Method and device for producing shaped microbial cellulose for use as biomaterial especially for microsurgery
A technology for microbial cellulose and cellulose generation, applied in the field of preparing shaped microbial cellulose
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
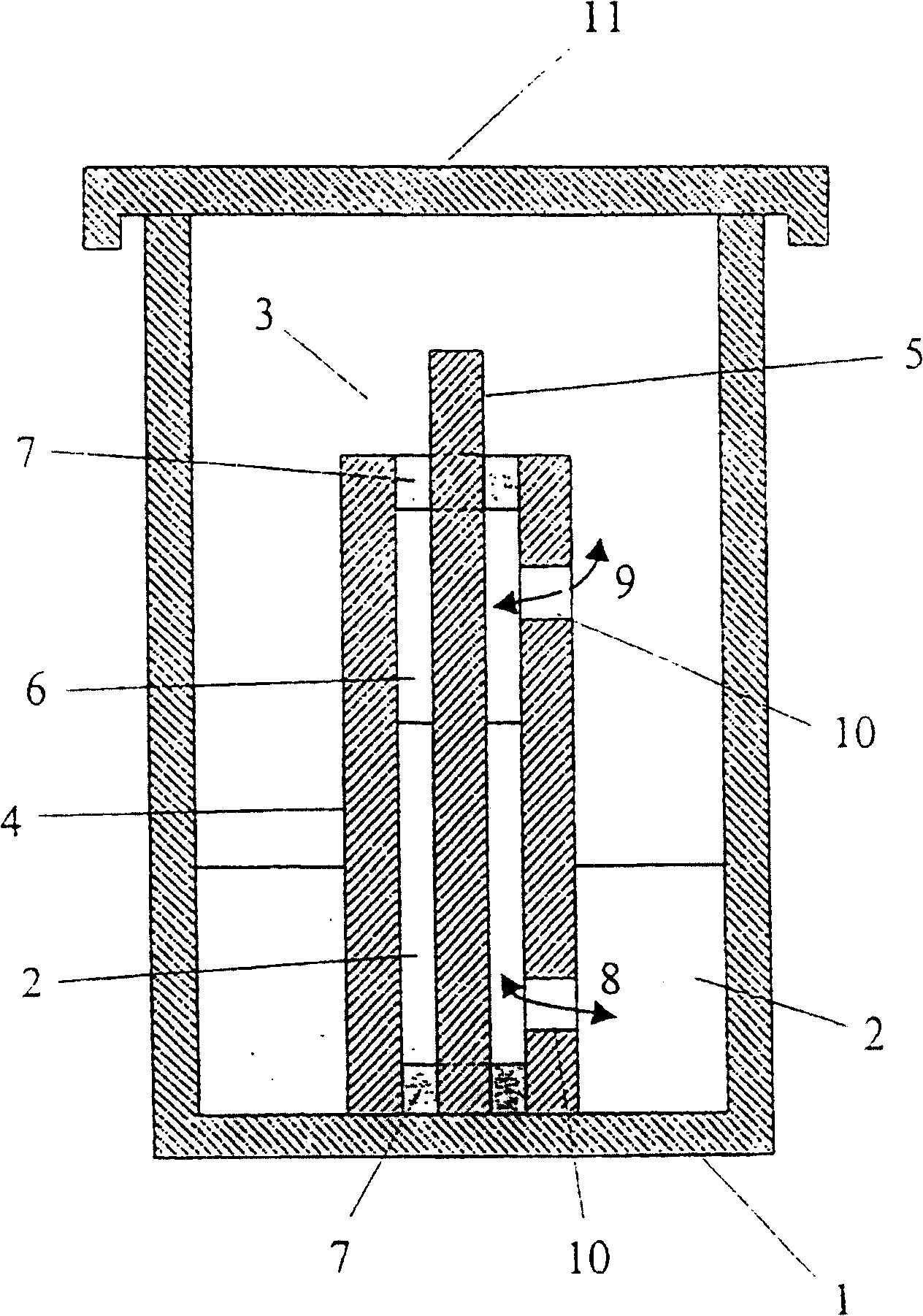
[0025] The culture broth is sterilized in a known manner, inoculated with cellulose-producing bacteria, such as the microorganism Acetobacter xylinum (xylanacetobacter), which produces a stable cellulose layer, and between the module walls, for example at 28° C. to 30° C. Cultivate in the gap. The biological material (cellulose) produced during the cultivation is separated from the walls of the modules and purified (see EP 396 344 A3).
[0026] According to the invention, however, the inoculated culture solution is not injected into the spaces between the walls of the modules, for example between glass master molds (Glasmatrix) which are preferably made of glass parts which can be separated from each other, but the molds are removed during the cultivation process. The part wall (glass master mold) is immersed in the container containing the inoculated culture solution, so that the culture solution enters the space between the module walls by capillary force. This ensures a mo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com