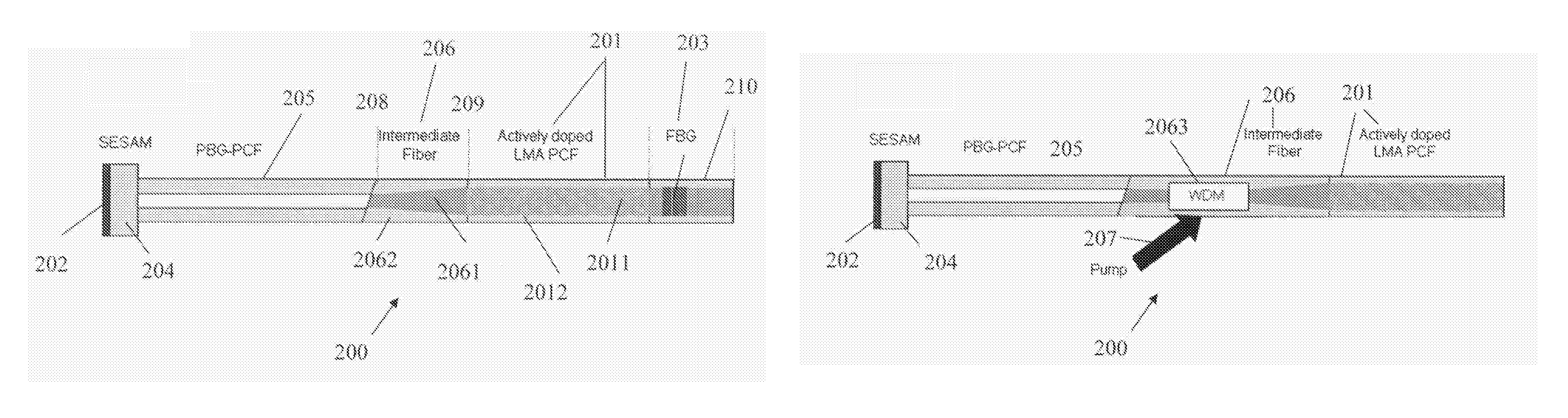
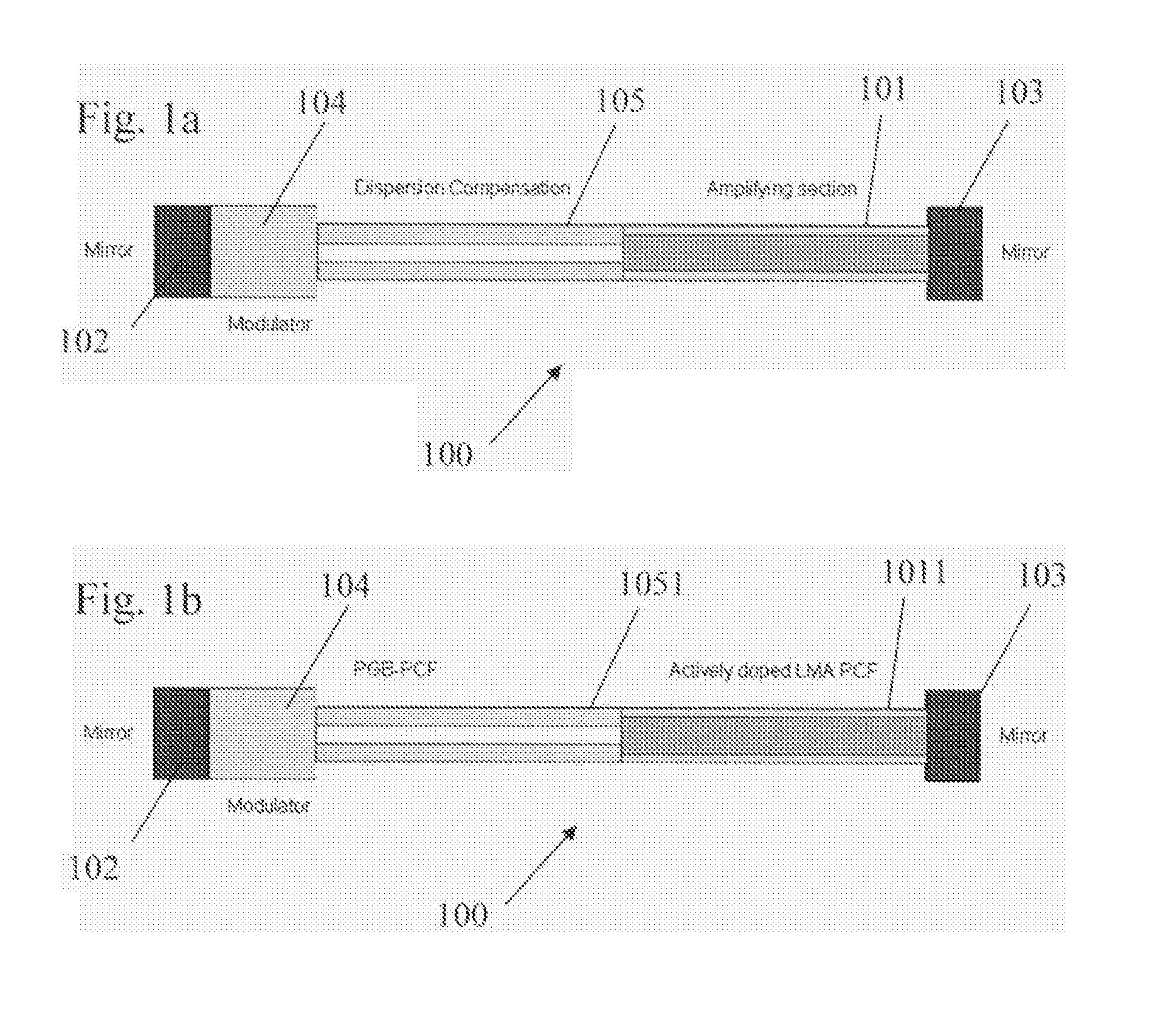
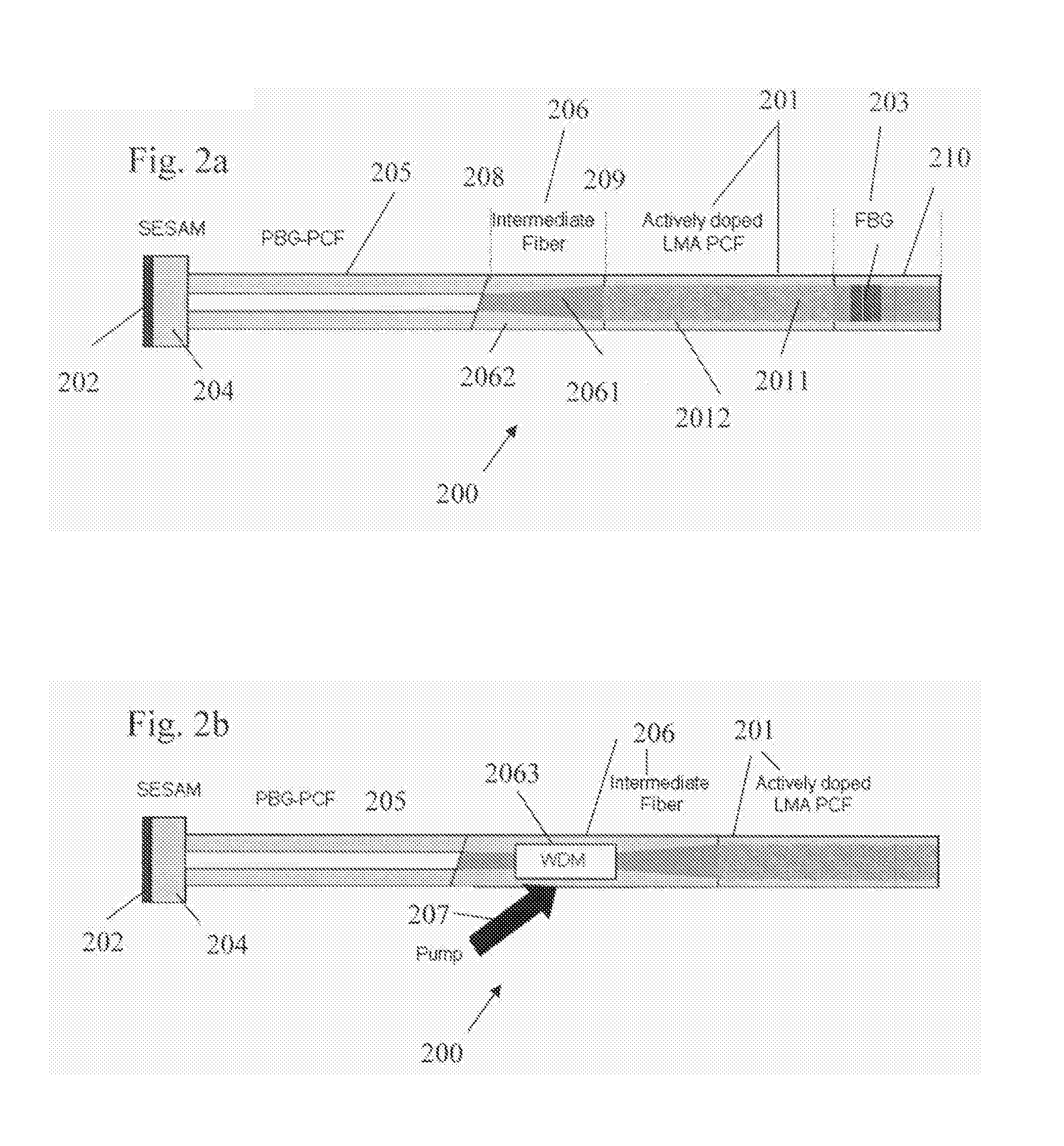
Optical system for providing short laser-pulses
a laser pulse and optical system technology, applied in the direction of cladded optical fibres, instruments, active medium materials, etc., can solve the problems of inability to achieve short wavelengths (1.3 m), and inability to achieve compact and robust lasers. achieve high non-linear thresholds, high values of anomalous dispersion, and high core diameters
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Manufacture and Properties of Hollow Core and Solid Core PBG-Fibers
[0138]The following example describes possible PBG-fibers with anomalous dispersion for intra-cavity dispersion compensation and extra-cavity pulse compression of ultra-fast fiber lasers (e.g. Yb-doped). PBG-fibers are potentially very attractive for these purposes due to their high non-linear thresholds, high values of anomalous dispersion and low bending loss. Various aspects of the manufacture, properties and applications of PBG-fibers are e.g. discussed by Knight et al. in “Photonic Band Gap Guidance in Optical Fibers”, Science, Vol. 282, 20 Nov. 1998, pp. 1476-1478 and by Broeng et al. in “Waveguidance by the photonic bandgap effect in optical fibres”, Journal of Optics A, Pure and Applied Optics, Vol. 1, 1999, pp. 477-482 and in the textbook of [Bjarklev et al.] (cf. e.g. chapter 4 on fabrication and chapter 6 on PBG-fibers).
[0139]FIG. 10 shows microscope photographs of transversal cross-sections of (a) a hollo...
example 2
An Optical System without an Intra-Cavity PBG Fiber
[0145]To introduce possible components of a system according to the invention, a mode-locked fiber laser without any intra-cavity PBG fiber is first described.
[0146]FIG. 14 shows a diagram of the laser configuration. The cavity of the oscillator (spatially limited by the two reflecting elements termed ‘Pigtailed mirror’ and ‘SAM’, respectively, in FIG. 14) consists of a polarization maintaining (PM) wave division multiplexer (‘WDM’ in FIG. 14), 32 cm of highly doped ytterbium PM fiber (300 dB / m absorption at 976 μm, termed ‘YB’ in FIG. 14), and a PM 20:80 coupler (termed ‘20:80’ in FIG. 14) with PM fiber pigtails (output coupling: 20%). The coupler also works as a polarizer, transmitting only the light in the slow axis, and hence ensures that the output from the cavity is linearly polarized. The primary output of the cavity is labeled “Out 1” in FIG. 14. The total length of fibers in the cavity is 1.40 m, and the repetition rate of ...
example 3
An Optical System with an Intra-Cavity Solid Core PBG Fiber
[0158]FIG. 21 shows a block diagram of an all-fiber laser system according to the invention comprising a solid core PBG-fiber (SC-PBG) in the laser cavity.
[0159]The cavity consists of a WDM, 8.5 cm of highly doped ytterbium fiber (1200 dB / m absorption at 976 nm), and a PM 20:80 coupler with PM fiber pigtails (output coupling: 20%), and the 0.36 m of SC-PBG fiber for intra-cavity dispersion compensation. The coupler also works as a polarizer, transmitting only the light in the slow axis, and hence ensures that the output from the cavity i linear polarized. The total length of PM fibers in the cavity was 0.95 m, and the total length of non-PM fibers in the cavity were 0.835 m (including the SC-PBG fiber). The non-PM fibers of the cavity were all kept straight in order to avoid polarization rotation.
[0160]The SC-PBG fiber was spliced to a standard fiber using a standard Ericsson Fusion splicer using an optimized splicing method...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com