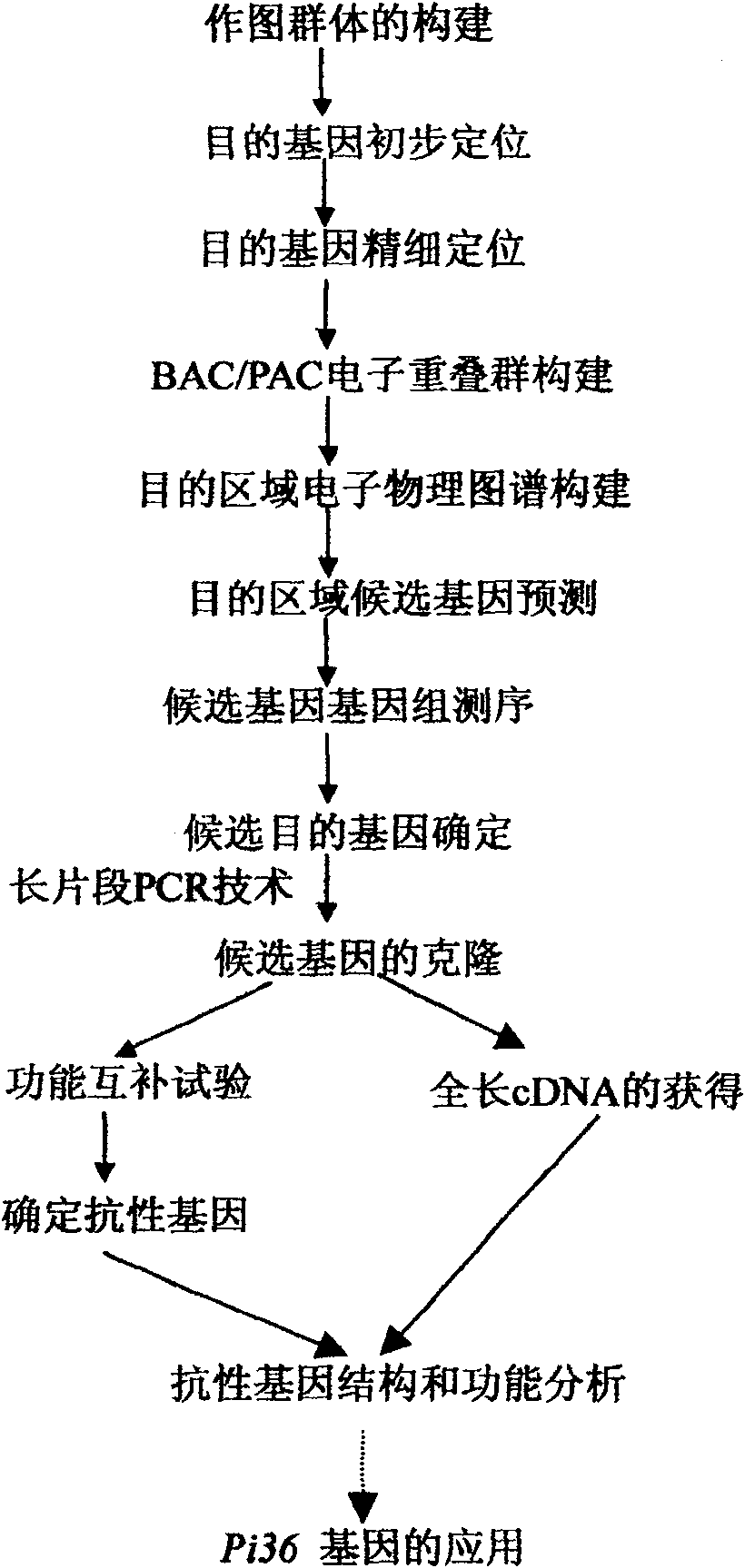
Resistance gene Pi36 of rice blast and its use
A rice blast and resistance gene technology is applied in the field of isolation, cloning and application of the rice blast resistance gene Pi36, and the effect of shortening the breeding time is achieved.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Genetic Analysis and Preliminary Mapping of Rice Blast Resistance Gene Pi36
[0039] Such as figure 1 , the present invention clones the resistance gene Pi36 by using the map-based cloning method. First, in order to discover and identify new resistance genes to rice blast, F from two hybrid combinations of indica rice resistant variety Q61 and japonica rice susceptible variety Aichixu and Lijiangxintuanheigu (LTH) were studied. 2 Group (F 2 -1 and F 2 -2), inoculate the bacterial strain CHL39 showing a clear non-affinity / affinity response to the parental species. The results show that the 2 F 2 The segregation ratio of resistant plants and susceptible plants in the population was 3:1. It was inferred that the resistance of Q61 to the inoculated strain CHL39 was controlled by a pair of dominant genes.
[0040] In order to quickly determine the chromosomal location of the main resistance gene, an F population consisting of 40 resistant and 580 susceptibl...
Embodiment 2
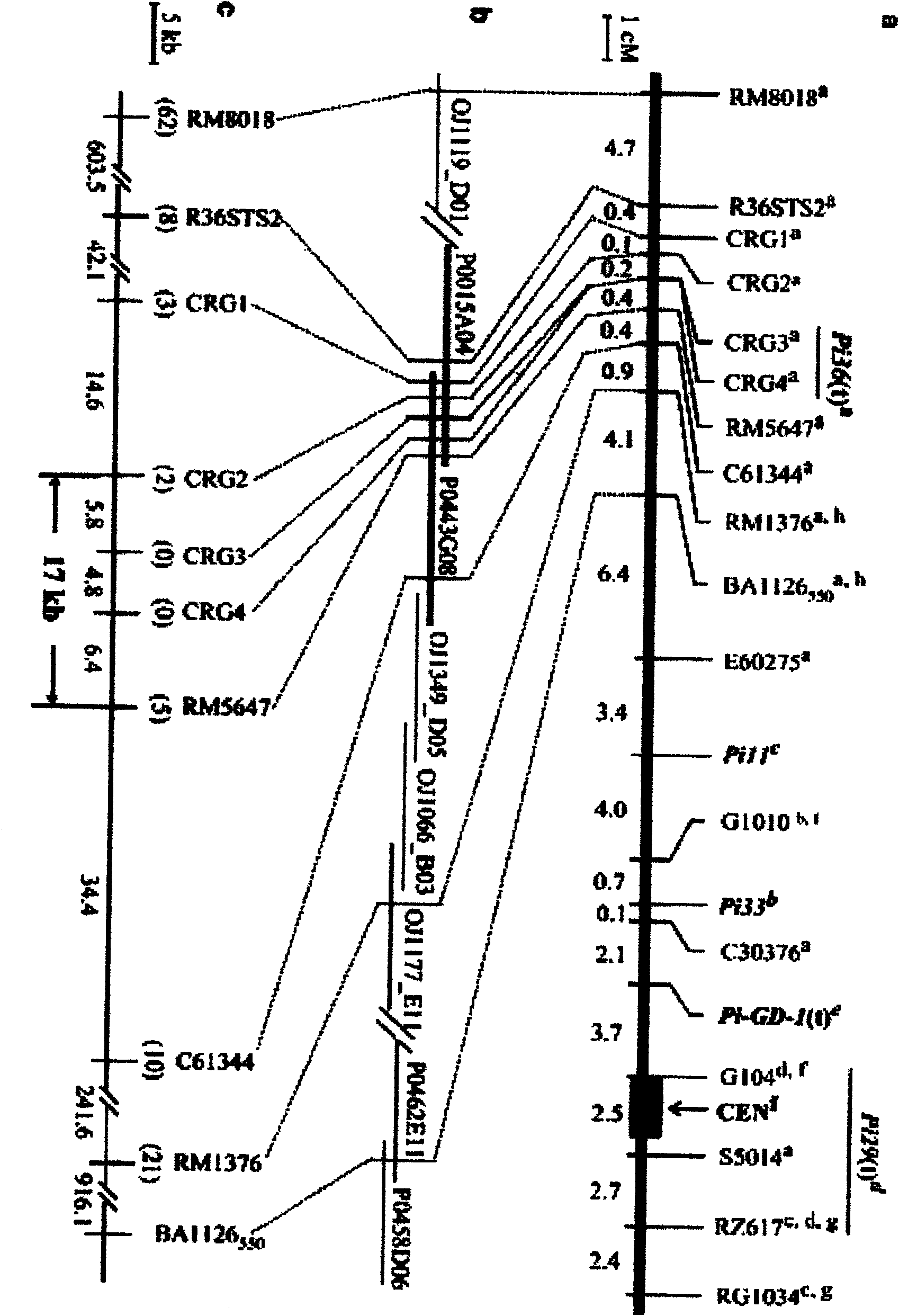
[0041] Example 2: Fine Mapping and Electron Physical Mapping of New Rice Blast Resistance Gene Pi36
[0042] In order to precisely determine the position of the Pi36 locus, we used the reference sequences in the public database to develop 5 polymorphic markers, 1 STS marker R36STS2 and 4 candidate resistance gene (candidate resistance gene, CRG) markers, CRG1 , CRG2, CRG3 and CRG4, and 580 strains of highly susceptible F 2 Individuals were subjected to linkage analysis. The results showed that the Pi36 locus was finely localized in a region of 0.6 cM between CRG2-RM5647 and completely co-segregated with the markers CRG3 and CRG4. In order to construct the physical map of this locus, we used the bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) and P1-mediated artificial chromosome (P1-derived artificial chromosome, PAC) clones of the reference species Nipponbare, and through bioinformatics analysis (bioinformatics analysis, BIA), and an electron physical map of this site was constructed...
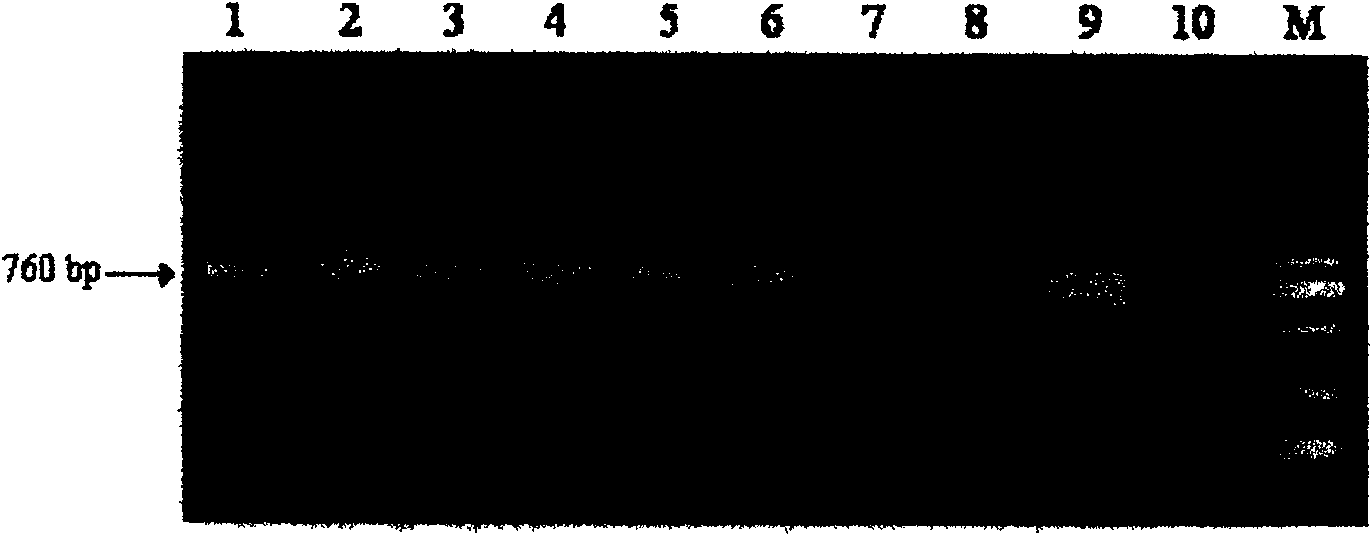
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3: Predictive Annotation and Sequence Analysis of the New Rice Blast Resistance Gene Pi36 Candidate Gene
[0044]In order to determine the candidate gene of Pi36, we use the reference sequence of Nipponbare, through three gene prediction software RiceGAAS (http: / / ricegaas.dna.affrc.go.jp), Gramene (http: / / 143.48.220.116 / resources / ) and Softberry's FGENESH (http: / / www.softberry.com) carried out gene prediction and annotation analysis on the target gene region, and initially identified the candidate resistance genes of Pi36 as Pi36-1, Pi36-2 and Pi36-3, among which Pi36-3 includes Pi36-1 and Pi36-2. Therefore, the function of Pi36-3 was confirmed by the following gene function complementation experiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com