Method for correcting astigmatism in electron emission spectromicroscopy imaging
a technology of electron emission spectromicroscopy and astigmatism, which is applied in the field of spectromicroscopy imaging, can solve the problems of limiting the resolution of electron emission imaging, over-intensities and under-intensities in the image obtained, and limiting the lateral resolution of peem imaging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
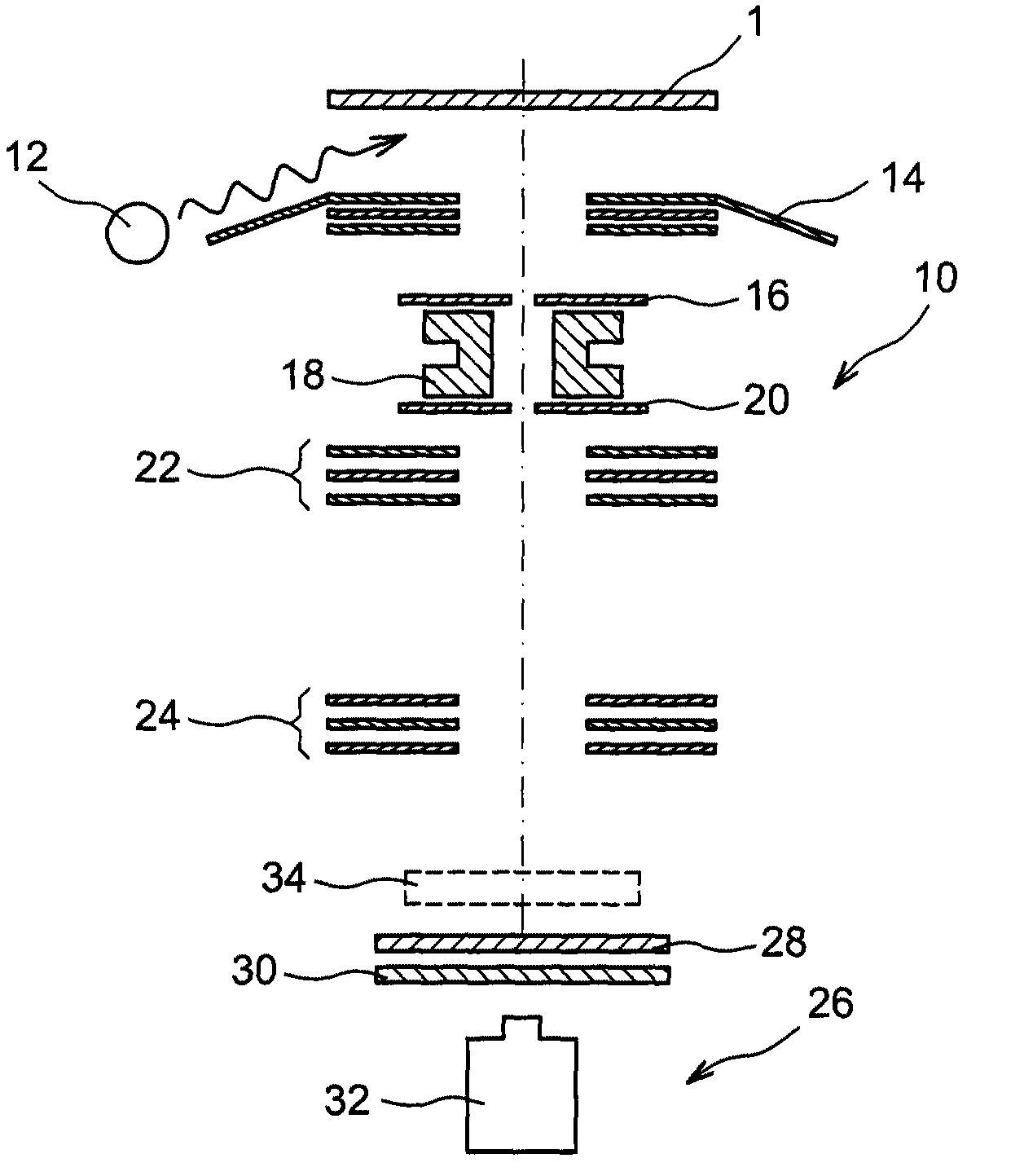
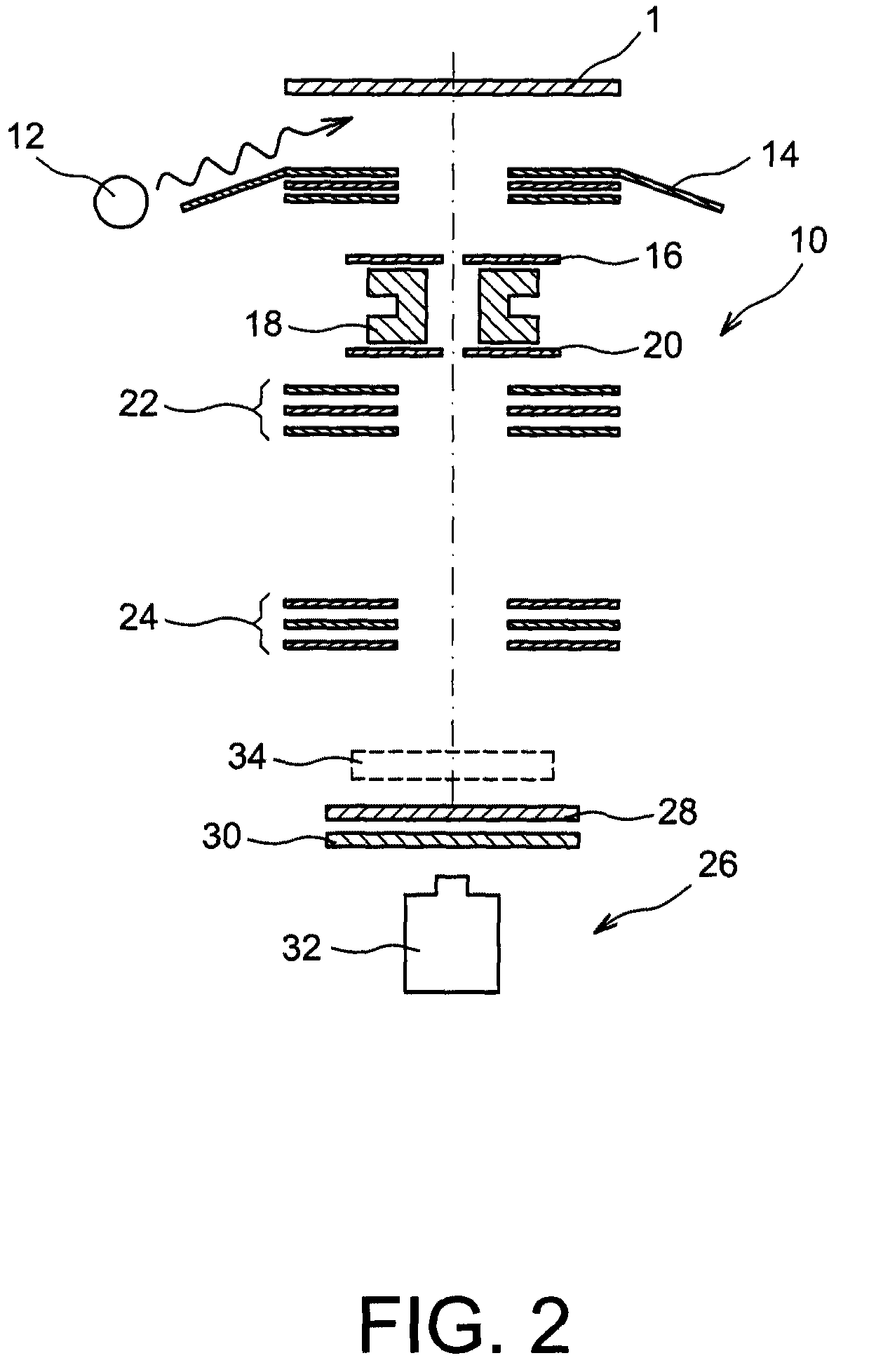
[0012]Thus there is a need to optimise the observation conditions during a method of electron emission spectromicroscopy imaging, for example with photoelectrons, of a structure of interest of a sample by correcting defects of the electronic optical column of a spectromicroscope, and particularly astigmatism.
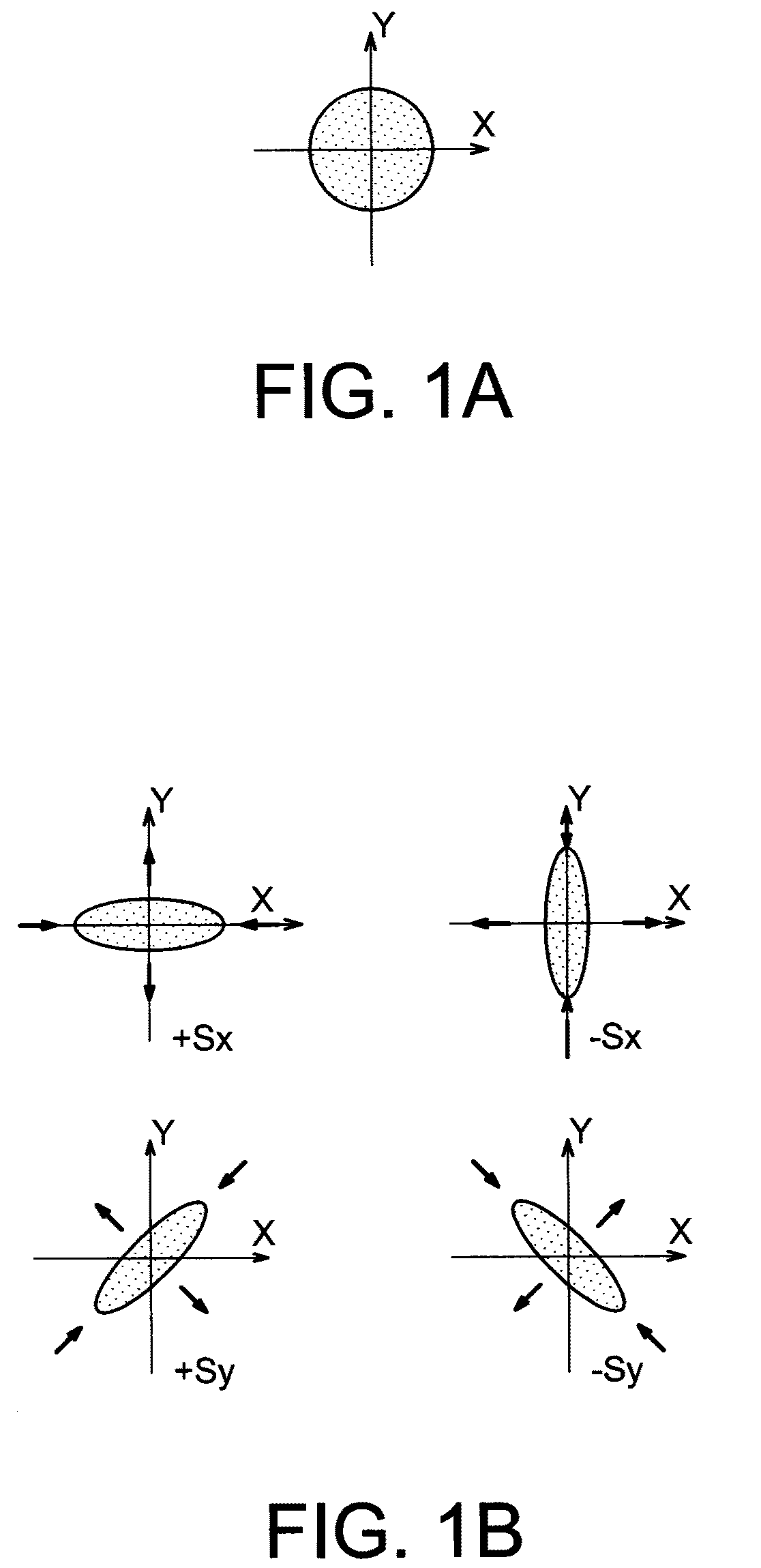
[0013]To do this, one embodiment proposes a method for correcting astigmatism of an electronic optical column of an electron emission spectromicroscope, comprising at least the steps of:[0014]forming a reference structure on a surface of a sample comprising a structure of interest to be imaged, the dimensions of the exterior contour of the reference structure, along two axes perpendicular to each other and lying in a plane parallel to the surface of the sample, being substantially similar,[0015]imaging the reference structure by the spectromicroscope with secondary electrons and with core level photoelectrons,[0016]eliminating astigmatism defects appearing during the imaging of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com