Magnetoresistive effect element, magnetic memory device and method of fabricating the same
element technology, applied in the direction of digital storage, semiconductor devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient output voltage for realizing a magnetic memory device having a higher density, insufficient value to achieve a further increase in storage speed or access speed, and insufficient value to achieve a further increase in the storing speed or access speed. , to achieve the effect of stable writing operation, convenient fabrication and efficient use of a stronger magnetic field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
modified examples
[0156]Next, an explanation will be given of modified examples, according to the embodiment in reference to FIG. 26 as follows.
first modified example
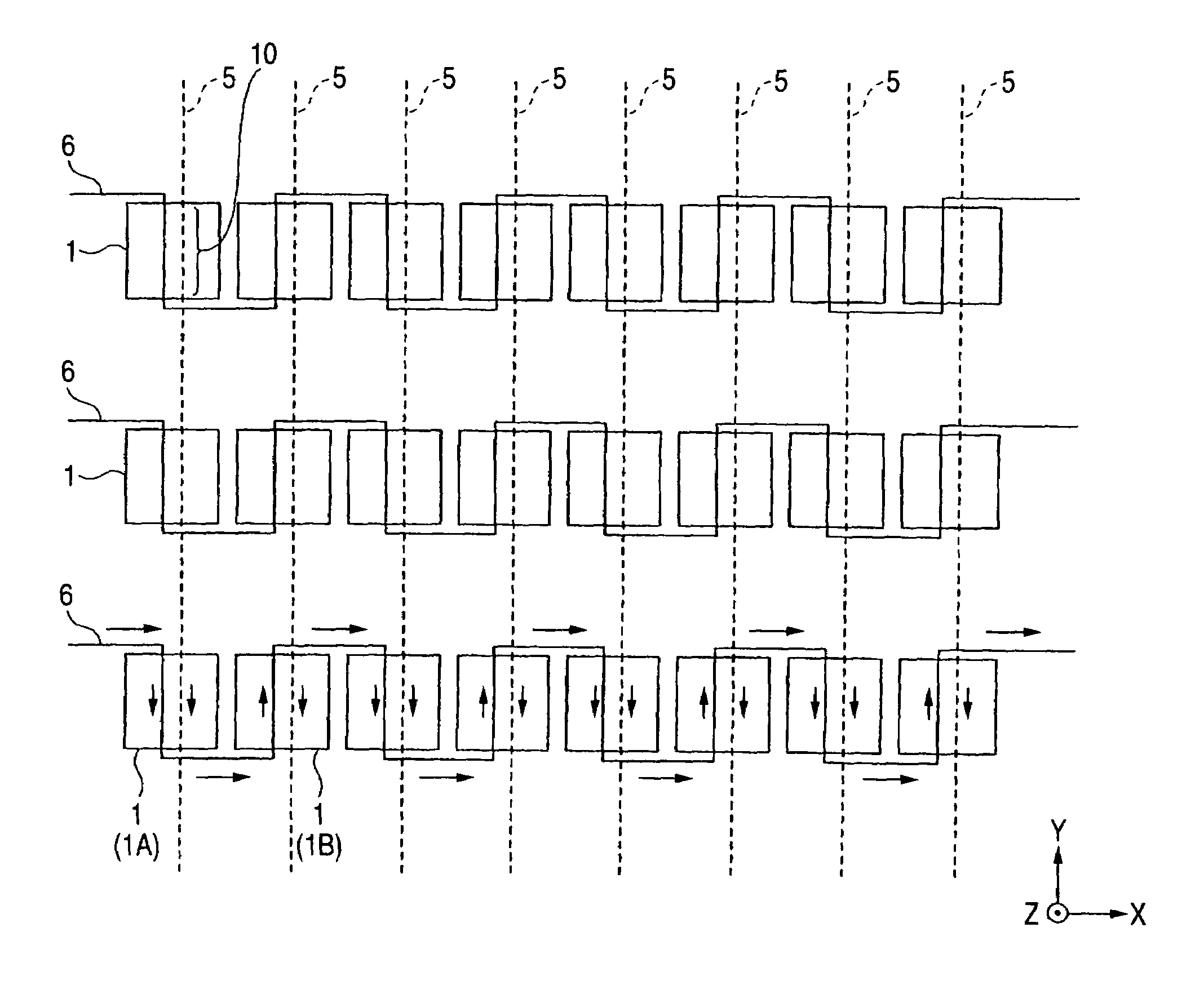
[0157]The TMR element 22 according to the embodiment is constituted by a structure referred to as the coercive force difference type having the first magnetic layer 2 having the coercive force larger than that of the second magnetic layer 8. In contrast thereto, a TMR element 22B shown in FIG. 26A shows a structure referred to as the exchange bias type for fixing the magnetizing direction of the first magnetic layer 2 by the exchange coupling.
[0158]Specifically, the TMR element 22B includes a nonmagnetic conductive layer 9, the second magnetic layer 8, the tunnel barrier layer 3, the first magnetic layer 2 and a third magnetic layer 15 in this order from the side of the annular magnetic layer 4. The third magnetic layer 15 is provided with antiferromagnetism, functions to fix the magnetizing direction of the first magnetizing layer 2 by exchange interactive operation with the first magnetic layer 2, and constituted by an antiferromagnetic material of, for example, a platinum mangane...
second modified example
[0160]FIG. 26B shows a constitution of a TMR element 22C in which a nonmagnetic conductive layer 35 and a fourth magnetic layer 18 are provided between the first magnetic layer 2 and the tunnel barrier layer 3 in the constitution of the TMR element 22 according to the embodiment.
[0161]Specifically, the TMR element 22C includes the nonmagnetic conductive layer 9, the second magnetic layer 8, the tunnel barrier layer 3, the fourth magnetic layer 18, the nonmagnetic conductive layer 35 and the first magnetic layer 2 in this order from the side of the annular magnetic layer 4. The fourth magnetic layer 18 forms an antiferromagnetic coupling with the first magnetic layer 2 via the nonmagnetic conductive layer 35 and the magnetizing directions of the first magnetic layer 2 and the fourth magnetic layer 18 are in parallel and opposite direction with each other. The fourth magnetic layer 18 is constituted by, for example, iron (Fe), NiFe, CoFe, NiFeCo or cobalt (Co) or the like.
[0162]Accord...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com