Composite rear earth alterant used for thermal fatigue resisting steel
A technology for compounding rare earths and modifiers, applied in the field of additives, can solve the problems of little breakthrough progress, easily damaged parts, low thermal fatigue resistance, etc., to reduce production costs, refine grains, and improve material performance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
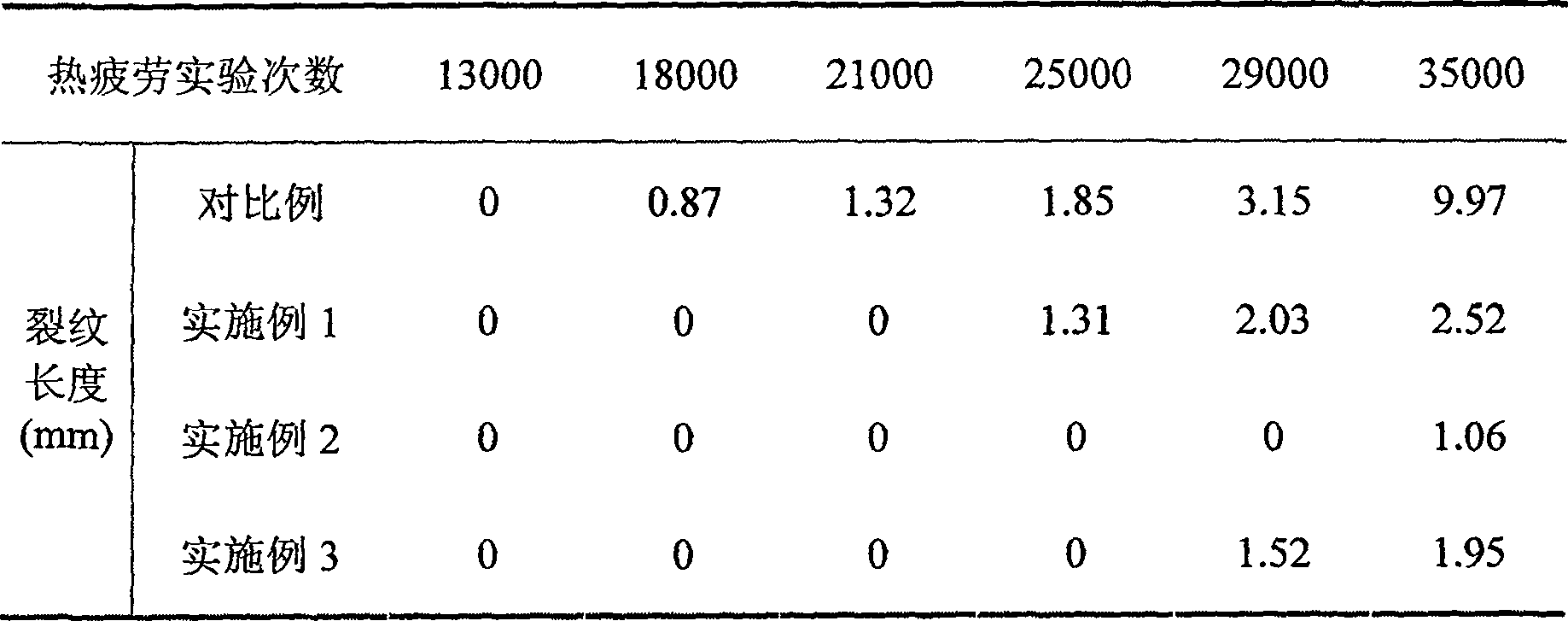
[0008] To the molten steel of same certain composition, the composite rare earth modifier of heat-resistant fatigue steel is used to carry out modification treatment, and the chemical composition (percentage by weight) of composite rare earth modifier is: RE is 55% (wherein, Y is 52% of RE weight, remainder The amount is other rare earth elements), B is 5.1%, Nb is 10%, V is 6%, Ca is 2%, Ba is 11%, and the balance is iron. Made into blocky off-white alloy with a particle size of 15mm and a melting point of 1200°C. The modified alloy is cast into a test bar, and then made into a sample for thermal fatigue test. The test results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0010] To the molten steel of the same composition as in Example 1, the composite rare earth modifier of heat-resistant fatigue steel is used to carry out modification treatment, and the chemical composition (percentage by weight) of the composite rare earth modifier is: RE is 62.1% (wherein, Y is RE weight % 59%, the balance is other rare earth elements), B is 7.2%, Nb is 15.1%, V is 2.3%, Ca is 7.5%, Ba is 3.1%, and the balance is iron. It is made into a blocky off-white alloy with a particle size of 10mm and a melting point of 1350°C. The modified alloy is cast into a test bar, and then made into a sample for thermal fatigue test. The test results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0012] To the molten steel of the same composition as in Example 1, the composite rare earth modifier of heat-resistant fatigue steel is used to carry out modification treatment, and the chemical composition (percentage by weight) of the composite rare earth modifier is: RE is 40% (wherein, Y is RE weight % 99.9%, the balance is other rare earth elements), B is 3%, Nb is 6.2%, V is 5.3%, Ca is 13.2%, Ba is 9%, and the balance is iron. It is made into a block gray-white alloy with a particle size of 20mm and a melting point of 1180°C. The modified alloy is cast into a test bar, and then made into a sample for thermal fatigue test. The test results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com