c-MET kinase binding proteins
An immunoglobulin and monomer technology, applied in the field of c-MET kinase-binding protein, can solve problems such as reducing tumorigenic potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0474] This example describes the selection of monomeric domains and the generation of multimers.
[0475] From any of a variety of human and / or non-human sequences, starting materials for identifying monomeric domains and generating multimers from selected monomeric domains and methods can be derived. For example, to produce selected monomeric domains with specific binding to a desired ligand or mixture of ligands, one or more monomeric domain genes are selected from families of monomeric domains that bind certain ligands. Nucleic acid sequences encoding one or more monomeric domain genes can be obtained by PCR amplification of genomic DNA or cDNA, or, optionally, can be produced synthetically using overlapping oligonucleotides.
[0476] Most commonly, these sequences are then cloned into a cell surface display format (ie bacterial, yeast or mammalian (COS) cell surface display; phage display) for expression and screening. The recombinant sequences are transfected (transduce...
Embodiment 2
[0481] This example describes in vivo in-protein recombination to generate a library of greater diversity
[0482] The monomer-encoding plasmid vector (pCK-derived vector; see below) flanked by orthologous loxP sites was recombined with the phage vector via its compatible loxP sites in a Cre-dependent manner. Recombinant phage vectors were detected by PCR using primers specific for the recombinant construct. DNA sequencing showed that the correct recombination product was produced.
[0483] Reagents and Experimental Methods
[0484] pCK-cre-lox-monomer-loxP. This vector has 2 particularly relevant features. First, it carries the P lac The cre gene under control encodes the site-specific DNA recombinase Cre. Cre was PCR-amplified from p705-cre (purchased from GeneBridges) with cre-specific primers, which incorporated XbaI (5') and SfiI (3') at the ends of the PCR product. The product was digested with XbaI and SfiI and cloned into the bla of pCK (pCK110919-HC-Bla (pACYC o...
Embodiment 6
[0518] This example describes the construction of an EGF-based monomer library.
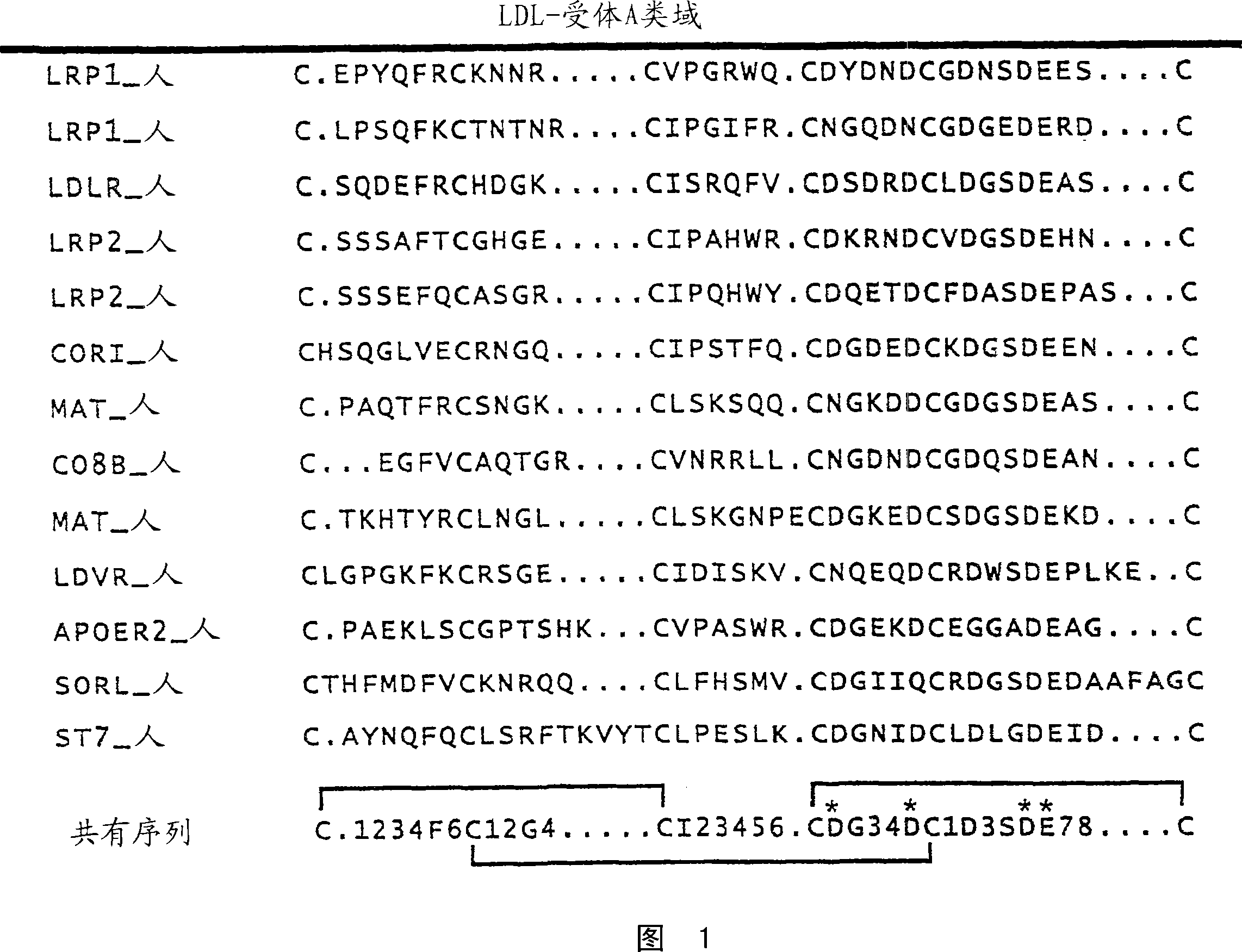
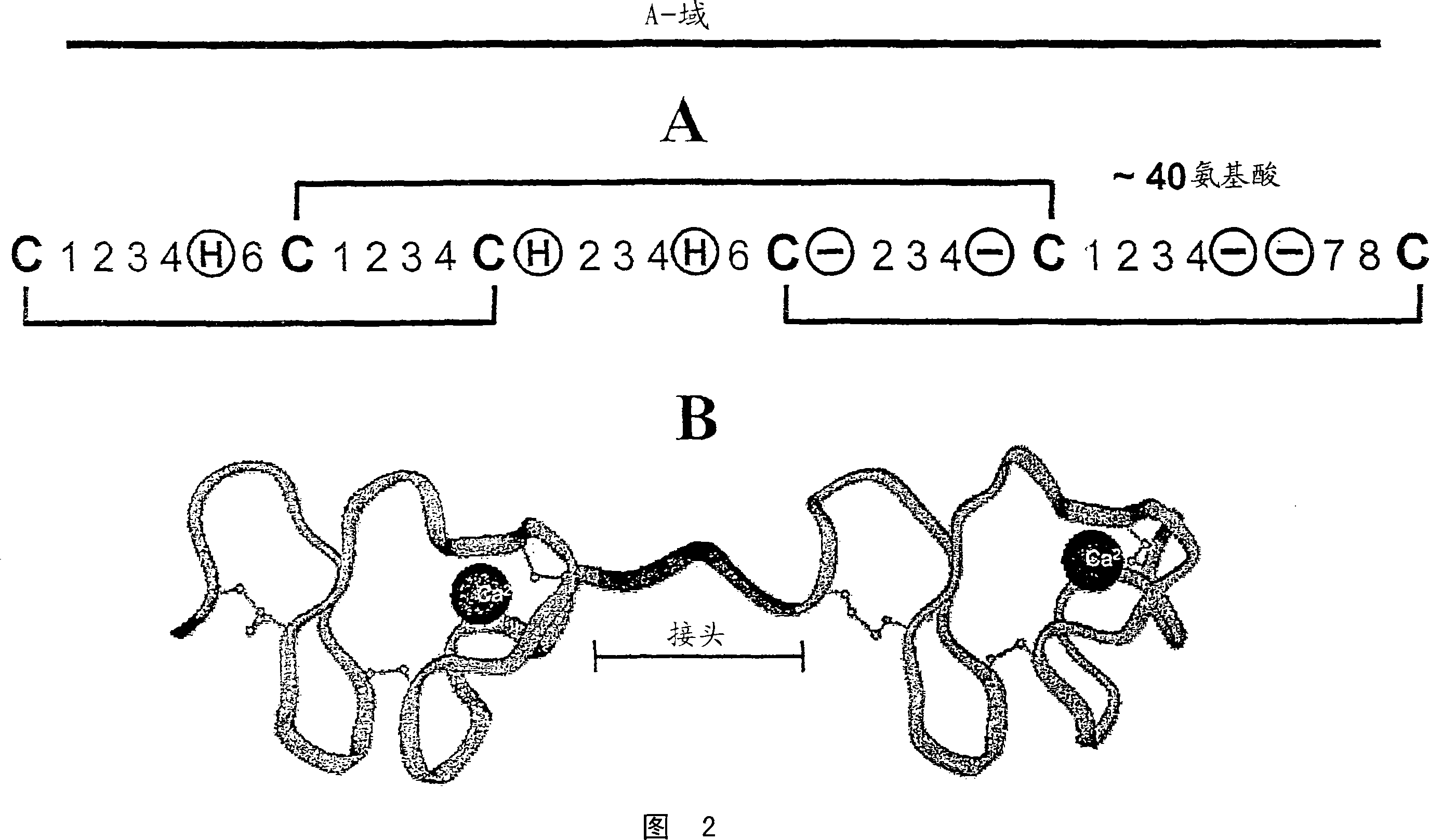
[0519] CaEGF domain library E3 encodes a protein domain of 36-43 amino acids with the following pattern:
[0520] X(5)C1-X(4 / 6)-C2-X(4,5)-C3-X(8)-C4-X(1)-C5-X(8 / 12)-C6
[0521] The table below describes each position, which amino acid is encoded in a library based on the natural diversity of human calcium-binding EGF domains:
[0522]
[0523] A library E3 of DNA sequences encoding monomeric calcium-binding EGF domains was generated by assembly PCR as described by Stemmer et al., Gene 164:49-53 (1995). The oligonucleotides used in this PCR reaction were 2 sets, 1 and 2. They are:
[0524] Group 1:
[0525] 1.5'-AAAAGGCCTCGAGGGCCTGGGTGGCAATGGT-3'
[0526] 2.5'-CCTGAACCACCACAKHKACCGYKSNBGCACGGAYYCGRCRMACATTCATYAAYATCTDYACCATTGCCACCC-3'
[0527] 3.5'-CCTGAACCACCACAKNTGSCGYYGYKMHSGCACGGAYYCGRCRMACATTCATYAAYATCTDYACCATTGCCACCC-3'
[0528] 4.5'-CCTGAACCACCACAKHKACCGYKSNBGCAARBAYBCGVAHYCWSKBYA...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Titer | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com