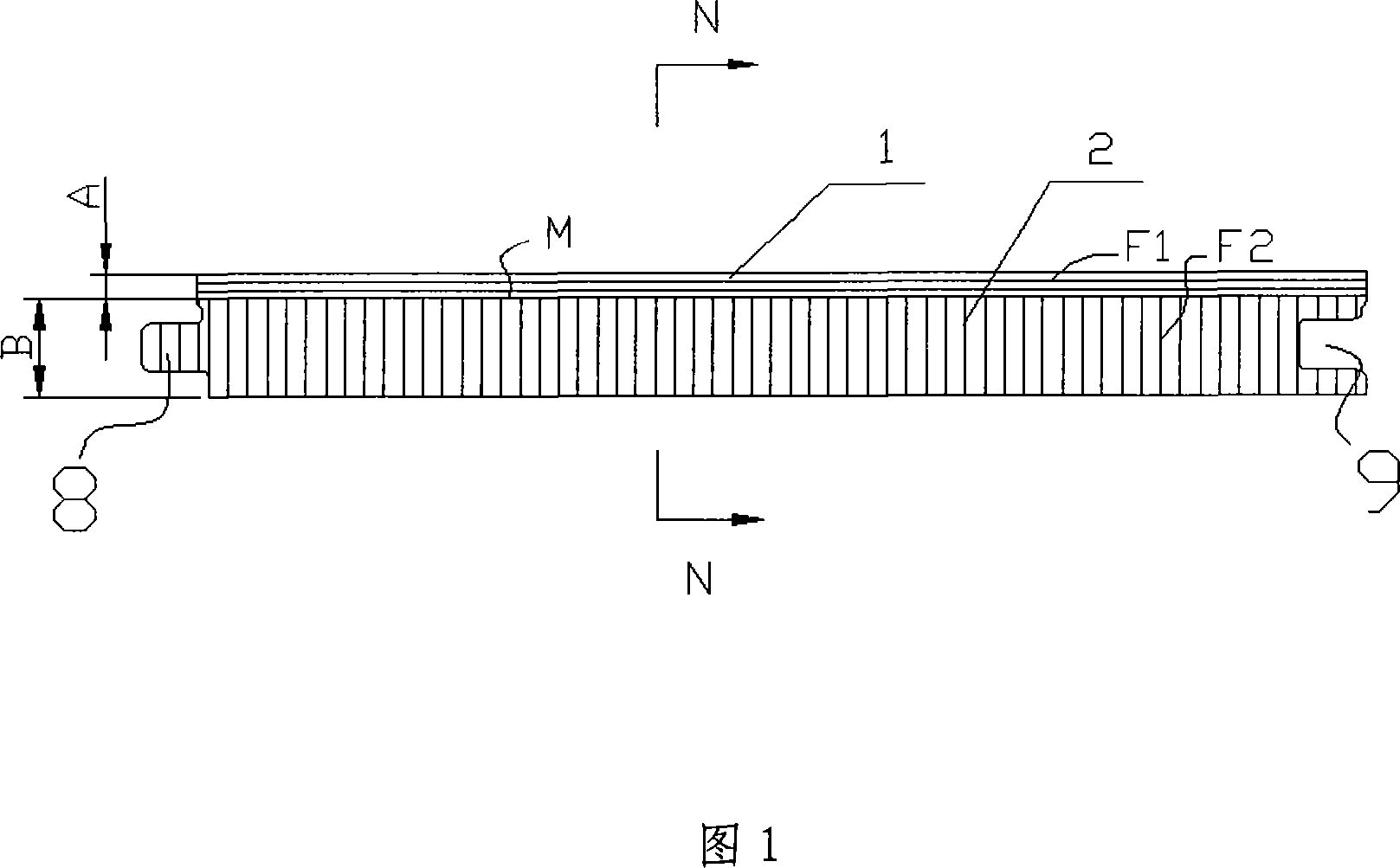
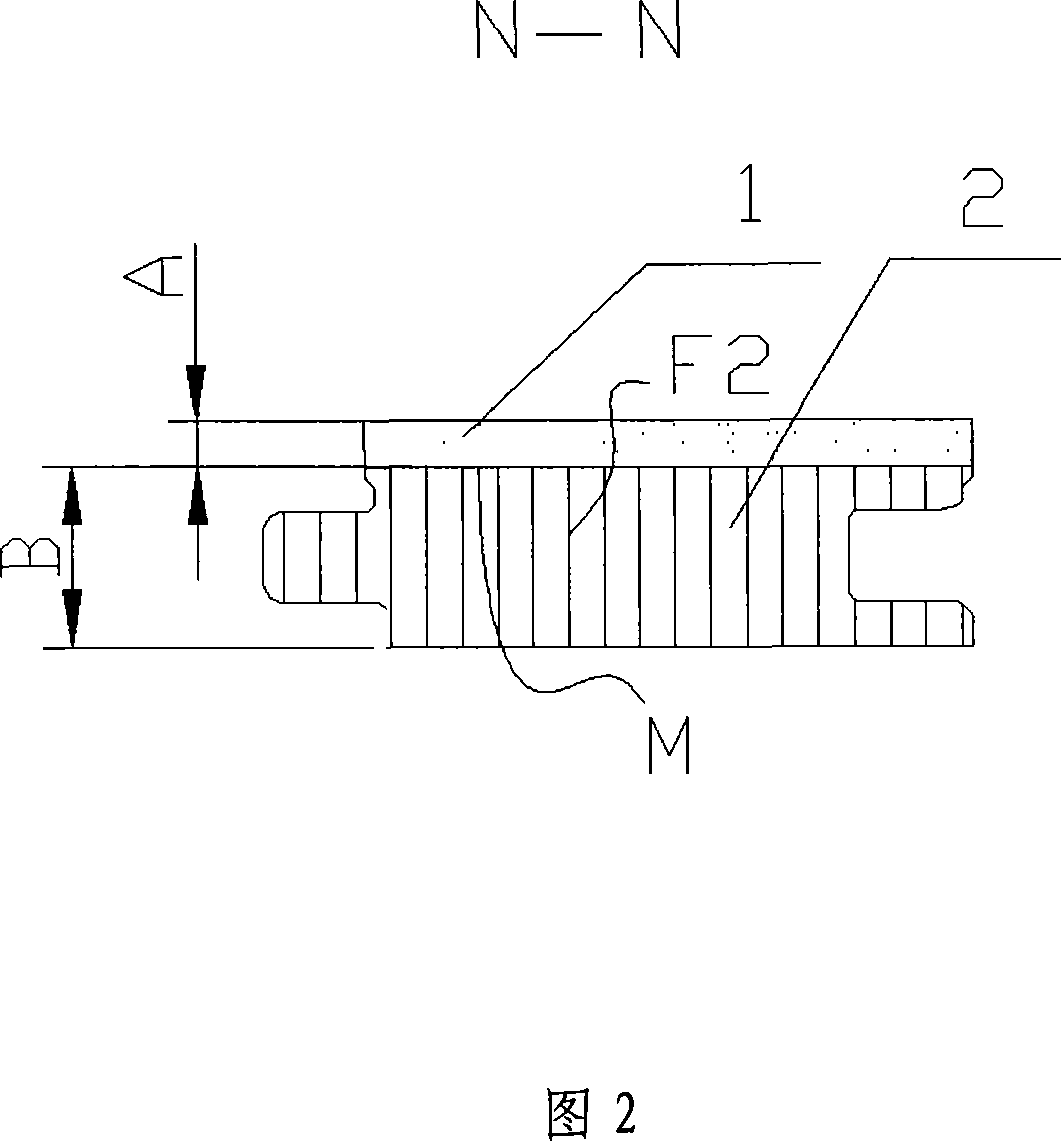
[0023] The floor shown in Fig. 1, 2, from top to bottom is table board 1, base material 2 successively, and forms with adhesive pressing between adjacent two boards. The surface board 1 is a sawn solid wood veneer or bamboo veneer, and the thickness A is 4mm. The surface M of the substrate 2 (that is, the joint surface with the surface plate 1) is a wood cross-section, and the thickness B is 6 mm. The fiber direction F1 of the surface board 1 is a horizontal direction, and the wood fiber direction F2 of the substrate 2 is a vertical direction, and they are perpendicular to each other.
[0024] Both sides of the base material 2 are provided with a tenon 8 and a tenon groove 9 .
Embodiment 2
[0025] Example 2: Making the base material with laminated veneer lumber
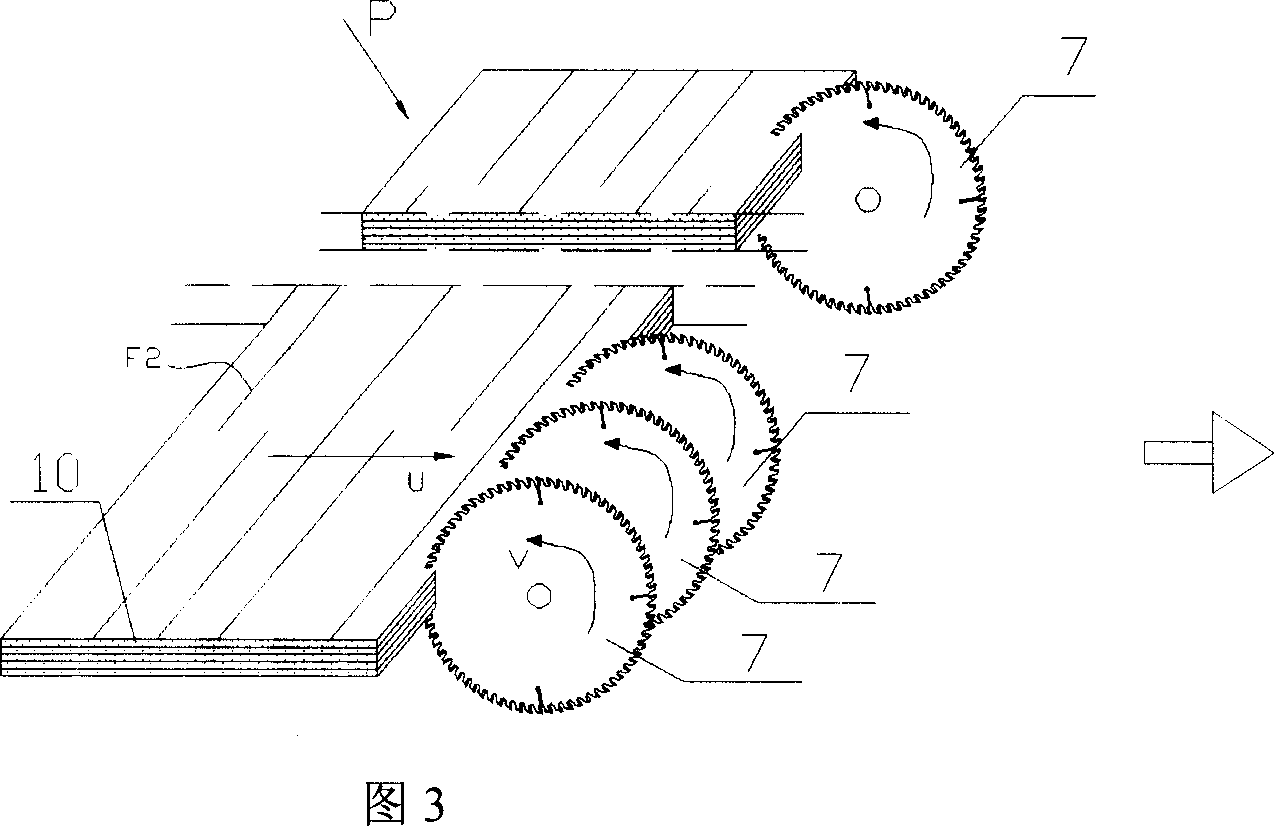
[0026] As shown in Fig. 3, the laminated veneer lumber P formed by coating and pressing the laminated veneer 10 parallel to the fiber direction of the multi-layer, its surface is the wood chord section, and the fiber direction is F2. Use the circular saw blade 7 to cut the laminated veneer lumber P into strips 4 in the transverse direction perpendicular to the fiber direction F2, turn the strips clockwise 90 degrees (as shown in Figure 4), apply glue on the side, and then press T Under the action of lateral pressure (as shown in Figure 5), the base material 2 (as shown in Figure 6) is obtained. The fiber direction F2 of the substrate 2 is a vertical direction, and the surface M is a transverse plane. It can be seen from the figure that the sawn width of the slats is the thickness B of the base material.
[0027] The surface board is bonded to the surface M of the obtained substrate 2, and the fiber dir...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Example 3: Making the base material with laminated veneer lumber
[0029] As shown in Figure 7, the laminated veneer lumber P formed by coating and pressing the laminated veneer 10 parallel to the fiber direction of the multi-layer, its surface is the wood chord section, and the fiber direction is F2. Use the circular saw blade 7 to cut the laminated veneer lumber P into strips 5 in the longitudinal direction parallel to the fiber direction F2, turn the strips clockwise 90 degrees (as shown in Figure 8), apply glue on the side, and then press T Under the action of side pressure (as shown in Figure 9), the base material 2 (as shown in Figure 10) is obtained. The fiber direction F2 of the substrate 2 is a horizontal direction, and the surface M is a radial section. It can be seen from the figure that the sawn width of the slats is the thickness B of the base material.
[0030] The surface plate is bonded to the surface M of the obtained base material 2, and the fiber di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com