Biologically active materials
a biological active material and material technology, applied in the field of biological active materials, can solve the problems of little selective concentration in tumour tissue, ubiquitous body distribution of drugs, and toxicity of parent drugs, and achieve the effect of reducing the degradation rate of dextrin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
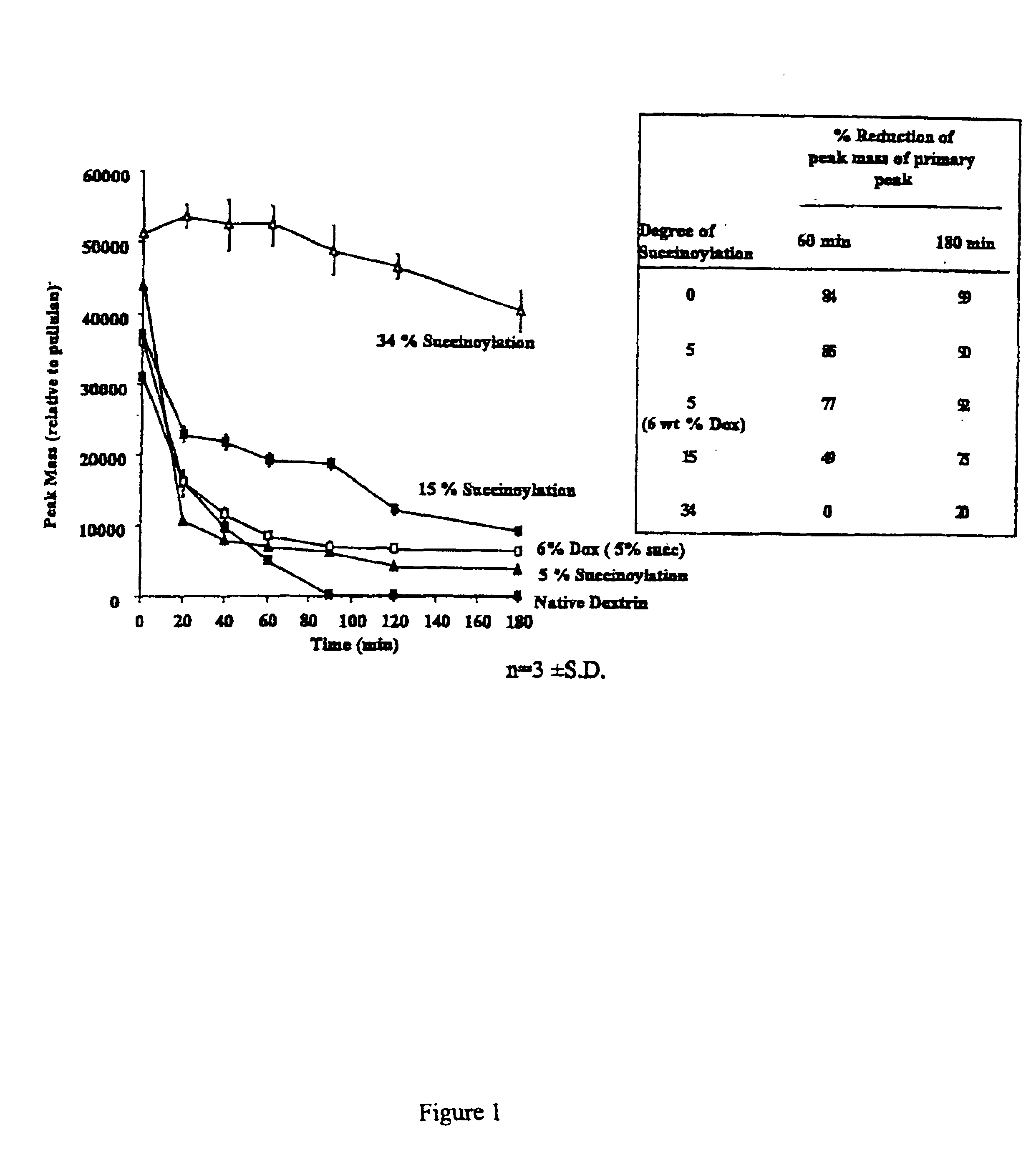
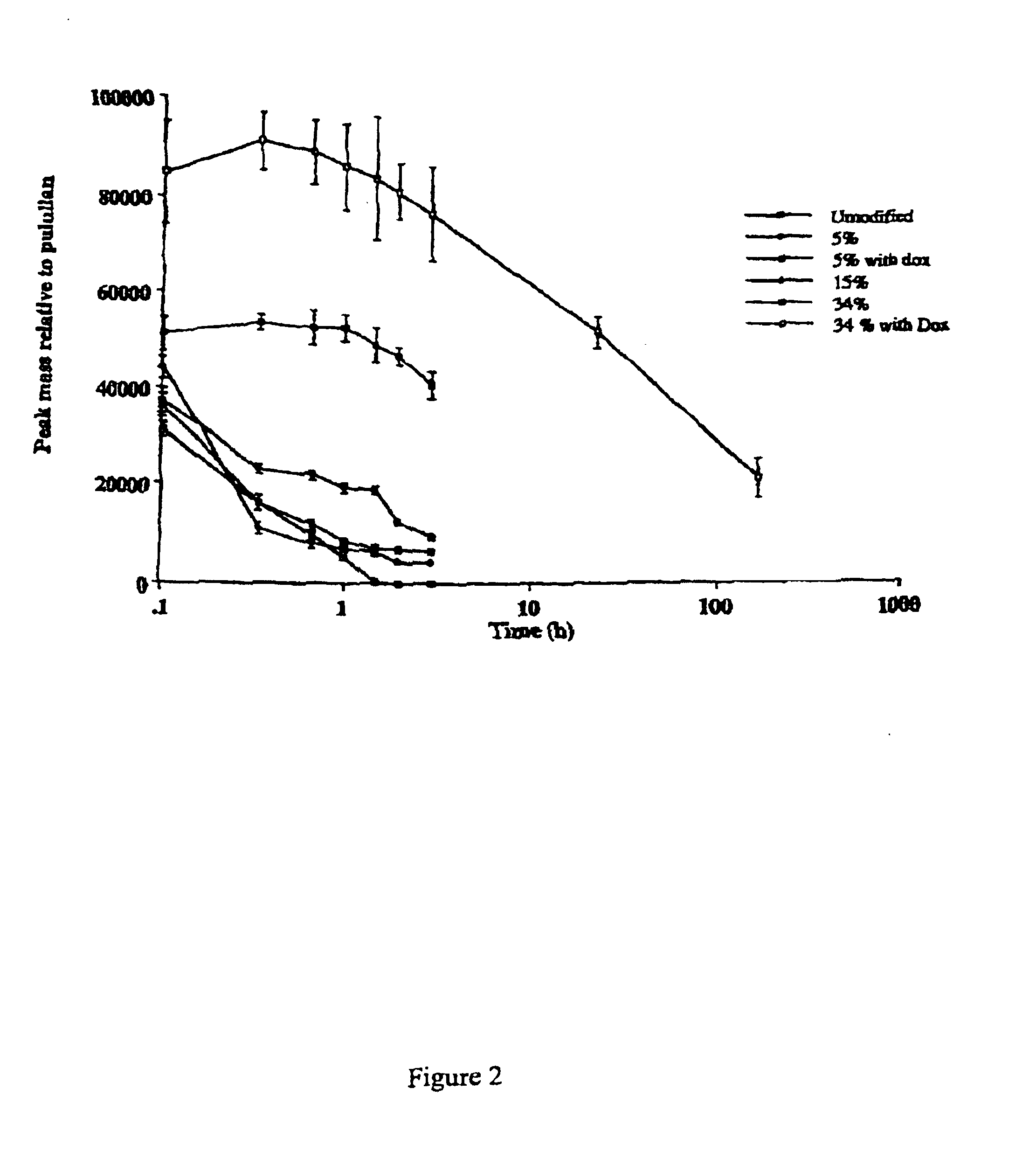
In this example the degradation of dextrins of different degrees of modification was compared. The results are shown in FIG. 1. It will be seen that native dextrin is rapidly degraded as are also dextrin with 5% succinoylation (whether with or without 6% Dox) and dextrin with 15% succinoylation. However, if dextrin is 34% succinoylated the degree of degradation is markedly less, there being zero % reduction of the peak mass of primary peak after 60 minutes and only 20% reduction after 180 minutes. In addition, FIG. 2 shows that 34% succinoylated dextrin doxorubicin conjugate is similarly stable over an extended time course when compared to unconjugated or low level succinoylated (5%) controls.
example 3
In this example increased uptake of 34% succinoylated dextrin-doxorubicin by tumour cells is shown. Male C57 were injected with 10.sup.6 B16F10 murine melanoma cells subcutaneously with either doxorubicin hydrochloride or dextrin-succinoyl-doxorubicin (34 mol % succinoylation, 11.8% doxorubicin) at 5 mg / kg doxorubicin equivalence into the intrapertinoneal cavity (i.p.).
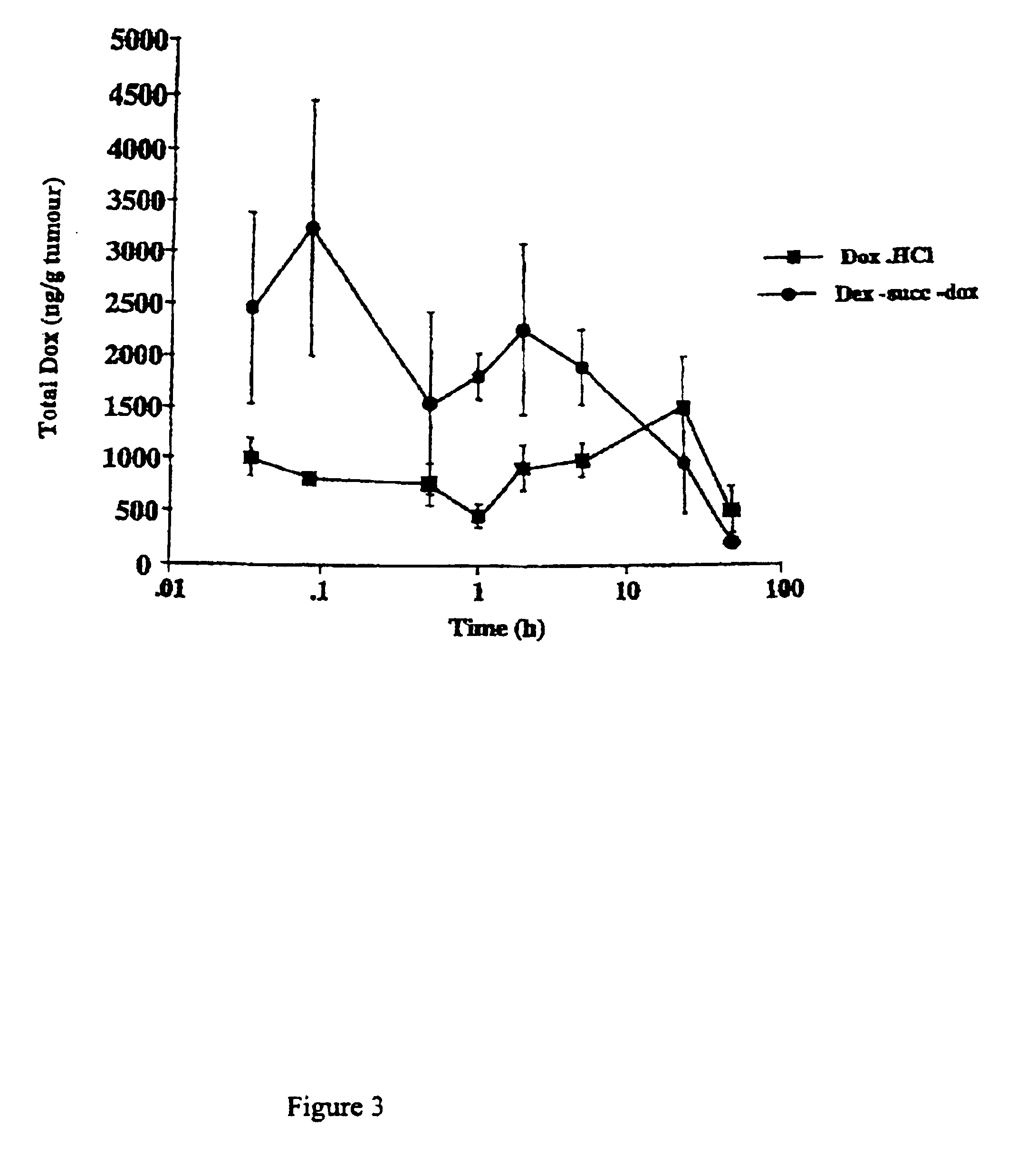
The mice were then culled after 2, 5, and 30 mins and after 1, 2, 5, 24, and 48 hours. Tumours were removed and weighed. The tumour was then homogenised and doxorubicin extracted and quantified by HLPC for total doxorubicin present, FIG. 3.
FIG. 3 shows there is approximately a three fold increase in tumour levels of doxorubicin were found for the conjugate for all time intervals from 2 min up to 24 hours. After this period, there is no difference between conjugate or the free drug. The elevated levels of the conjugate were at their highest 5 min after injection.
example 4
In this example the pharmacology of succinolyated dextrin doxorubicin is determined and is presented in Table 2. Twenty four C57 black mice were injected subcutaneously (s.c.) with 10.sup.5 B16F10 murine melanoma cells as described above and then monitored daily for well-being and the presence of palpable tumours. When the tumours were palpable, mice were randomly assigned into groups of six and their tumours measured with a micrometer gauge. Tumour size and mouse body weight is recorded. Each group is then injected intra-peritoneally with either sterile saline (negative control), free doxorubicin (5 mg kg.sup.-1) in sterile saline or dextrin-doxorubicin (11.8 wt %, 34% succinolyation) at either 5 mg kg.sup.-1 or 10 mg kg.sup.-1, on days 0,1 and 2. The mice were monitored daily and tumour size and body weight recorded. Once the tumour area exceeded 2.89 cm.sup.2 the mice were culled according to UKCCCR guidelines. Mouse survival is then expressed as % T / C (test / control saline).
The a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com