Method and system of automatic bandwidth detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
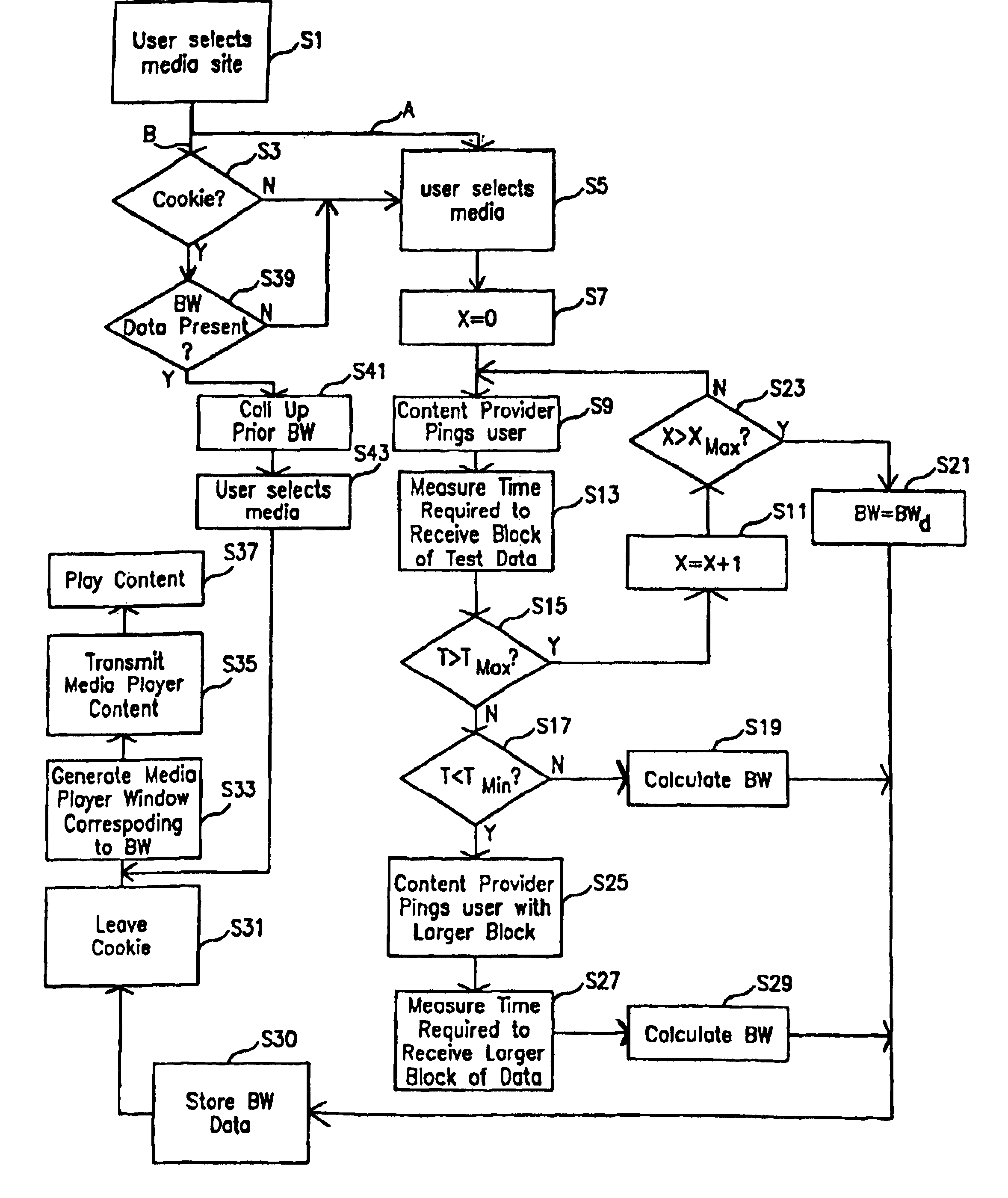
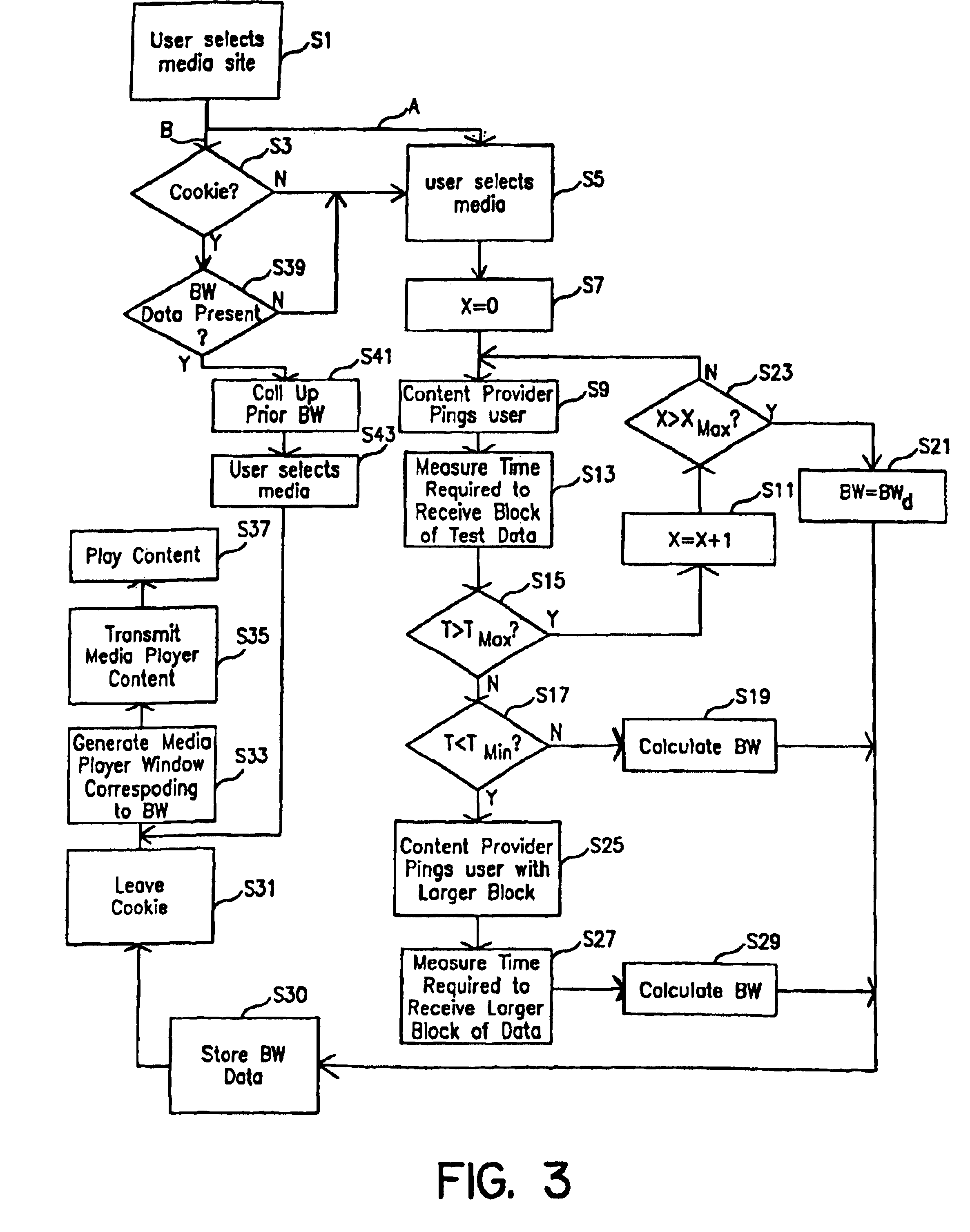
[0029]The present invention is directed to methods of controlling and displaying data, in particular, streaming media data, using an Internet browser interface. More specifically, the present invention relates to the transmission of streaming data from a server computer to a client computer over the Internet, and to the measurement and characterization of client's Internet connection. This enables the content provider to send streaming media data to the user in the appropriate manner for the bandwidth of the user's Internet connection. As explained in greater detail below, this can be achieved by automatically sending a block of test data from the content provider to the user.
[0030]Once the bandwidth of the user's Internet connection is measured, the content provider's server can send the requested data to the user along with information establishing the format of the media player window in which that data will appear. By way of non-limiting example, the information establishing the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com