Semiconductor device and its making method
A semiconductor and manufacturing technology, applied in the field of sensor semiconductor devices and their manufacturing, can solve the problems of inability to form a dam structure, reduce adhesion, colloid overflow, etc., so as to avoid the weak dam structure and the seepage of the light-transmitting cover. Leakage problems, improved reliability, reduced size effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
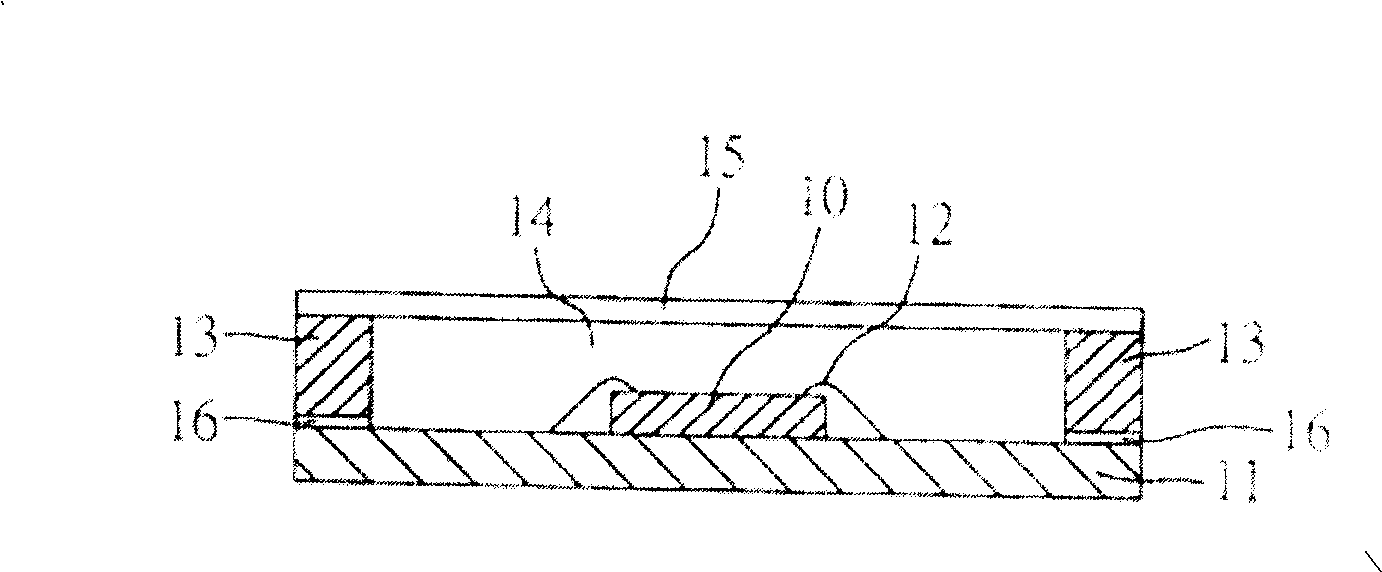
[0033] see Figure 5A to Figure 5D , which is a schematic cross-sectional view of the fabrication method of the semiconductor device of the present invention. It is also illustrated by taking mass production of the sensing semiconductor device of the present invention in a batch manner as an example. Of course, if the actual manufacturing process permits, the sensing semiconductor device of the present invention can also be produced in a single-chip manner.
[0034] Such as Figure 5A As shown, a substrate module sheet 51A having a plurality of substrates 51 is provided, and at least one sensor chip 50 is mounted on the substrate 51 , and the planar size of the sensor chip 20 is smaller than the planar size of the substrate 51 . The form of the substrate module 51A can be arranged in a matrix or in a strip; the sensor chip 50 has an active surface 501 and a relative non-active surface 502, and the active surface 501 of the sensor chip 50 is provided with a sensor In the sens...
Embodiment 2
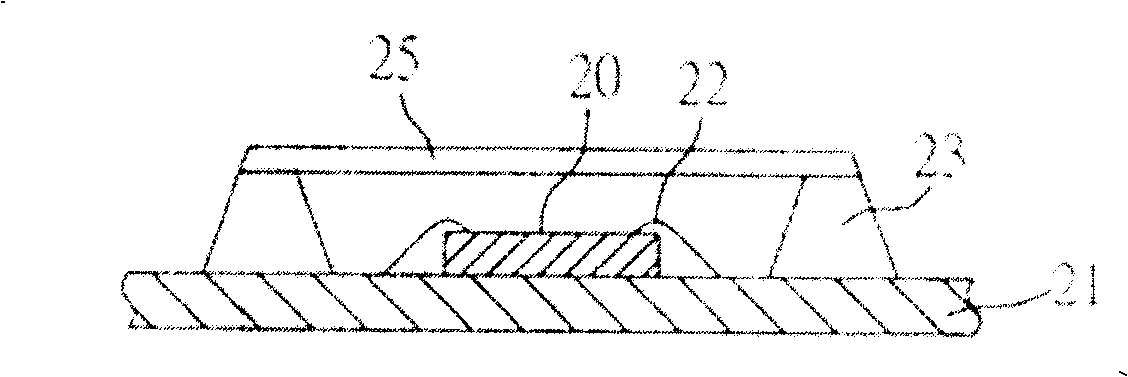
[0041] Please also refer to FIG. 6A to FIG. 6D , which are schematic cross-sectional views of Embodiment 2 of the manufacturing method of the semiconductor device of the present invention. In Example 2, the semiconductor device is made by a method similar to the above, the main difference is that after laying the second insulating layer on the insulating layer, an adhesive layer is formed on the second insulating layer to connect the light-transmitting cover body.
[0042] As shown in FIG. 6A , a substrate module sheet 61 having a plurality of substrates 61 is provided, and at least one sensor chip 60 is mounted on the substrate 61 , and the planar size of the sensor chip 60 is smaller than the planar size of the substrate 61 . The form of the substrate module sheet 61A can be arranged in a matrix or in a strip; the sensor chip 60 has an active surface 601 and a relative non-active surface 602, and the active surface 601 of the sensor chip 60 is provided with a sensor In the ...
Embodiment 3
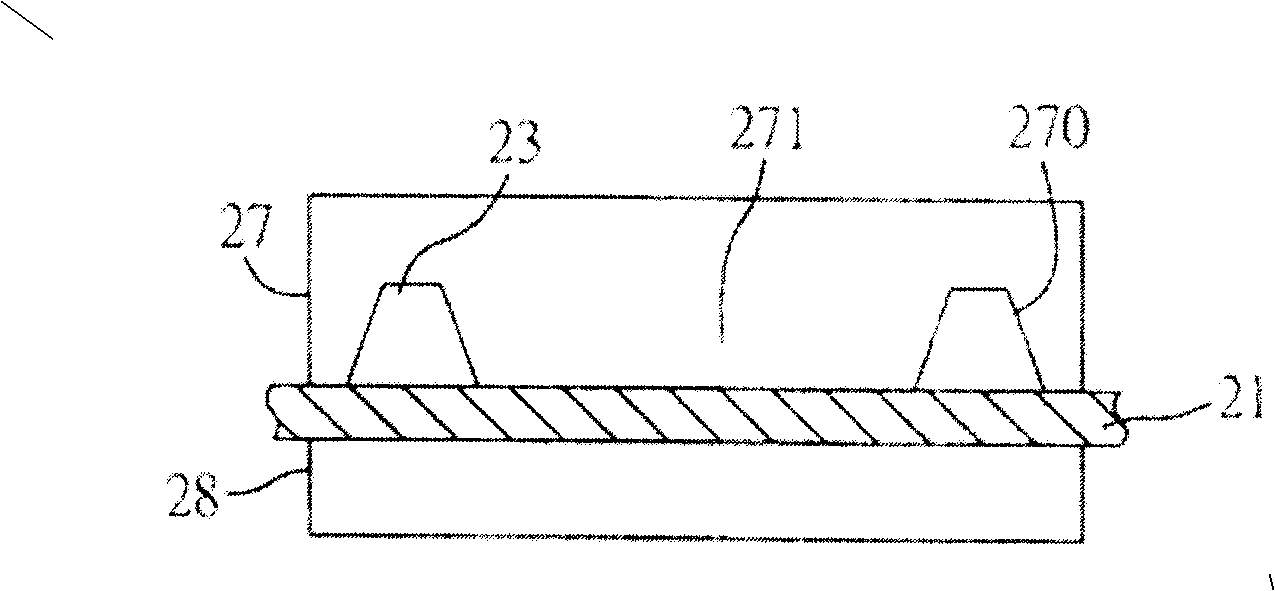
[0047] Please also refer to FIG. 7 , which is a schematic cross-sectional view of Embodiment 3 of the semiconductor device of the present invention.
[0048] The semiconductor device of the third embodiment is substantially the same as that of the second embodiment, and is mainly formed by the above-mentioned manufacturing method. The main difference is that the second insulating layer 732 disposed on the first insulating layer 731 corresponding to the sensor chip 70 When choosing to cover the bonding wires 72 , it should be noted that the second insulating layer does not extend to cover the sensing chip 70 , so as to avoid glue overflowing to the sensing region 703 of the sensing chip 70 .
[0049]Therefore, the semiconductor device and its manufacturing method of the present invention is to connect the sensing chip corresponding to each of the substrates on the substrate module sheet with a plurality of substrates, so that the sensing chip is electrically connected to the sub...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com